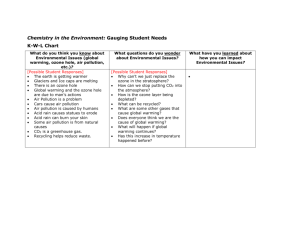
Effects of acid rain
advertisement

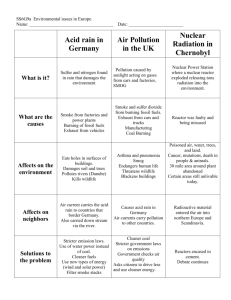
Topic: Ecology Aim: Describe the effects of environmental changes on humans and other populations. Do Now: Take out your ecology reading notes. HW: Earth Day Poster due Tuesday. Don’t forget the CL Evolution test is due Monday!!! Which phrase best describes an ecosystem? 1. all the living organisms in a specific location 2. all the nonliving materials in a specific location 3. some nonliving materials passing through living organism in a specific location 4. living organisms and nonliving materials interacting in a specific location Ecological Terms (1) Commensalism (2) Mutualism (3) Parasitism (4) Decomposers (5) Predator 1. The relationship between the crocodile and the leech Parasitism 2. Bacteria or fungi Decomposers 3. One organisms is benefits and the other is not affected Commensalism 4. Organisms hunt for animals as a source of food Predator 5. Both organisms benefit Mutualism http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V8pMMw3mtSw 1. Describe • Normal, GRADUAL changes that occur in the types of species ecological succession. that live in that area 2. Describe • The first to inhabit an area pioneer • Ex: organism – Lichens and identify – Moss an example – Bacteria of pioneer organisms. 3. Describe • The end stage of succession a climax • Community of plants that is community. stable and UNDISTURBED (Not replaced by another community) 4. Identify • Wildfire some • Avalanche factors that • Human activities can disrupt a climax community. 5. Observe Figure 3 on p. 742. a. Where did this 1988 fire occur? • Yellowstone National Park b. What was still found in the soil after the fire that caused succession to begin again? • Seeds protected under the soil c. Identify • Secondary Succession the type of succession that was occurring? Primary succession begins in a place previously without plants. Secondary succession begins in a place that already has soil and was once home to living things. Stages of Succession in a Pond 6. Describe • Any natural resource that is recycled or replaced constantly renewable resources by nature. and identify • Sun, water, air, crops 4 examples of renewable resources. 7. Describe • nonrenewable resources and identify 4 examples • of nonrenewable resources. Natural resources that are used up more quickly than they can be replaced by natural processes Plastics, paints, gasoline, petroleum, minerals, metals 8. Describe • Fuels formed in Earth’s crust fossil fuels. over hundreds of millions of years 9. Identify 5 examples of fossil fuels that we use everyday. • • • • • Gasoline Diesel fuel Jet fuel Coal Natural Gas 10. Identify • Because they are limited, in the 2 problems future they may become more caused by expensive and difficult to obtain the burning • Environmental problems of fossil – Mining coal leads to the stripping fuels. . away of thick layers of soil and rock which can destroy ecosystems • Burning of fossil fuels leads to air pollution (smog, acid rain, global warming) • Rain falls 11. Describe at on roads least 3 and causes of parking water lots can pollution. wash oil and grease into soil and nearby streams • Rain washes agricultural pesticides and fertilizers into lakes, streams and rivers • Industrial wastes are sometimes released into surface waters Topic: Ecology Aim: Describe the effects of environmental changes on humans and other populations. Do Now: Take out your ecology reading notes. HW: Earth Day Poster due tomorrow. CL Plants due Friday CL Ecology due Monday 1.Identify process A. Identify the cell organelle where it occurs. respiration mitochondria 2. Identify process B. Identify the cell organelle where it occurs. photosynthesis chloroplasts 3. Which material cycle is represented in the diagram? Carbon cycle 1. Identify a plant’s response to external stimuli. TROPISM 2. Identify the chemical that causes that response. AUXINS Identify the tropisms below. 1. Plant grows towards water. HYDROTROPISM 2. Plants response to touch. THIGMOTROPISM 3. Roots grow down towards gravity. Stems grow up and away from gravity. GRAVITROPISM OR GEOTROPISM 4. Plant bends towards light. PHOTOTROPISM 1. Which group contains only abiotic factors? Support your answer. 2. Identify the group that represents an ecosystem. Support your answer. A, C and D because it consists of biotic and abiotic factors interacting together. Barnacles often attach themselves to whales and receive free transportation to parts of the ocean. The whales are not affected by this activity. Identify this relationship. Support your answer. Commensalism One organism benefits while the other is not affected. 1. What process is occurring in the diagram? Ecological succession 2. What would most likely be found in stage 1? Pioneer species 3. Identify Stage IV. Climax community 4. Will stage IV be replaced by another community? Support your answer. No , it will not because it is a stable community. 5. Identify a factor that can disrupt a climax community. Natural disaster, hurricane, tornado, deforestation, industrialization 1. Which would NOT be considered a renewable resource (1.) coal (2.) solar power (3.) ocean waves (4.) hydroelectric power 2. Identify a renewable resource not seen in the previous question. water, trees 3. Identify another nonrenewable resource. fossil fuels: natural gas, oil, petroeum 12. Describe • 2 NEGATIVE • effects of water • pollution. Poison fish and other wild life Can be harmful to people who swim in or drink water Mercury and other metals can build up in tissues of fish transferred to people and animals Air pollution 1. Identify • Byproducts of burning fossil the greatest fuels contributor to air pollution. 2. Identify at least 6 health hazards of air pollution. • • • • • • Irritated noses Irritated eyes and throats Asthma attacks Heart or respiratory diseases Cancers Nerve damage 3. What is acid rain? • Acidic form of precipitation that can damage trees, crops, lakes and bodies of water 4. Identify the pollutants that cause acid rain • Sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides • From burning of coal and fossil fuels Effects of acid rain: • Washes nutrients from the soil (damage to trees and plants) • Runoff from acid rain gets into lakes and rivers 5. Where is the ozone layer located? • Upper atmosphere • Stratosphere 6. Describe • It acts as a protective shield the that protects the earth from importance harmful UV radiation. of the ozone http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qUfVMogIdr8 layer. 7. Identify • Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s) the • Halons chemicals that break • Methyl chloroform down the ozone layer. 8. Identify what releases CFC’s. • Used in aerosol propellants – hairspray and deodorants • Coolants in refrigerators and air conditioners 9. Describe global warming. • Carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels builds up in the atmosphere warming of earth Greenhouse Effect 10. Identify • Carbon dioxide the gas that contributes to global warming. 11. Describe • Polar ice caps melt ocean 3 negative levels rise effects global warming has on ecosystems. • Climate change – Erratic weather – Changes in rainfall patterns – Increase in the # of storms and hurricanes – Warner weather Let’s summarize… 1. Describe ecological succession. 2. Describe how humans can disrupt a climax community. Explain what happens after this disruption. 3. Explain the causes and effects of air pollution. 4. Explain the causes and effects of acid rain. 5. Explain the causes and effects of global warming. 6. Explain the causes and effects of ozone depletion. The diagrams best illustrates (1.) ecological succession (2.) organic evolution (3.) the effects of acid rain (4.) a food chain If no human intervention or natural disaster occurs, by the year 2050 this area will most likely be a (1.) pond (2.) field (3.) forest (4.) desert Which sequence best represents the stages of succession that would most likely occur in NY State? (1) bare rock beech-maple forest moss lichens (2) Grassland pine forest beechmaple forest marsh lake (3) Lake marsh grassland shrubs beech-maple forest (4) pine forest grassland shrubs lichens Which statement concerning the climax stage of an ecological succession is correct? (1.) It is the first community to inhabit an area. (2.) It consists entirely of plants. (3.) It persists until the environment changes. (4.) It changes rapidly. For 25 years, hay was cut from the same 10 acres on a farm. During these years, shrews, grasshoppers, spiders, rabbits, and mice were seen in this hayfield. After the farmer retired, he no longer cut the hay and the field was left unattended. What will most likely occur in the former hayfield over the next few decades? 1. The plant species will change, but the animal species will remain the same. 2.The animal species will change, but the plant species will remain the same. 3.Neither the plant species nor the animal species will change. 4.Both the plant species and the animal species will change. 1. Which substance is the major cause of the loss of our stratospheric ozone shield? (1.) CFC's (2.) oxygen (3.) acid rain (4.) carbon dioxide 2. Give an example of a negative effect of ozone depletion. More cases of skin cancer Destroy producers malnutrition Eye defects 1. Which is NOT an expected effect of global warming? (1.) Melting of polar ice caps. (2.) Flooding of coastal areas. (3.) Increased crop yields. (4.) Alteration of rainfall patterns 2. What are two possible causes of global warming? Burning of fossil fuels Deforestation Increase in factories There is ample evidence to suggest a direct relationship between global warming and increased (1.) ozone concentration (2.) carbon dioxide concentration (3.) acid rain (4.) CFC's 1. Methods used to reduce sulfur dioxide from smokestacks are an attempt by humans to (1) lessen the amount of insecticides in the environment (2) eliminate diversity in wildlife (3) lessen the environmental impact of acid rain (4) use nonchemical controls on pest species 2. What are some of the causes of acid rain? Factories Release of sulfur and nitrogen in to atmosphere 3. List some of the negative effects of acid rain. Destroy producers Lake acidification Destroy aquatic life 1. Deforestation will most directly result in an immediate increase in (1) atmospheric carbon dioxide (2) atmospheric ozone (3) wildlife populations (4) renewable resources Bacteria of decay are important components of an ecosystem because they (1) recycle organic matter (2) are involved in photosynthesis (3) absorb solar energy (4) slow the spread of disease 1. Identify a carnivore from the food web. wolves, worms 2. Describe the complete path of energy from the Sun to that carnivore. sun grass deer wolves sun grass rabbits wolves 1. Identify a carnivore from the food web. wolves, worms 2. Describe the complete path of energy from the Sun to that carnivore sun grass deer wolves sun grass rabbits wolves pond algae rotifers worms 3. Why are decomposers are necessary in this food web? Decomposers break down all dead organisms and return some nutrients back to the soil to be used again by plants. 4. Significant decrease in the wolf population occurs. After a period of one year, what change in the grass population would most likely be observed? A decrease in the wolf population would cause an increase in the rabbit and deer population. This would cause the grass population to decrease.