Social Studies Curriculum
advertisement

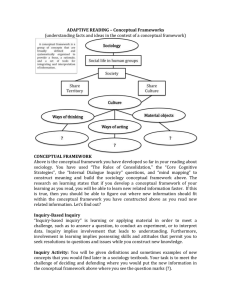
Social Studies Curriculum TCH 347 Social Studies in the Elementary School Department of Education Shippensburg University Han Liu, Ph. D. Curriculum Definition #1 What a student should know and be able to do, which is defined by the state standards linked to high-stake tests. Curriculum Definition #2 What a student should know and be able to do Grade-level content expectations Instructional methods Any classroom learning materials Curriculum for Social Studies Curriculum Content Curriculum Organization Curriculum Delivery Conceptual Structure Curriculum Scope & Sequence Social Studies Skills Social Studies Content (Basic Disciplines) Culture History Geography Economics Civics Current Affaires Sociology Anthropology Psychology Philosophy Social Studies Curriculum Organization Interdisciplinary Approach is applied in Elementary and middle schools, such as family life, cultural diversity, improve the environment… Separate Subject Approach is applied in high schools, such as U.S History, American Government, Economics… Multidisciplinary Approach is applied in teaching units, such as U.S. state, Latin America, middle east… Special topics, such as globalization, the Middle East, etc. Approaches to Deliver Social Studies Curriculum Conceptual Approach Topical Approach Emphasizing the mastery of social studies concepts Focus on topics, such as WW II, civil rights movement, etc. Inquiry Approach Generating questions Making Hypothesis to address the questions Testing the hypothesis Conceptual Structure for Social Studies Facts Vocabulary Concepts Concept Clusters Themes Generalizations Descriptive Generalizations Prescriptive Generalizations Scope and Sequence Scope: Sample . Basic Contents defined by state standards Comparative Studies & Global Perspective Special Topics: Peace Studies, Environmental Issues… Sequence: Textbook p.10, Figure 1.1 Sample. Textbook p.20, Units of Instruction in the K-8 Curriculum Basic sequence defined by state standards based on knowledge acquisition theory and grade levels School’s decisions Teacher’s decisions Skills for Social Studies Thinking Skills Language & Communication Skills Vocabulary Building Skills Research Skills Data Processing Skills Technology Skills Thinking Skills Inductive Thinking Deductive Thinking Critical Thinking Creative Thinking Analogical Thinking Problem Solving Decision-Making Generalizing Particularizing Metacognition Language and Communication Skills Receptive Skills Expressive Skills Reading Listening Speaking Writing Presenting Comprehensive Communication Skills Debating Vocabulary Building Skills Semantic map (relationship between/among concept clusters) Clusters Pairs Mnemonics Research Skills Problem Identifying Predicting/Hypothesizing Inquiry Method Selecting Data processing Analyzing Synthesizing Interpreting Inferring Evaluating/Appraising Data Processing Skills Data Source Identifying Data collection Data Tabulation Data Organizing Data Aggregation Data Analysis Data Presentation Technology Skills Searching Classifying Organizing Tabulating Communicating Transmitting Presenting Graphing Multimedia integrating Teaching aids developing