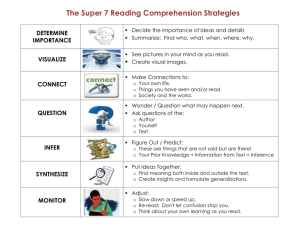
Big Question:
advertisement

Big Question: How can our determination affect our ability to succeed? Author: Pam Munoz Ryan Genre: Biography Story Sort Vocabulary Words: Arcade Games Study Stack Spelling City: Vocabulary Spelling City: Spelling Words Causes Discrimination Actions Victims momentous – very important opera –a play in which music is an essential and prominent part; a play set to music prejudice – unreasonable dislike of an idea or group of people • privileged – having some special rights, advantage, or favored • recital – a musical program, given usually by a single performer •enraged – made very angry; made furious • application - questionnaire form aud – (Greek)to hear; Example: audience duc – (Latin) to lead; Example: conductor bene – (Latin) good ; Example: benefit jud - (Latin) to judge; Example: prejudiced gram - (Greek) – to write; Example: program Present Tense Present Participle Past Tense Past Participle become (is, are) becoming became (has, have, had) become choose (is, are) choosing chose (has, have, had) chosen fall (is, are) falling fell (has, have, had) fallen find (is, are) finding found (has, have, had) found get (is, are) getting got (has, have, had) gotten give (is, are) giving gave (has, have, had) given go (is, are) going went (has, have, had) gone hear (is, are) hearing heard (has, have, had) heard is/are (is, are) being was/were (has, have, had) been know (is, are) knowing knew (has, have, had) known leave (is, are) leaving left (has, have, had) left sing (is, are) singing sang (has, have, had) sung speak (is, are) speaking spoke (has, have, had) spoken Test Tip: Some irregular verbs, such as cost, cut, hit, hurt, let, put, and shut, have the same spelling for the present, past, and past participle forms. Example: I put on my hat. (present) I put my on my hat yesterday. (past) I have put on my hat many times. (past participle) • international • prehistoric • untrustworthy • constellation • honorary • disagreement • preparation • Philadelphia • promotional • constitution • unbreakable • biodegradable • coordination • compassionate • impossibility • entirety • executive • companionship • unthinkable • predicament • inappropriately • nonnegotiable • nondiscriminatory • instantaneously • decaffeinated Sometimes authors write broad statements that apply to many examples. These statements are called generalizations. Often, clue words such as most, all, sometimes, always, and never help to identify generalizations. Generalizations supported by facts and logic are called valid generalizations. Faulty generalizations are not supported by facts. Generalizations should always be supported with facts from the text or your knowledge of the world. Support Generalization Support Similes and metaphors are comparisons of two unlike things, concepts, or people. A simile states that A is like or as B. A metaphor is a more direct comparison than a simile. It states that A is B. A suffix is a word part that is added to the end of a base word. A suffix changes the meaning of the base word. Use your knowledge of suffixes to help you determine the meaning of an unknown word. Complete the chart by writing the meaning of each suffix and providing a definition for each word.