goal_6
advertisement

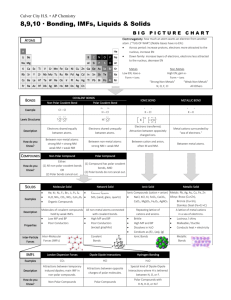
Periods Families(Groups) --same # valence electrons As a general rule, metals don’t like to form bonds(compounds) with other metals(They will with themselves). Metals(+ ions) would rather form bonds with nonmetals(- ions)!! Covalent Bonding • Involves the sharing of electrons. • Covalent bonds form between nonmetals and nonmetals. Lewis Dot Structures (aka Electron Dot Diagrams) • Lewis dot structures are a shorthand to represent the valence electrons of an atom. • The structures are written as the element symbol surrounded by dots that represent the valence electrons. Lewis Dot Structures(cont.) • Lewis structures can also be used to show covalent bonding between atoms. • The bonding electrons are placed between the atoms and can be represented by a pair of dots or a dash (each dash represents one pair of electrons, or one bond). Show the Lewis Dot Structures for the following compounds: O2 F2 H2O Covalent Bonds(cont.) • Sometimes electrons are shared equally among nonmetals in a covalent bond. Sometimes they are not. • It’s as if one element is pulling on the electrons just a little bit harder than the other. Covalent Bonds(cont.) Polar Covalent Bonds Non-Polar Covalent Bonds • One element is pulling harder on the electrons than the other(s). • Unequal sharing of electrons. • This cause them to set up “poles”. • One element will become slightly positive and the other slightly negative. • Both elements are pulling just as hard on the electrons. • Equal sharing of electrons. Solutions with Polar and Non-Polar Compounds: • As a general rule, “Likes dissolve Likes” – Polar substances dissolve polar substances! • Ex. H2O dissolves NaCl(all ionic compounds are polar) – Non-Polar substances dissolve Non-polar substances. • CO2 will dissolve in ethanol(CH3CH2OH) because both are non-polar. – Polar substances will not dissolve in Non-Polar substances!!! • Water and Oil do not mix!!! Which compound is least affected by temperature? Which compound’s solubility decreases as temperature increases? How many grams of KNO3 will dissolve in 100 g of water at 60o C? 110 g At what temperature will approximately 95 g of NaNO3 dissolve in 100 g of water? 30 oC At what temperature will the same amount of KNO3 and NaNO3 dissolve in 100 g of water? ~ 68 oC Name the following compounds: 1. NaCl Sodium Chloride 2. CaO Calcium Oxide 3. KF Potassium Fluoride 4. Na2CrO4 Sodium Chromate 5. Ca(ClO3)2 Calcium Chlorate 6. Al2(CO3)3 Aluminum Carbonate Writing Chemical Formulas: Lithium and Selenium Li+1Se-2 Li2Se Calcium and Chlorate Ca+2ClO3-1 Ca(ClO3)2 Beryllium and Phosphorus Be+2P-3 Be3P2 Gallium and Carbonate Ga+3CO3-2 Ga2(CO3)3 Write the formulas for the following compounds: 1. Calcium Phosphate Ca+2PO4-3 Ca3(PO4)2 2. Aluminum Acetate Al+3C2H3O2-1 Al(C2H3O2) 3 3. Francium Phosphide Fr+1P-3 Fr3P Determine the oxidation state of both elements in the following examples: • CuF2 Cu+2F-1 • Co2S3 Co+3S-2 • Fe2O3 Fe+3O-2 Chemical Equations: • Reactants “yield” Products • Reactants Products • Must know the 4 types of chemical reactions: 1. 2. 3. 4. Decomposition AB A + B Synthesis A + B AB Single Replacement AB + C AC + B Double Replacement AB + CD AD + CB