Case Study at PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta
advertisement

PUBLICATION TEXT
COST ANALYSIS OPEN REDUCTION INTERNAL FIXATION
OF FEMUR FRACTURE BASED ON ACTIVITY BASED
COSTING METHOD
(Case Study at PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta)
Arranged by :
VALYANDRA PRASZITA PR
20121030036
MASTER OF HOSPITAL MANAGEMENT PROGRAM
POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM
UNIVERSITY OF MUHAMMADIYAH YOGYAKARTA
2014
1
Cost Analysis Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Femur Fracture Based on Activity
Based Costing Method
(Case Study at PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta)
Valyandra Praszita PR 1, Firman Pribadi 2, Arlina Dewi 2
Student of Hospital Management Program, Postgraduate Program, University of
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta, 2Lecturer of Hospital Management Program, Postgraduate
Program, University of Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
1
Abstract
Background : Hospital is an organization that engaged in the field of health care . One of
its services is open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) surgery. PKU Muhammadiyah
Hospital of Yogyakarta’s Data shows number of patient with ORIF of shaft femur
fracture surgery without complications each year was increasing. Unit cost analysis in
the hospitals is still using the conventional system . So that, it need to study the pricing of
goods as a unit costing ORIF surgery without complications using Activity-Based Costing
systems with existing advantages compared to conventional accounting system.
Methods : This research is a qualitative descriptive study that analyze the unit cost of
ORIF of shaft femur fracture without complications using Activity Based Costing (ABC),
to get the cost comparison . Object of this research is all the activities that occur from the
beginning of the preparation of ORIF surgery in a central surgical installation space
until the process is complete.
Results : Based on the calculation, the unit cost of ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complications with activity-based costing method in Operating Room is IDR
3,419,481.89. With the difference between the unit cost of ORIF shaft femur fracture ABC
method with a unit cost of hospital is IDR 612,224.11.
Conclusion : There is a positive difference between the calculation of unit cost of ORIF
shaft femur fracture with the ABC method with a unit cost of hospital . So that needs to be
done by the efficiency of the hospital .
Key words : ORIF shaft femur fracture without complications , Activity Based Costing
2
INTRODUCTION
Development of health services in Indonesia is growing quite rapidly. This
is consistent with the need for hospital services increased. Apart from being a
place for social purposes such as service in the field of public health, hospitals
also carry out its objectives as a business entity (develop and promote the
business) both material and non- material1.
According to the Law of the Republic of Indonesia no. 44 in 2009, the
hospital is an institution for the public health service with its own characteristics
that are influenced by the development of health science, technological advances,
economic and social life of the people who should still be able to improve the
quality and services more affordable for the people to realize the level of healthheight .
Hospital by the World Health Organization (WHO) is an integral part of
the organization and the medical , health care serves to provide both curative and
rehabilitative communities, where the output services reach families and
environmental services.
Hospital is one of the service companies that produce the product
diversity. Diversity of products resulting many hospital costs and activity types
that occur in hospitals, so that the overhead of loading requires accuracy in
determining the cost of the product.PKU Muhammadiyah hospital is a private
hospital in Yogyakarta. One of its services is open reduction internal fixation
(ORIF) especially femur fracture.
Femur fracture is one of the most frequent case with high rate of morbidity
and mortality in patients with low extremity trauma. Except pathologic fracture,
need to get heavy direct trauma will cause this fracture such as traffic accidents,
falling down from the high location or motorbike accidents, and another trauma.
Indirect trauma or light trauma is rarely to get this fracture. It’s caused that femur
bone was protected by thick muscles around it. That is why close fracture will be
the mostly effect. The worst complication is osteonecrosis, non-union and death
will be the future complication if the fracture not treated properly2.
3
Femur fracture still becomes serious problem in health. Not only high rate
of incidence, but also high cost for the treatment. More than 275.000 case of
femur fracture was happened every year and spent out more than 3 billion US
dollars3. Beside that based on PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital’s data, number of
ORIF shaft femur fracture without complication on 2010 (38 cases), 2011 (39
cases), 2012 (45 cases) and 2013 (51 cases). It shows that the number of ORIF
shaft femur fracture is increasing every year.
Calculation of unit
cost
ORIF shaft femur fracture
at
PKU
Muhammadiyah hospital of Yogyakarta still use conventional accounting system.
The weakness of conventional accounting system that is the problem in the
imposition of indirect costs (overhead costs) to products or services are only using
the unit level activities to impose indirect costs on hospital services. This often
results in large cost distortions and inaccurate. Efforts to reduce the distortion due
to the use of traditional methods can be used a novel approach that uses a basic
activity is activity based costing or method ABC4.
Activity based costing is a method applying the concepts of accounting
activity to produce a product cost calculation more accurate. However, from a
managerial perspective, the ABC system offers more than just the cost of accurate
product information but also provide information about the cost and performance
of activities and resources and can trace accurately the costs to cost objects in
addition to the product, such as customers and channel distribusi5.
It is therefore necessary to study the pricing of goods as a unit cost ORIF
shaft femur fracture without complications at PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital of
Yogyakarta by using activity-based costing with existing advantages compared to
conventional accounting system. From the background above, the formulation of
the problem is obtained:
1. What is the unit cost ORIF shaft femur fracture without complication
measures calculated using activity-based costing method in PKU
Muhammadiyah hospital in Yogyakarta ?
2. Is there any difference between the unit cost ORIF shaft femur fracture
without complication calculated by activity-based costing method with
4
the unit cost currently implemented in PKU Muhammadiyah hospital
in Yogyakarta ?
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Types of Research
The study was conducted using qualitative descriptive method by
conducting case studies in PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta6.
Calculation of unit costs were calculated using activity-based costing (ABC).
Location and Time Research
This research has been carried out in PKU Muhammadiyah in Yogyakarta
in July-December 2013.
Subject and Object Research
The subjects in this study subjects in this study was a chief financial
officer, head of the central surgery, an orthopedist, a surgical nurse, medical
record head, the head of the CSSD (central sterile supply department) and section
maintenance tools to obtain comprehensive data on the PKU Muhammadiyah
hospital in Yogyakarta. Object of this research is all the activities that occur from
the beginning of preparation for ORIF shaft femur fracture without complications
in the surgical installation of a central space until the process is complete .
Inclusion criteria for this study were patients with diagnosis ICD-X : S
72.9 and INA-CBGs : M-4-10 shaft femur fracture and age more than 16 years
old. Exclusion criteria were multitrauma which should apply other operation out
of diagnosis ICD-X : S 72.9 and INA-CBGs : M-4-10 shaft femur fracture and if
the patient is unstable so that the operation cannot be done.
Research Variables
The variables of this study is the unit cost ORIF shaft femur fracture
without complication and activity in the operating room.
Research Instruments
1. Guidelines for documentation ie medical records, clinical pathways ORIF shaft
femur fracture without complications .
5
2. Interview guide.The interview is one method of data collection by asking
directly or communicating directly with respondents to obtain information on the
issues under study.
3. Observation using a checklist to guide clinical pathways such as direct
observation of the research object, the activities undertaken during the surgical
patient in the operating room.
4. Stopwatch is a measure of time used to measure the length of time of each
activity undertaken, ranging from the patient to the operating room after surgery.
Data analysis
The data in this study using primary data and secondary data. Primary data
of information directly from the source by means of direct interviews with
respondents and observation of activities undertaken. Secondary data in the form
of documents is done by tracking the distribution of operating costs and hospital
medical record month of January to December in 2012. The data have been
processed and analyzed by the method of activity-based costing (ABC).
1. Determine the activity centers on the unit in question.
2. Determining the cost categories and cost drivers of each category of costs.
3. Direct charge ORIF shaft femur fracture without complications.
4. Determining the cost of direct and indirect resource overhead of each
resource overhead activities using the proportion of the time.
5. Determine the activity centers ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complications found in clinical pathways.
6. Overhead charge to the centers of each activity in clinical pathways.
7. Sum the direct costs and overhead.
8. Comparing the cost of using the ABC calculations with fees set by the
hospital .
RESULTS
Overview of Research Subjects
Based on the interview with the Head of Finance, Head of the Central
Surgical Installation, Physician Specialist and Head of the content of the CSSD.
6
Each study subject was given the opportunity to express opinions. ORIF shaft
femur fracture uncomplicated calculation in PKU Muhammadiyah hospital
Yogyakarta is the conventional method which is based consumables and labor
costs.
Presentation of Data ORIF Shaft Femur Fracture Without Complications
The process of calculating the unit cost ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complications in the central installation using the ABC (activity based costing)
with7:
a. Determine the activity centers on the unit, costs and cost drivers of each
category of costs .
Table 1. Activity Centre in Operating Room
Activity Center
Operating Room (Preoperative)
Check the vital signs by doctor/nurse
Check the fracture location
Assemblying electrolyte infusion by nurse
Operating Room (durante operation)
Vital signs by doctor of anesthesia
Check the vital signs by doctor/nurse
Intra operation position
Regional anesthesia (spinal) by doctor of
anesthesia
Implementation of ORIF surgery
Check the amount of bleeding and complications
Operating Room (Post Operative)
Total Score by doctor of anesthetic
Patient handover by nurses
Handover of the goods of patients by nurses
Cost Driver
Number of activity
Number of activity
Number of action
Number of action
Number of activity
Number of action
Number of activity
Number of action
Number of activity
Number of activity
Number of activity
Number of activity
Sumber: RS PKU Muhamadiyah Yogyakarta Tahun 2012 (telah diolah kembali)
b. Direct cost ORIF shaft femur fracture without complication
The direct costs of a service is the cost that arises when a service is
done. Direct costs that arise are specialist medical services, sterilization of
7
instruments, the instruments used during ORIF shaft femur fracture,
consumables and linen laundry.
Table 2. Sterilization Cost per one time in CSSD
Sterilization Process
Cost
Information
Component
Equipment
and
Materials
3 liters of water
disinfectant
x@Rp.
4.000,00 (per tablet)
Autoclave Tape
Autoclave machine
UV Lamp 4 bohlam
x@Rp. 300.000,00
Rp. 12.000,00 Disinfectant use presept tablet. 1 liter
of water using 1 tablet .
Rp. 4.000,00
Rp. 4.148,00* There are two autoclave machine that
still has economic value. Autoclave
machine price Rp. 62.500.000,00. Cost
drivers is the use of two autoclave
machine in 2012 in the CSSD, which
is 3013 times.
Rp. 2.400,00 In the sterilization process using 4
pieces of UV lamp has a lifetime of
2000 hours. Cost drivers is time. In all
sterilization process takes 4 hours.
Office
cost
and
subscriber in CSSD
(2012)
Rp.
19.926.032,00
Rp. 4.536,00** Cost driver is time. In one process
uses
electricity
to
autoclave
sterilization for 2 hours.
Human Resources
Employee
fee
in
CSSD
(2012)Rp.
206.772.864,00
Rp. 99.590,00*** Cost driverare the number of gauze ,
linen and instruments.In the year 2012
the number is 228.013 sterilized gauze
sheets, 3.504 linen sets and 26,065 sets
of instruments.
Totals
Rp. 126.674,00
* (price of autoclave machine x 2) / 5 years
2 (price per one machine)
3013 time use
** cost of office and subscriber/366 days
x 2 hours
24hours
***In one process operation requires
{gauze 36 (sheets) / 228.013 + linen 1(set)/3.504+instrument 1(set)/26.065} x employee fee
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
8
Table 3. Direct Cost ORIF Shaft Femur Fracture Without Complications
No.
1
2
3
4
Cost Category
Number
Medical services fee for orthopedist
Medical services fee for anesthesiologist
Sterilization (in CSSD)
Alkes/obat
Spuit terumo 2.5 cc
1
Spuit terumo 5 cc
1
Spuit terumo 10 cc
1
Ringer lactate 500 ml
3
Chloret sod 0.9 500 ml
1
Spinocan G 26
1
Sedacum 15 mg inj
0,4
Ephedrin inj Ethica
1
Ketorolac 30 mg inj
1
Bupivacain inj 0.5%
1
Ondansetron 4 mg/2 ml inj
1
Pethidin HCL 50 mg inj
1
Morphin 10 inj
1
Ceftriaxone 1gr inj
1
Braunol sol
150
Alkohol 70% /cc
150
Mess Aesculap No.23
1
Sofratulle
1
FC Noctra No.16
1
Urine bag NS Ramson
1
Kasa lipat 5cm x 13cm x 12 ply
40
Handscoen ST 8 Gamex
1
Handscoen Ortho NO.6.5
3
Transfusi set Terumo
1
Aquadest OPLS 25 cc
3
Aquadest steril Wida 1L
1
Suction bag
0,5
Polysorb 0 CL 933
1
Polysorb 2/0 CL 916
1
TOTAL
Total Price
Rp
700.000
Rp
280.000
Rp
126.674
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp
3.000
3.675
4.800
29.250
8.925
35.100
12.000
11.400
12.600
20.625
7.275
11.250
9.600
9.000
17.850
3.900
2.550
15.825
14.625
5.175
34.050
15.000
61.275
21.675
7.425
9.375
38.700
86.625
85.125
1.704.349
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
9
Table 4. Direct Cost screw-plate ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complication
Tools
Broad plate 10 holes *
Cort screw 4.5 D 38 mm
Cort screw 4.5 D 40mm
Cort screw 4.5 D 42mm
TOTAL
Number
1
3
5
2
Rp
Rp
Rp
Rp.
Rp
Cost
782.850
242.550
404.250
134.400
1.563.750
Note:
*The most frequent used of broad plate for ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complication in PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
c. Determine overhead costs, both direct reource and indirect resource.
In calculating the overhead costs can be divided into two, namely
the indirect overhead costs of resource and resource overhead direct. In
table 6 there are indirect costs of resource overhead PKU Muhammadiyah
hospital in Yogyakarta is Rp 16.786.832.708,80 which will be charged to
the functional units of the PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta
on the basis of the proportion of the number of employees in each
functional unit. Operating room has a proportion of 6%, so the installation
of a central surgical got imposition of indirect resource overhead of
Rp1.007.209.962,53.
ORIF shaft femur fracture without complication is a type of major
surgery. Based on table 7 for major surgery will get indirect imposition of
resource overhead of Rp. 62.781.444,57*. If based on the large amount of
surgery to any major surgery received indirect imposition of resource
overhead of Rp. 43.658,86**.
10
Table 5 .Indirect Resource Overhead
Indirect Resource Overhead at PKU
Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta
(2012)
Labour-related
Employee fee
Equipment-related
Furniture and office equipment costs
Depreciation costs of the installation and
machine
Spaced-related
Maintenance and repair costs
Depreciation costs of nonfunctional building
Service-related
Cost of goods procurement usage
Office and subscription costs
TOTAL
COST
Rp
8.318.871.403
Rp
293.911.128
Rp
108.085.548
Rp
Rp
395.923.835
3.181.579,80*
Rp
2.919.068.372
Rp
4.697.790.843
Rp 16.786.832.708,80
* Total of big operation x imposition x imposition of indirect resource overhead
Total of all operation x imposition
**Rp. 62.781.442,00 / 1.438 (total of big operation)
***(nonfunctional building floor area/total floor area)xdepreciation cost of buildings
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
Based on interviews with the head of the operating room, load type
of operation is based on the factors in table 7. Then the load is inserted
into the table 8 according to the type of operation .
Factors
Imposition
Difficulty Doctor
Assistant Number
Time
Tool
Risk
Total
Table 6. Factors Imposition
Small
Medium
Big
Operation Operation Operation
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
5
10
15
Special
Operation
4
3
3
5
5
20
Advanced
Operation
6
3
4
5
7
25
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
11
Table 7 . Types and Charging Operations
Types of Operation
Total of Action
Imposition
Small Operation
306
0.5
Medium Operation
1451
1
Big Operation
1438
1.5
Special Operation
1275
2
Advanced Operation
144
2.5
Total
4614
7.5
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012(reprocessed)
Indirect overhead costs of resource loading will be charged to the
patient based on the activity obtained by patients who can be seen in the
following table :
Table 8. Imposition of Indirect Overhead Resource
Activity in Operating Room
Operating Room (Preoperative)
Check the vital signs by doctor/nurse
Check the fracture location
Assemblying electrolyte infusion by nurse
Operating Room (durante operation)
Vital signs by doctor of anesthesia
Check the vital signs by doctor/nurse
Intra operation position
Regional anesthesia (spinal) by doctor of anesthesia
Implementation of ORIF surgery
Check the amount of bleeding and complications
Operating Room (Post Operative)
Total Score by doctor of anesthetic
Patient handover by nurses
Handover of the goods of patients by nurses
TOTAL
Time
(minute)
5
1
5
5
Cost
(rupiah)*
Rp1.323
Rp264,60
Rp1.323
Rp1.323
5
10
1
120
1
Rp1.323
Rp2.645,99
Rp264,60
Rp31.751,90
Rp264,60
5
5
2
165
Rp1.323
Rp1.323
Rp529,20
Rp43.658,86
*(time / total of time) x total cost
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 ( already reprocessed)
After receiving indirect resource overhead, we proceed to the
calculation of the direct costs of resource overhead in the same way as
before, namely divided into 4 categories, namely labor-related, equipmentrelated, space-related and service-related. However, the direct costs are not
calculated resource overhead operating room buildings (space-related ) is
12
due to not having economic lives longer (20 years). Based on table 10 for
big operation get imposition overhead indirect resource is Rp.72.952.665*.
Table 9. Direct Resource Overhead
Direct Resource Overheadin operating room at PKU
Muhammadiyah hospital of Yogyakarta (2012)
Labour-related
Employee fee
Equipment-related
Medical equipment cost in operating room
Non medical equipment cost in operating room
Maintenance tools and building
Service-related
Cost of goods procurement usage
Electricity costs in operating room
Water costs in operating room
Phone costs in operating room
Cleaning costs in operating room
TOTAL
Cost
Rp995.866.516
Rp58.346.400
Rp11.250.400
Rp5.395.000
Rp24.669.892
Rp49.365.168
Rp106.948
Rp2.935.150
Rp22.452.546
Rp1.170.388.020
* Total of big operation x imposition x imposition of direct resource overhead
Total of all operation x imposition
**Rp. 72.958.274,00/ 1.438 (total of big operation)
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
If it is based on a large number of operations for each of the major
surgery will get direct charging of resource overhead of Rp.50.732,03**.
Beside direct charging of resource overhead, there is also cost for standard
set ORIF.
Standard set of instruments used during ORIF shaft femur fracture
consists of several tools. Total working time obtained from interviews
with the head of the central part of the installation and its surgical nurses
in that section. From interviews it was found that these tools have a life of
about 10 months or 2000 operating times. So the cost of one set of
standards set ORIF shaft femur fracture is Rp. 56.992*.
13
Table 10 . Instruments used During Operation
Tools
Number of Tools
Doek clamp
Pean bengkok sedang
Needle holder
Handle mes no.4
Pinset
Scissors
Reduction forceps
Bone
holding
forceps
(Verbrugge)
Bone levers / Hohmann
retractor
Raspatorien kecil
Large fragment instrument
set (Synthes)
Zimmer Hall surgical drill
TOTAL COST
Cost
6
2
1
1
2
1
2
1
Rp.71.700
Rp.34.000
Rp.17.000
Rp.10.000
Rp.34.000
Rp.17.000
Rp.1.800.000
Rp.900.000
2
Rp.1.420.000
1
1
Rp.906.250
Rp.85.875.000
1
Rp.22.900.000
Rp.113.984.950
* total cost/2000 operations
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
Direct imposition of resource overhead fee will be charged to the
patient based on the activity obtained by the patient, can be seen in Table
11.
14
Table 11. Imposition Direct Overhead Resource
Activity in Operating Room
Cost*
(rupiah)
Time
(minute)
Operating Room (Preoperative)
Check the vital signs by doctor/nurse
Check the fracture location
Assemblying electrolyte infusion by nurse
Operating Room (durante operation)
Vital signs by doctor of anesthesia
Check the vital signs by doctor/nurse
Intra operation position
Regional anesthesia (spinal) by doctor of anesthesia
Implementation of ORIF surgery
Check the amount of bleeding and complications
Operating Room (Post Operative)
Total Score by doctor of anesthetic
Patient handover by nurses
Handover of the goods of patients by nurses
TOTAL
5
1
5
5
Rp3.264,36
Rp652,87
Rp3.264,36
Rp3.264,36
5
10
1
120
1
Rp3.264,36
Rp6.528,73
Rp652,87
Rp78.344,75
Rp652,87
5
5
2
165
Rp3.264,36
Rp3.264,36
Rp1.305,75
Rp107.724,03
*(time / total of time) x total cost
Source: PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital in Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
d. Summing the direct and overhead costs are included in clinical pathways
Table 12. Total of All Cost
No
Cost Structure
1
Direct cost ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complication
2
Direct cost screw-plate
3
Overhead cost ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complication in operating room
TOTAL
Coat
Rp 1.704.349
Rp 1.563.750
Rp 151.382,89
Rp 3.419.481,89
DISCUSSION
Based on the research that has been done, it can be seen that the unit cost
charged by the hospital for the ORIF shaft femur fracture without complication in
operating room is of Rp. 4.031.706 while calculating unit cost of ORIF shaft
femur fracture without complication in the operating room of a central unit using
activity based costing Rp 3.419.481,89. The difference between the unit cost is Rp
15
Rp. 612.224,11, where the unit cost of PKU Muhammadiyah hospital Yogyakarta
bigger than the unit cost of the activity based costing method. The comparison can
be seen in the following table:
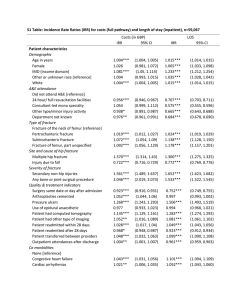
Table 13. The Differences between Unit Cost ORIF shaft femur fracture without
Complication with ABC Method, Rates and Unit Cost PKU Muhammadiyah
Hospital of Yogyakarta
Parameter
ABC
Rates in PKU
Unit Cost Hospital
Muhammadiyah
(Real Cost)
Hospital
Yogyakarta
Medical services
Rp. 700.000
Rp. 1000.000
Rp. 700.000 (-30%)
orthopedist
Anesthesia specialist
Rp. 280.000
Rp. 400.000
Rp. 280.000 (-30%)
medical services
Sterilization (in
Rp. 126.674*
Rp.180.000
Rp. 162.000 (-10%)
CSSD)
Consumables
Rp. 597.675*
Rp. 796.900**
Rp. 597.675 (-25%)
Screw – plate
Rp 1.563.750*
Rp 2.085.000
Rp 1.563.750 (-25%)
Accomodation
Rp. 151.382,89
Rp. 870.000
Rp. 728.281 (-10%)
a. Indirect resource
overhead
Rp. 43.658,86
b. Direct resource
overhead
Rp. 107.724,03
TOTAL
Rp 3.419.481,89
Rp. 5.331.900
Rp. 4.031.706
* ) Is obtained when the observation
** ) Obtained from the average consumables in three patients without complications ORIF shaft
femur fracture for class three in 2012
Source: RS PKU Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta in 2012 (reprocessed)
1 . Direct Cost
Calculation ORIF shaft femur fracture without complication for the initial
phase is to determine the activity obtained through clinical pathway that have
been tailored to the activity in PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta.
ORIF shaft femur fracture without complications in PKU Muhammadiyah
hospital Yogyakarta involves the operating room. Surgery is categorized in major
surgery. The cost of the first-ever direct cost for ORIF shaft femur fracture
without complication Rp. 1.704.349. For the largest direct cost is the cost of
medical services the doctor, which was Rp. 980.000,00 consisting of medical
services orthopedist and anesthesiologist. Based on PKU Muhammadiyah hospital
of Yogyakarta policies, medical services doctors captured 70 % of hospital rates.
16
In addition to the cost of medical services other costs that also arises is
consumable materials, in this case is the use of drugs and medical devices for the
operating room. According to observations, drugs using generic drugs and
medical consumable materials as required. In the ABC method, consumables
obtained when direct observation, but at the rates of hospital obtained from an
average of consumables in three patients without complications ORIF shaft femur
fracture class three in 2012. This is due to the lack of consumables package in
operation ORIF shaft femur fracture. The unit cost of hospital acquired with
reduced rate margin consumables, amounting to 25%. Each patient using
consumables vary, depending on current conditions in the operating room.
Then is the cost of sterilization. Sterilization performed in different units,
namely in the CSSD (central supply sterile departement). Where there is a
process of washing and sterilizing instruments. Obtained difference of Rp.
35.326,00 from the hospital unit cost, and the difference of Rp. 53.326,00 from
hospital rates.
2. Overhead Costs
The second cost structure that emerges is overhead. Overhead costs are
costs that are difficult or can not be connected and charged directly to the
production units, and accurately traced to a cost object. Overhead is divided into
two general categories: direct and indirect resource overhead and resource
overhead7. In the biggest overhead structure that emerged is non functional
payroll costs, such as wages or salaries structural other non-functional. The author
in this case do not know whether non-functional for staff salaries necessary to
efficiency or not, further analysis is required in this regard.
The second largest cost structure that appears in overhead costs is the cost
of the office and subscriptions. Through interviews have been conducted with the
Finance Manager
PKU Muhammadiyah
hospital, office expenses
and
subscriptions are costs which includes electricity charges, telephone charges,
cleaning charges, water charges and other subscription costs, including the cost of
taxes. There needs to be a more detailed breakdown of the costs that can be
known about the need for cost efficiency or not.
17
In terms of overhead costs that also arises is cost-realted equipment and
service-related.PKU Muhammadiyah hospital of Yogyakarta in terms of
equipment both medical and non medical already have economic value as well as
building PKU Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta. This is because the
economic value of time specified by the RS PKU Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta is
up.
In PKU Muhammadiyah hospital itself to have economic value of three
categories, namely for the equipment includes tools have economic value 4 years,
for machines have economic value for buildings 10 years and 20 years have
economic value. It is probably one of the reasons why the calculations with the
ABC method to be much lower with the specified hospital.
If operating room building, operating tables, anesthesia machines and
operating lamp has economic value, obtained for all operating costs are operating
roombuilding (with an area of 240 m2) Rp.11.703, operating table Rp. 82.358,
anesthesia machines Rp. 54.507 and operating lamp Rp. 12.050. If the above four
components are added, the fee is Rp. 160.618 so that the difference in unit cost by
the ABC method and unit cost hospitals to Rp. 561.920.
Based on the difference in unit cost obtained, it was concluded that the
unit cost is lower with the ABC method and more in line with the
activity. However this needs to be considered by the costs incurred in other units,
such as the operation needs to be considered by ORIF shaft femur fracture with
activity
and
hospitalization
costs. So
that
the
management
of
PKU
Muhammadiyah Hospital of Yogyakarta to review the pricing of goods in action
ORIF shaft femur fracture without complications if it is appropriate what is not.
Efficiency in economics is used to refer to a number of concepts related to
usability and maximizing the utilization of all resources in the production process
of goods and service8.Activity-based costing (ABC) is an information system that
is changing the way costs are used in the management of business process
management. If the conventional management, business process management is
broken down into functions, the ABC system, the management of business
processes is done in an integrated manner based activity9.
18
Cost calculation using activity-based costing system approach is more
accurate in determining the fee structure for the ABC system costs calculated in
accordance with the actions, activities and products that used10. Cost analysis is an
activity to calculate costs for different types of services offered, either in total or
per service per client by counting all units where the charge contained in a unit
that does not produce (cost centers) distributed to the units that produce
products and salary11. Analysis of the activity is the identification, description and
evaluation of activities undertaken. Analysis of activity should result in any
activity resulting, how many people are doing the activity, the time and resources
required to perform the activity and calculation activity value12.
CONCLUSION
Unit cost (unit cost) actions ORIF shaft femur fracture without
complicationin PKU Muhammadiyah hospital of Yogyakarta using activity-based
costing method is Rp. 3.419.481,89.
The differences between ORIF shaft femur fracture without complication
in operating room by ABC method and hospital is Rp. 612.224,11 where the unit
cost in PKU Muhammadiyah hospital of Yogyakarta greater than the unit cost of
the activity based costing method. The biggest differences are in the cost of
accommodation.
REFERENCES
1. Anton, 2005, Activity based cost system sebagai dasar penentuan harga
pokok tarif rawat inap di rumah sakit pku muhammadiyah yogyakarta,
skripsi S1, Fakultas Ekonomi, Universitas Ahmad Dahlan Yogyakarta.
2. Wardhana, A. (2006). Perbedaan Lama Perawatan Penderita Fraktur
Tertutup Femur dan Cruris yang Dilakukan Open Reduction Internal
Fixation di Rumah Sakit PKU Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta:
FK UMY.
3. Noiser, L. (2009). An overview of Shaft Femur Fractures. Journal of
Trauma , 7: 18-22.
4. Ikhsan, A & Dharmanegara, A 2010, Akutansi dan manajemen keuangan
rumah sakit al-islam bandung, Tesis S2, Program Magister Manajemen
UNPAD, Bandung
5. Marismiati, 2011, ‘Penerapan metode activity based costing system dalam
menentukan harga’. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Informasi Akuntansi, vol. 1, no.
1, hh 22-36.
19
6. Sanusi, A 2011, Metodologi penelitian Bisnis, Salemba Empat, Jakarta.
7. Baker J, 1998, Activity-Based Costing and Activity-Based Management for
Health Care, Aspen Publisher, United States.
8. Sullivan, Arthur, 2003. Urban Economics, McGraw-Hill, Fifth Edition,
New York.
9. Mulyadi, 2007, Activity-based costing system, sistem informasi biaya
untuk pemberdayaan karyawan, pengurangan biaya, dan penentuan
secara akurat kos produk dan jasa, UPP STIM YKPN, Yogyakarta.
10. Lievens, P., & Anseel, F., 2004, Confirmatory Factor Analysis and
Invariance of an Organizational Citizenship Behavior Measure Across
Samples in a Dutch-Speaking Context, Journal of Occupational and
Organizational Psychology , 77, 299–306
11. Kartadinata, Abas. 2000. Akuntansi dan Analisis Biaya. PT. Rineka Cipta,
Jakarta
12. Hansen dan Mowen, 2005, Management accounting, vol. 2, edk 7,
Salemba Empat, Jakarta.
20