IMD Year 1+2 - Academic Study Skills
advertisement

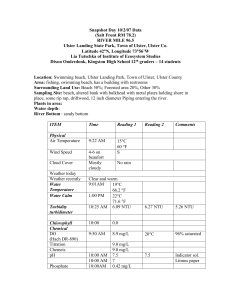
Academic Study Skills Induction Skills Audit Week 1 introduction useful software finding resources in the lrc Week 2 how to use wifi, printers and ad network how to use the imac suite how to access features of Blackboard com149 practical task on personal usage of the web (individual and group task) Week 3 Personal skills Week 4 Literacy skills Week 5 Numeracy skills Week 6 Visual/creative design skills Week 7 Information literacy skills Week 8 Presentation skills Week 9 Review - http://imdweb.infj.ulst.ac.uk/induction/files/Wk7-CWTutorial-2010.pdf Skills Audits Task: the Wheel of Life, which allows students to make a self-assessment of skills at a generic level, e.g. communication, and then provides links to appropriate resources in the manner suggested below. The easy-to-use interface might provide an entry point for students before they complete a more rigorous skills assessment. Task: http://faccompeng.ulster.ac.uk/wheel_of_life/ PACE http://pace.ulster.ac.uk A. Personal skills Helps deal with some of the personal competencies which contribute to the development of transferable employability skills and which students cite as issues when referring themselves to the Counselling Service. The key issues reviewed in this context include: time management and related issues such as procrastination, goal setting, and revision planning; reflection and self-awareness in relation to learning styles and personal strengths and weaknesses; the application of interpersonal skills to the learning process. The latter grouping includes issues such as listening and conflict resolution in group work. Task: They offer an opportunity for blended learning with face-to-face discussion and direction. These resources contain advice in a variety of formats: text, videos as well as interactive exercises such as games and quizzes. LearnHigher: http://www.learnhigher.ac.uk/Students.html This resource contains numerous sections on listening and interpersonal skills, time management, group work, critical thinking and reflecting. It contains both text based and interactive material and the site is easy to navigate. 1.UlsterGradNAV: http://gradnav.ulster.ac.uk This resource is widely used by all the Career Development Centre staff when teaching, and it is popular with students. It contains advice, videos as well as interactive and downloadable activities and contains a number of relevant sections on skills, personality, self awareness etc. B. Literacy skills Literacy skills are wide-ranging. preparation for writing (resources gathering; structuring ideas; planning the narrative); accurate communication (grammar, punctuation and spelling; coherent linkage of ideas; register and style); academic integrity (referencing and plagiarism). In addition, students need guidance and support in the interpretation of feedback received on coursework in order to use this constructively. Task: The most useful packages provide information for staff and students in a variety of formats: text, podcasts, videos, interactive quizzes. They are also written in a user-friendly manner, and provide information in bite-sized chunks so as to facilitate scaffolded learning. University of Manchester ‘Study Skills Website’: http://www.humanities.manchester.ac.uk/studyskills/ Faculty of Humanities focused. Range of links and sub-links. Writing section has subsections on plagiarism referencing etc. http://www.nottingham.ac.uk/csc/academic-integrity/student/tutorial/academic-integrity/what-isacademic-integrity.php Largely focused on plagiarism – tutorial for students. Interactive quiz links from other institutions. University of Ulster Library Training page http://library.ulster.ac.uk/training/ Brief comments with further links on: citation styles; evaluating resources; plagiarism; using the internet; research support; university email; library skills. C. Numeracy skills The needs of students for maths support will vary both with their existing expertise and with the demands of their course. At the most basic level, students may need support in elementary areas such as the rules of arithmetic and working with ratios and percentages. Also, many students are required to work with data and be able to describe and present data sets in a meaningful way. Even for those courses where mathematics is a prerequisite for entry, or which involve more sophisticated mathematical ability, students do not always present with strong mathematical competencies. A range of resources is also required, therefore, for students on science and engineering courses in more advanced topics such as statistical analysis, algebra, geometry, and calculus. Task: The study skills materials are available in a range of media types including succinct factsheets, detailed tutorial booklets, video tutorials and self-assessment materials. Mathtutor – www.mathtutor.ac.uk Mathtutor is the sister site to mathcentre, developed by the same consortium of universities. Where Mathcentre is essentially a resource site, providing materials to cover a range of learning requirements, Mathtutor organizes the material into a more structured sequence of lessons under seven main areas, namely: Arithmetic Algebra Functions and graphs, sequences and series Geometry and vectors Trigonometry Differentiation Integration Each main area is divided into a sequence of lessons and each lesson is available in text or video format, along with exercises and diagnostic tests. D. Visual/creative design skills study skills support for creative/design based courses. exploration and interpretation of ideas and artefacts through 2- and 3-dimensional representation techniques (drawing, painting, 3-d modelling etc.); portfolio skills (communication of a creative narrative through completed work). Task: These cover such skills as visual practice resources, time management skills, creative problem solving and team work. Staff in visual and creative design areas have also adopted micro-blogging (e.g. Twitter) and social networking sites (e.g. Facebook) to develop key skills as well as being useful communication tools. An introduction to visual design for website designers: http://www.lukew.com/ff/entry.asp?981 Creative problem solving skills: http://www.mycoted.com/Category:Creativity_Techniques E. Information literacy skills recognise a need for information; distinguish ways of addressing gap and select appropriate sources; construct search strategies; locate and access information; compare and evaluate information; organise, apply and communicate information; synthesise and create information. Task: A suite of student support resources for Information Literacy skills (University of Ulster Library Information Skills Unit) is developed and maintained by the Library at http://library.ulster.ac.uk/skills/infoskills/. F. Presentation skills Presentation skills are broadly divided into planning, structuring, preparing and presenting skills. More specific presentation skills relate to researching the topic, overcoming nerves, minimising stress, defining objectives, organisation, time management, enhancing audience participation, body language, designing visual aids, use of illustrations and diagrams, and verbal communication. Task: Resources provided by the University of Hull, Loughborough University, the University of Manchester and the Open University have been identified as the most appropriate to address students’ presentation skill needs. http://www2.hull.ac.uk/student/studyadvice.aspx VARK VARK Learning Styles questionnaire: http://www.vark-learn.com/english/page.asp?p=questionnaire This online resource is a questionnaire which provides automated results and a helpful study guide. There is a link for the survey on the Ulster PACE.