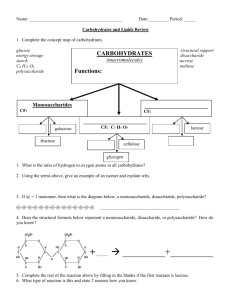
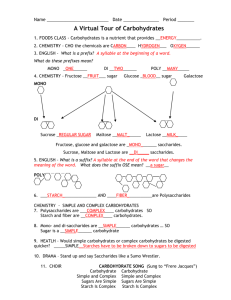
What is the structure of carbohydrates?
advertisement

What do the following have in common?? What does this scuba diver eat to provide energy on a big dive? • • • • Meat? Bread? Fruit? Butter? • Do you know what these foods do? Carbohydrates Your questions for carbohydrates: (set up cornell notes to help you study!) 1. Why are carbohydrates considered organic? 2. What are the 3 main structures of carbohydrates? 3. What are the building blocks of carbohydrates? 4. What are the 3 main functions of carbohydrates? Carbohydrates and Diabetes? • How do carbohydrates play into your diet? • What do people with diabetes have to watch out for? • Is being diabetic weird? • Halle Berry What are carbohydrates?? • • They come from plants!!! 1. They are organic molecules (made of carbon) Structure of Carbohydrates Repeating units to make long chains • One unit= monomer • Long chains= polymers Structure of Carbohydrates Repeating units to make long chains Structure of Carbohydrates Repeating units to make long chains mono- (one) di- (two) poly-(many) 2. Structure of Carbohydrates Another name for a carbohydrate is saccharide mono + saccharide = monosaccharide (one sugar) di + saccharide = disaccharide (two sugars) poly + saccharide = polysaccharide (many sugars) Structure of Carbohydrates 3. Building Block = monosaccharide monosaccharide monosaccharide monosaccharide monosaccharide monosaccharide monosaccharide 4. Uses of Carbohydrates Carbohydrates have 3 functions 4. Functions of Carbohydrates 1. Supplies Energy – Gives immediate energy – Short term energy storage Function of Carbohydrates 2. Supplies Dietary Fiber – Fiber = the parts of plants your body can't digest – Good sources of fiber are fruits, vegetables, wholegrains, and beans Function of Carbohydrates 3. Provides structure in plants – Cellulose (gives plants a shape!) – Makes up cell walls Carbohydrates Recap 1. Are they organic or inorganice? 1. 2. Organic molecule-Contain Carbon! What is the structure of carbohydrates? 2. Building Blocks = Monosaccharides that build disacharides! 3. What are the building blocks of carbohydrates? 3. Monosacharides!! 4. What are the functions of carbohydrates? 1. Supplies energy 2. Supplies dietary fiber 3. Provides structure in plant cells cellulose) (cell wall, and For each cereal: 1. Total Carbohydrate: 2. Dietary Fiber: 3. Sugars: Carbohydrate Mini Lab! • We are going to use a special chemical to figure out if foods are made of simple sugars (monosaccharides) or starches (polysaccharides) Use your notes to fill out the pre lab questions. • Iodine is usually a orange/red color. • In the presence of a starch (polysaccharide) it turns blue black. Monosaccharide (1 sugar) OR Disaccharide (2 sugars) So what color will a simple sugar be? (mono or disaccharide) Polysaccharide (Many sugars) So what color will a starch be? Extra Slides Below Structure of Carbohydrates All carbohydrates: • C-H-O (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen) • Ratio of 1:2:1 • Examples: sugars and starches Glucose = C6H12O6 Structure of Carbohydrates Repeating units to make long chains • Like a train • Like legos Students will identify the building blocks of macromolecules in order to classify common foods as either simple sugars or starches using iodine as an indicator. 1. Where would you find carbohydrates, protein, and lipids all discussed in the same place? 2. Which of the following supplies the body with immediate energy? A. Protein B. Fats (lipids) C. Carbohydrate D. DNA