Earth Science
advertisement

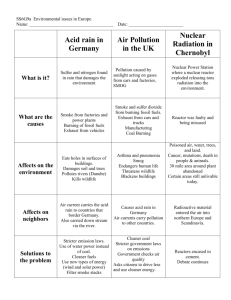
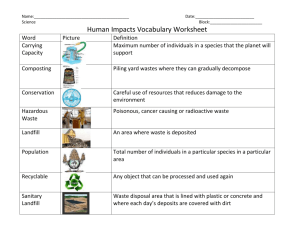
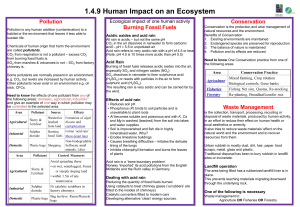
Earth Science Chapter 15 Section 2 A. Air Quality: Harmful substances in the air, water or soil are known as pollutants. Most air pollution is the result of burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, gasoline and diesel fuel. Burning fossil fuels produces a number of air pollutants, including, particles and gases that can form smog and acid rain. B. Particles: Natural Sources: Salt from ocean spray Molds and pollen by winds Forest fires, dust storms, soil erosion, Volcanoes put ash and dust and poisonous gases into the atmosphere. Human Activities: Burning fossil fuels Construction and farming C. Smog: The brown haze that forms over cities is called photochemical smog. A fossil fuel gives off unburned hydrocarbons, a substance composed of carbon and hydrogen. The burning of these fuels causes the some of the nitrogen in the air to combine with oxygen forming nitrogen oxides. The nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons and other air pollutants then react with one another in the presence of sunlight to form a mix of ozone and other chemicals, called photochemical fog. D. Temperature Inversion: During normal atmospheric conditions warm air at the surface rises and pollutants are carried away. During a temperature inversion a layer of warm air prevents the rising air from escaping. The polluted air is trapped and held close to the earth’s surface. The smog becomes more concentrated and dangerous. E. Acid Rain: One result of air pollution is acid rain. Acid rain forms when nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides combine with water in the air to form nitric acid and sulfuric acid. Acid rain can make water so acidic that plants, amphibians, fish and insects can no longer survive in it. F. Improving Air Quality: Filtering smoke stacks Improvements in Auto exhaust emissions Some people think stricter regulations are needed. Others believe reducing pollution is too expensive.