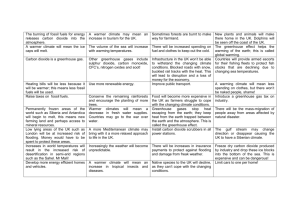
Name HUMAN IMPACT VOCAB QUIZ (Chapter 6) _____ the
advertisement

Name ______________________ HUMAN IMPACT VOCAB QUIZ (Chapter 6) _____ the development of highly productive crop strains and the use of modern agriculture techniques to increase yields of food crops A. SOIL EROSION B. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT _____ wearing away of the surface soil by water and wind C. MONOCULTURE _____ farming strategy in which large fields are planted with a single crop variety year after year D. NONRENEWABLE RESOURCE _____ way of using natural resources without depleting them and of providing for human needs without causing long term harm to the environment E. GREEN REVOLUTION F. RENEWABLE RESOURCE _____ a necessity of life (resource) which can NOT be replenished by natural means; Ex: fossil fuels _____ a necessity of life (resource) which can regenerate quickly and that is replaceable; Ex: trees, water * * * * * * * * * * * * _____ a mixture of chemicals (smoke + fog) that occurs as a gray-brown haze in the atmosphere _____ the sum total of the variety of organisms in the biosphere; It is a measure of the health of an ecosystem * * * A. POLLUTANT B. ACID RAIN C. BIODIVERSITY _____ destruction of forests D. CONSERVATION _____ a process caused by a combination of poor farming practices, overgrazing, and drought that turns productive land in areas with dry climates into deserts E. DEFORESTATION F. DESERTIFICATION ______ the wise management of natural resources, including the preservation of habitats and wildlife _____ rain containing nitric and sulfuric acids caused by burning fossil fuels _____ harmful material that can enter the biosphere through land, water, or air G. SMOG _____ a species likely to become endangered if not protected A. ENDANGERED SPECIES _____ plants or animals that have migrated or been introduced into places where they are not native and for which there are no natural predators or parasites to control their population B. THREATENED SPECIES _____ term used to refer to a species that has died out D. EXTINCTION C. INVASIVE SPECIES _____ a species whose population size is rapidly declining and will become extinct if the trend continues without intervention * * * * * * * * * * * * * * _____ increase in the average temperatures of the Earth A. ALTERNATIVE ENERGY _____ refers to any source of usable energy intended to replace the undesired consequences of using fossil fuels as an energy source B. OZONE LAYER * C. CARBON FOOTPRINT _____ the total set of GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, event or product D. GLOBAL WARMING _____ atmospheric layer in which ozone (03) gas is relatively concentrated which protects us from the sun’s ultra-violet radiation F. BIOLOGICAL MAGNIFICATION E. HABITAT FRAGMENTATION _____ increasing concentration a harmful substance in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain or web _____ splitting of ecosystems into small areas * * * * * * * * * * _____ Agreement signed by almost 200 countries, including the United States, which agreed to REDUCE (and eventually stop) the use of OZONE DEPLETING chemicals. _____ governmental body whose job it is to monitor and enforce environmental regulations, provide education on environmental issues, conduct environmental research, and provide funding for environmental programs. _____ Agreement, aimed at reducing GLOBAL WARMING, which has been ratified by 104 nations that asks participants to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions by 2012 to a percentage of their 1990 emission levels. * * * * * A. KYOTO ACCORD B. MONTREAL PROTOCOL C. ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY Name ______________________ HUMAN IMPACT VOCAB QUIZ (Chapter 6) _____ the development of highly productive crop strains and the use of modern agriculture techniques to increase yields of food crops A. MONOCULTURE B. RENEWABLE RESOURCE _____ wearing away of the surface soil by water and wind C. GREEN REVOLUTION _____ farming strategy in which large fields are planted with a single crop variety year after year D. NONRENEWABLE RESOURCE _____ way of using natural resources without depleting them and of providing for human needs without causing long term harm to the environment E. SOIL EROSION F. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT _____ a necessity of life (resource) which can NOT be replenished by natural means; Ex: fossil fuels _____ a necessity of life (resource) which can regenerate quickly and that is replaceable; Ex: trees, water * * * * * * * * * * * * _____ a mixture of chemicals (smoke + fog) that occurs as a gray-brown haze in the atmosphere _____ the sum total of the variety of organisms in the biosphere; It is a measure of the health of an ecosystem * * * A. CONSERVATION B. POLLUTANT C. DEFORESTATION _____ destruction of forests D. SMOG _____ a process caused by a combination of poor farming practices, overgrazing, and drought that turns productive land in areas with dry climates into deserts E. DESERTIFICATION F. BIODIVERSITY ______ the wise management of natural resources, including the preservation of habitats and wildlife _____ rain containing nitric and sulfuric acids caused by burning fossil fuels _____ harmful material that can enter the biosphere through land, water, or air G. ACID RAIN _____ a species likely to become endangered if not protected A. INVASIVE SPECIES _____ plants or animals that have migrated or been introduced into places where they are not native and for which there are no natural predators or parasites to control their population B. THREATENED SPECIES _____ term used to refer to a species that has died out D. ENDANGERED SPECIES C. EXTINCTION _____ a species whose population size is rapidly declining and will become extinct if the trend continues without intervention * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * _____ increase in the average temperatures of the Earth A. HABITAT FRAGMENTATION _____ refers to any source of usable energy intended to replace the undesired consequences of using fossil fuels as an energy source B. BIOLOGICAL MAGNIFICATION C. CARBON FOOTPRINT _____ the total set of GHG (greenhouse gas) emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, event or product D. ALTERNATIVE ENERGY _____ atmospheric layer in which ozone (03) gas is relatively concentrated which protects us from the sun’s ultra-violet radiation F. OZONE LAYER E. GLOBAL WARMING _____ increasing concentration a harmful substance in organisms at higher trophic levels in a food chain or web _____ splitting of ecosystems into small areas * * * * * * * * * * _____ governmental body whose job it is to monitor and enforce environmental regulations, provide education on environmental issues, conduct environmental research, and provide funding for environmental programs. _____ Agreement signed by almost 200 countries, including the United States, which agreed to REDUCE (and eventually stop) the use of OZONE DEPLETING chemicals. _____ Agreement, aimed at reducing GLOBAL WARMING, which has been ratified by 104 nations that asks participants to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions by 2012 to a percentage of their 1990 emission levels. * * * * * A. MONTREAL PROTOCOL B. KYOTO ACCORD C. ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY