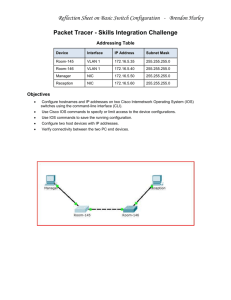
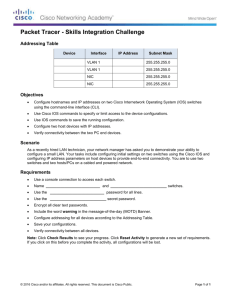
File - UAE Assignment Help
advertisement

Internship Report ICAD Student Name: Mouza Al Suwaidi Student ID: k- 21270211 Semester: Year: 2015 4/23/2015 DEDICATED TO: This internship report is dedicated to my parents, husband and all my friends for helping me in each and every difficulty I Faced in this internship report completion and to my teachers and all those who taught me, trained me and polished my abilities during my internship at ICAD residential city. 1 APPROVAL OF THE INTERNSHIP REPORT I, hereby declare that this Internship Report is submitted to the partial fulfillment of the internship program. During the last four months. Any part of this report has not been reported or copied from any report of the university and others. Approved by Academic Mentor Company Supervisor: ______________ ________________ 2 ABSTRACT The purpose of this report is to provide a comprehensive overview of my role as an internee at the IT Department of the ZonesCorp. The tasks assigned to me includes: Securing network, Configure routers, VLAN and firewall, testing components like Server team, Application team, Storage team, Database team, add new devices to the monitoring system For the internship, I upgraded the part of the network infrastructure. Our focus was to gain knowledge and to understand the things that we studied during our semesters. This report is the reflection of my learning and it gave me a chance to learn a lot and to implement it in practical life. I worked on following: 1) Network Security 2) Router configuration 3) VLAN configuration 4) Firewall working The router, VLAN and firewall configurations were completed successfully. All the relevant IT teams successfully tested their components, including Server team, Application team, Storage team, Database team. All the new devices have been added to the Monitoring system and the NOC team was responsible for monitoring the complete infrastructure. 3 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT I would like to thanks and the server team, help desk team, NOC team and the Maintenance team for sharing information about the main components about the network in the HQ and the remote sites. It was a great learning experience in this project, I have learnt incredibly about the different components of the Network structure starting from the business case to implementing the devices. I want to also thank the team at and to all who shared their experiences. I would also like to thank ICAD for their support and trust in me which encouraged me to do more. 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS Executive Summary………………………………………………………8 Introduction………………………………………………………9 Hardware overview………………………………………………………………...9-16 Campus Hierarchical Network Design Overview………………………………...16-21 Security……………………………………………………………………………21-26 The Work Flow of Main Campus Data Center…………………………………26 Work piece and work tasks I have been executing…………………………………...27-36 Procedures I have been following while performing my tasks……………………….36 How good I have been in performing my tasks……………………………………….37 Challenges I have faced while performing my tasks………………………………….37 The Overall Benefits I gained From the Internship…………………………………...37 Practical Skill…………………………………………………………………………37-38 Theoretical Knowledge………………………………………………………………38 Interpersonal Communication Skills………………………………………………38-39 Team Playing Skills………………………………………………………………39 Leadership Skills……………………………………………………………………39-40 Work Ethics Related Issue………………………………………………………40 Entrepreneurship Skills……………………………………………………………40-41 Conclusion………………………………………………………………………41 Recommendations……………………………………………………………42-43 Bibliography……………………………………………………………………44-45 5 LIST OF TABLES Basic Cisco Catalyst Switch Configuration Command……………………………14-15 Access Switch Configuration………………………………………………………15-16 Basic configuration of VLAN addressing table.…………………………………. 28-29 Basic configuration of VLAN port assignments (S2 and S3)………………………29 LIST OF FIGURES Core Layer………………………………………………………………………17 Distribution Layer………………………………………………………………19 Access Layer……………………………………………………………………20 ASA firewalls connectivity……………………………………………………23 Configuration of security settings………………………………………………24 The work flow of data center………………………………………………….26 Sample network using VLANS……………………………………………30 LIST OF ACRONYMS & ABBREVIATION ARP ASA CRAC DHCP DMZ DNS FTP GLBP HA HSRP ICT IGMP IIS Address resolution protocol Adaptive security appliances Computer room Air conditioning Dynamic host configuration protocol Demilitarized room Domain name system File transfer protocol Gateway load balancing protocol High availability Hot standby router protocol Information communication technology Internet group membership protocol Internet information services 6 INSA IP IPS IT L2 L3 LAN VPN LWAPP NAT POE Qos RU SSP VLAN VRRP VTP WCS Internet network security agency Internet protocol Introsuion prevention system Information technology Layer 2 Layer 3 Local area network Virtual private network Light weight access point protocol Network Address translation Power over Ethernet Quality of services Rack unit Security services processor Virtual local area network Virtual router redundancy protocol Virtual trunking protocol Wireless control system 7 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY This report is about to explain what I did and learned during my internship period with ICAD, main campus data center. The key purpose of this internship is to learn and apply the knowledge acquired during the studies in a real world, in order to tackle with the problems using the knowledge and skills learned during the academic years. I have discussed every major aspect of the campus network observed and perceived during my internship program. This report is divided into four sections. Section one will discuss about the background of ICAD and ICT Development office. In section two, overview of network design of campus and basic switch configuration. Section three discuss about the overall benefits I gained during the internship program. The last section is about conclusion and recommendations of the previous sections (ICT development office and main campus data center). The internship program gives students an opportunity to spend their time in a true manner and with the spirit to learn practical orientation of theoretical study framework. This report is about my internship that I have undergone at ICAD development office (main campus data center). During my internship I am able to learn practical aspect of network and gained good working experience. 8 INTRODUCTION Internship is the beginning of the road that will take me to the point I want to be at after my graduation. Internship is a practice I need to perform, because it prepares me for the business life that I aim for. HARDWARE OVERVIEW Cisco Catalyst 6500 E: (Webroot, 2001) (Cisco, ASA5585S20-10K-K9, 2015) The 15U Rack, 9-slot Catalyst 6509-E switch is an enhanced version of the Catalyst 6509 switch. It offers high port densities that are ideal for many wiring closet, distribution, core network and data center deployments. It supports end-to-end operational consistency benefits. The horizontal 9-slots framework supports redundant power supplies and supervisor engines, and slots for more than eight modules. Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series modules includes: Supervisor engines, Fast Ethernet modules (IEEE 802.3af Power over Ethernet Gigabit Ethernet modules (IEEE 802.3af [PoE]), 10 Gigabit Ethernet modules, Flex WAN modules, and Shared Port Adaptors/SPA Interface Processors. [PoE]), A multi-Gigabit services module includes: 9 Content services, firewall, intrusion detection, IPsec, VPN, network analysis, and SSL acceleration Cisco Catalyst 4500 E switch: The Cisco Catalyst 4500 E Series Switches enable borderless networks, security, mobility, application performance, video, and energy savings over an infrastructure. Infrastructure supports resiliency, virtualization, and automation. It provides high borderless performance, scalability, mobility, secure user experience through Layer 2-4 switching investments and services reduction of total cost of ownership and superior investment protection. Cisco Catalyst 4500 E switches have a centralized forwarding architecture that enables collaboration, virtualization, and operational manageability through simplified operations. Backward and forward compatibility span multiple generations. It also provide exceptional investment protection and deployment flexibility which meet the evolving needs of organizations of all sizes The Cisco Catalyst 4500 E Series platform has 10 Gigabit Ethernet (GE) uplinks which supports PoEP. PoEP enable the customers to future proof their network. 10 Cisco Catalyst 3750 Series: (HP) The Cisco Catalyst3750 Series is an inventive line of multilayer Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet switches featuring Cisco Stack Wise technology. Cisco Stack Wise technology allows customers to build a unified and highly resilient switching system (one switch at a time). For mid-sized organizations branch offices, the Cisco Catalyst 3750 Series eases deployment of converged applications and adapts to change business needs. Business needs can be change by providing configuration flexibility, support for converged network patterns, and automation of intelligent network services configurations. Additionally, the Cisco Catalyst 3750 Series is optimized for high-density Gigabit Ethernet deployments and includes a diverse range of switches that meet access, aggregation, and small-network backbone-connectivity requirements. Cisco Catalyst 2960 Series: (HP) The Cisco Catalyst 2960-S and 2960 Series Switches are the leading Layer 2 edge which provides improved ease of use, highly secure business operations, improved sustainability, and a borderless network experience. The Cisco Catalyst 2960-S Series switches includes new Cisco Flex Stack switch stacking capability with 1 and 10 Gigabit connectivity, and Power over Ethernet Plus (PoE+) which offers fast Ethernet access connectivity and PoE capabilities. The Cisco Catalyst 2960-S and 2960 Series are fixedconfiguration access switches which are designed for enterprise, midmarket, and branch office networks to provide lower total cost of ownership. 11 Twin Gig Converter Module: The Cisco Twin Gig Converter Module converts a single 10 Gigabit Ethernet X2 interface into two Gigabit Ethernet port slots, which can be populated with suitable Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) optics. It provides a total of 12 wire-speed Gigabit Ethernet ports if used in all 6X2 interface slots. The flexibility provided by the Twin Gig Converter Module enables customers to aggregate Gigabit Ethernet and 10 Gigabit Ethernet LAN access switches on a single line card. Cisco ASA 5520 And 5540 Security Appliance: (Cisco, 5500%20series%20corrected.pdf, 2011) The Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance integrates a firewall, IPsec, and VPN capability which provides all-in-1 solution for the enterprise network. Cisco Asa 5585-X Security Appliance: The ASA 5585-X adaptive security appliance is a 2 RU, two-slot chassis accommodating up to two AC power supply modules, which contains the necessary cooling components for operation, although a fan module can be installed in the second bay. The Security Services Processor (SSP) resides in slot 0 (the bottom slot). The optional Intrusion Prevention System Security Services Processor (IPS SSP) resides in slot 1 (the top slot). All port numbers are numbered from right to left start with 0. 12 Cisco 5500 Wireless Controller: (Cisco, 5500_wlanctrl_install_guide_ipland, 2009) The Cisco 5500 Series Wireless Controller is a highly scalable and flexible platform that enables system wide services for mission-critical wireless in medium to large-sized enterprises and campus environments. It designed for 802.11n performance, maximum scalability and capability which supports up to 250 lightweight access points and 7000 clients and make it ideal for large-sized enterprises and high-density applications. The 5500 Series offers enhanced uptime with RF visibility and protection, the ability to instantaneously manage up to 500 access points, superior performance for reliable streaming video and toll quality voice, and improved fault recovery for a consistent mobility experience in the most demanding environments. A core component of the Cisco unified wireless solution delivers wireless security, intrusion detection, radio management, quality of service (QoS), and mobility across an entire enterprise. The controllers work in concurrently with other controllers, Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS), and access points to provide network managers with a robust wireless LAN solution. The Cisco 5500 Series Wireless Controller supports the Office Extend access point, which provides secure communications from a controller to an access point at a remote location. Cisco Aironet 1250 Lightweight Access Point: (cisco1131g.pdf, 2008) The lightweight access point (model: AIR-LAP1252) is part of the Cisco Integrated Wireless Network Solution. It requires no manual configuration before being 13 mounted but it automatically configured by a Cisco wireless LAN controller using the Light weight Access Point Protocol (LWAPP). In the Cisco Centralized Wireless LAN architecture, access points operate in lightweight mode. The lightweight access points associate to a controller. The controller manages the configuration, firmware, and controls transactions such as 802.1xauthentication. Additionally, wireless traffic is tunneled through the controller. A key hardware feature of the access point includes: Two radio module slots for single or dual-radio operation, Ethernet port and console port, LED’s, Multiple power sources, UL 2043 compliance, and Anti-theft features. A table 1 shows the Basic Cisco Catalyst Switch Configuration Command and its descriptions. Cisco IOS commands and parameters Explanation Router (config) #IP DHCP excluded- Specifies the IP address or range of IP address low addresses (high address). addresses not to be assigned by the DHCP server to clients. Router (config) #IP DHCP pool pool name. Creates the DHCP pool name and enters DHCP pool configuration mode. 14 Router (config-DHCP) #network network- Specifies the subnet network address and address subnet mask. mask of the DHCP pool. Router (config-DHCP)#default-server DNS Specifies the IP address of the DNS server, server address (DNS server address 2..8) up to eight DNS server addresses can be specified. Router(config-DHCP) default-router Specifies the default router address offered default router addresses (default router 2 to the client. Up to eight addresses can be address.. default router 8 address) specified. Router (config-DHCP) #lease days infinite Specifies the IP address lease time in days (0-365) or specifies infinite lease. Default lease time is one day. Table 1 Basic Cisco Catalyst Switch Configuration Command (DHCP) A table 2 shows the configuration of trunk port on switch. Only trunk ports need to be manually configured. The command below was performed on Switch to configure a trunk port. Switch Switch 1 and 2 Port Ge-0/0/0, ae0 Port Mode trunk 15 Virtual Chassis Ae0,ae1 trunk Virtual Chassis Ge-0/0/2 access Virtual Chassis Ge-1/0/2 access Table 2 Access Switch Configuration (Switch) CAMPUS HIERARCHICAL NETWORK DESIGN OVERVIEW (HA_campus_DG) In 1999, Cisco introduced the hierarchical design model. It uses a layered approach to network design as shown in Figure (2.3). The building block components are access layer, distribution layer, and the core layer (backbone layer). The key advantages of this model are its hierarchical structure and its modularity. In a hierarchical design, the capacity, features, and functionality of a specific device are optimized for its position in the network and the role that it plays. It promotes scalability and stability. The number of flows and their associated bandwidth requirements increases when traverse points aggregate and move up the hierarchy from access to distribution and distribution to core. Functions are distributed at each layer. A hierarchical design avoids the need for a fully-meshed network. The building blocks of modular networks are easy to replicate, redesign, and expand. It didn’t require 16 redesigning the whole network each time a module is added or removed. Distinct building blocks can be put in-service and taken out-of-service without impacting the rest of the network. This capabilities facilitates troubleshooting, problem isolation, and network management. Core Layer: (HA_campus_DG) In hierarchical model, the individual building blocks are interconnected by using a core layer (backbone layer). A figure 1 shows that the core layer serves as backbone for the network. The core needs to be fast and extremely resilient because for connectivity purpose every building block depends on it. Current hardware accelerated systems have the potential to deliver complex services at wire speed. However, in the core of the network “less is more” approach should be taken. A minimal configuration reduces configuration complexity by limiting the chances of operational error. Figure 1 core layer (HA_campus_DG) 17 Although it is possible to achieve redundancy with a highly-meshed topology because that type of design does not provide consistent convergence if a link or node fails. Also, peering and adjacency issues exist with a highly-meshed design. Highly-meshed design makes routing difficult to configure and scale. Additionally, as the network grows or changes the high port count adds unnecessary cost and increases complexity. Key Design Issues: (HA_campus_DG) The other key design issues are as follows: Designing the core layer as a high-speed, Layer 3 (L3) switching environment utilize only hardware-accelerated services. Layer 3 core designs are superior to Layer 2 and other alternatives because they provide: Faster convergence around a link or node failure. Increased scalability because neighbor relationships and meshing are reduced. More efficient bandwidth utilization. Use redundant point-to-point L3 interconnections. It generates the fastest and most deterministic convergence results. Avoid L2 loops and the complexity of L2 redundancy, such as Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and indirect failure detection for L3. Distribution Layer: (HA_campus_DG) The distribution layer aggregates nodes from the access layer and protect the core from high-density peering as shown in Figure 2. In Addition, the distribution layer creates a fault boundary which provides a logical isolation point in the event of a failure 18 originating in the access layer. It deployed as a pair of L3 switches. The distribution layer uses L3 switching for its connectivity to the core of the network and L2 services for its connectivity to the access layer. The Key considerations for the distribution layer are Load balancing, Quality of Service (QoS), and ease of provisioning. Figure 2 distribution layer (HA_campus_DG) (Cisco, Campus_Network_for_High_Availability_Design_Guide.pdf, 2008)In distribution layer, the high availability is provided through dual equal-cost paths from the distribution layer to the core and from the access layer to the distribution layer which results in fast, deterministic convergence in the event of a link or node failure. When redundant paths are discovered then fail-over depends mainly on hardware link failure detection instead of timer-based software failure detection. Convergence based on these functions, which are implemented in hardware, is the most deterministic. Access Layer: (HA_campus_DG) The access layer is the first point of entry into the network for edge devices, end stations, and IP phones as shown in the figure 3. In access layer, switches are connected to two separate distribution layer switches for redundancy. If the connection between the 19 distribution layer switches is an L3 connection, then there will be no loops and all uplinks actively forward traffic. Figure 3 access layer (HA_campus_DG) Features: (HA_campus_DG) A robust access layer provides the following key features: High availability (HA) which supported by many hardware and software attributes. The hardware and software attributes of the access layer that support high availability include the following: (Cisco, Campus_Network_for_High_Availability_Design_Guide.pdf, 2008) System-level redundancy using redundant supervisor engines and redundant power supplies. It will provide high-availability for critical user groups. Default gateway redundancy using dual connections to redundant systems (distribution layer switches) that use GLBP, HSRP, or VRRP. It 20 will provide fast failover from one switch to the backup switch in the distribution layer. Operating system high-availability features, such as Link Aggregation (Ether Channel or 802.3ad). It will provide higher effective bandwidth while reducing complexity. Prioritization of mission-critical network traffic using Quality Of Services. It will provide traffic classification and queuing. Security services for additional security against unauthorized access to the network through the use of tools. Security includes 802.1x, port security, DHCP snooping, Dynamic ARP Inspection, and IP Source Guard. Efficient network and bandwidth management using software features such as Internet Group Membership Protocol (IGMP) snooping. IGMP snooping helps to control multicast packet flooding for multicast applications. Inline power (POE) for IP telephony and wireless access points that allow customers to converge voice onto their data network and also provide roaming WLAN access for users. Foundation services. SECURITY (Wallace, 2009) As the world is becoming more interconnected with the advent of the Internet and new networking technology so it also increasing the chances of attacks which require 21 more security. There are large amount of personal, commercial, military, and government information on networking infrastructures worldwide. Network security is becoming of great importance because of intellectual property that can be easily acquired through the internet. Perimeter Security: (cisco, 2009) A network /internetwork perimeter is a secure boundary of a network that includes firewalls, routers, ids, VPN, mechanisms, DMZ and screened subnets. DMZ is outside the Firewall. Screened subnet is an isolated sub-network connected to a dedicated firewall interface. Cisco ASA Firewall: (pii/B978159749100650007X, 2007) A firewall is a network system that manages access between two or more networks. Types Of Firewall: (pii/B978159749100650007X, 2007) Firewall operations are based on one of three technologies: Packet Filtering: Packet filtering limits the information that is allowed into a network which is based on the source and destination addresses. Proxy Server (Application Layer): In proxy server, requests connections on behalf of a client. 22 Stateful Packet Filtering: Stateful packet filtering limits the information that is allowed into a network which is based destination address, source addresses, and contents of the state table. A figure 4 shows ASA firewall connectivity inside and outside the network. The higher the security level of an interface the higher the trust level of the network connected to that interface and vice-versa. As a result, the above figure assign a security level of 100 to an inside interface of a given LAN and the 0 security level to the outside interface which is connected to the Internet/ internet service provider. Figure 4 ASA firewall connectivity (pii/B978159749100650007X, 2007) Server Farm Security: (Cisco, 5500_wlanctrl_install_guide_ipland, 2009) The first action should be considered to secure server farms is deploying the multilayer defense mechanism. For additional protections from internal and external attack, Cisco ASA 5500 firewalls and IPS modules will be deployed to each council’s server farm. The Cisco ASA5500 firewalls and IPS modules will be configured to filter 23 and inspect traffics that flow to and fro from those critical application servers according to access policies set by the ICAD. A figure 5 shows how to set up a security in switch. Figure 5 Configuring Security Settings 24 ASA Firewall Placement: The ASA firewall will be placed between the core or distribution switches and the redundant server farm switches to secure any traffic flow between the server farms and the LAN users. NETWORK DEVICE SECURITY (DEVICE HARDENING) (Wallace, 2009) Physical security/controls help to protect the data environment and prevent potential attackers from readily having physical access to the data. Examples Of Physical Controls: Examples of physical controls are as following: Security Systems: Security system is use to monitor intruder’s physical security barriers (for instance: locked doors) while entering to data centers and accessing network devices. Climate Protection Systems: Climate protection system is use to maintain proper temperature and humidity, and to alert in the event of fire. 25 Security Personnel: Security personnel is use to protect the data. THE WORK FLOW OF MAIN CAMPUS DATA CENTER A figure 6 shows that main campus data center is under System & Network administrator. The workflow of main campus data center is from the president to network Administrator it is hierarchical steps. Figure 6 26 WORK PIECE AND WORK TASKS I HAVE BEEN EXECUTING Work tasks which I have been executing during my internship period is basic switch configuration, VLAN, Trucking configuration, VTP, DHCP, Network, Network Address Translation, Microsoft Window Server 2008, Active Directory Domain Services, DNS, IIS, FTP and active Directory. VLAN Configuration (Boger, 2010) The hierarchical topology segments the network into physical building block and simplifies operation and increase of availability. Each layer of hierarchical infrastructure has a specific role. By default, switches break up collision domains and routers break up broadcast domains. The supervisor said that by creating virtual local area network (VLAN) in the distribution layer, switches break up broadcast domains in a pure switched internetwork. VLAN is a logical grouping of network users and resources connected to administratively defined ports on a switch. He said that when you create VLANs, you’re given the ability to create smaller broadcast domains within a layer 2 switched internetworks by assigning different ports on the switch to service different sub networks. A VLAN is treated like its own subnet or broadcast domain, means that frames broadcast into the network are only switch between the ports which is logically grouped within the same VLAN. 27 VLAN consists of two basic goals. Firstly, create the VLAN and secondly, assign the proper port to that VLAN. VLAN can be created on a VTP server switch or they can be created on each individual switches. In ICAD, residential area network created all VLNs on VTP server switches which makes it more manageable and scalable. I have chosen the distribution layer switches to operate on a VTP server mode and I have made all the access switches to operate in VTP clients. Hence, All the VLANs configured in distribution switch will be propagated to all the respected access switches. Note: By default, all VLANs are allowed on all trunks. You can explicitly control which VLANs are allowed on a trunk by using the switch port trunk allowed “VLAN VLAN-id” command on the interface at each end of the trunk. In addition, it can specify a native VLAN other than the default VLAN 1, using the switch port trunk native “VLAN VLAN-id” command. These two measures can help to reduce the possibility of VLAN attacks. The Fast Ethernet ports connected to the hosts on the network can be set up as static access because they are not to be used as trunk ports. To set the access mode use the “switch port mode access” command. A table 3 shows the basic configuration of VLAN addressing table. Device Interface IP address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.00.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.00.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.00.13 255.255.255.0 N/A 28 PC1 NIC 172.17.10.21 255.255.255.0 172.17.10.1 PC2 NIC 172.17.20.22 255.255.255.0 172.17.20.1 PC3 NIC 172.17.30.23 255.255.255.0 172.17.30.1 PC4 NIC 172.17.10.24 255.255.255.0 172.17.10.1 PC5 NIC 172.17.20.25 255.255.255.0 172.17.20.1 PC6 NIC 172.17.30.26 255.255.255.0 172.17.30.1 Table 3 addressing table for configuring VLAN (Vlan) A table 4 shows the basic configuration of VLAN port assignments (S2 and S3). Ports Assignment Network Fa0/1-0/5 802.1q trunks (Native VLAN) 172.17.99.0/24 Fa0/6-0/10 VLAN 30-guest (default) 172.17.30.0/24 Fa0/11-0/17 VLAN 10-faculty/staff 172.17.10.0/24 Fa0/18-0/24 VLAN 20sludenis 172.17.20.0/24 Table 4 basic configuration of VLAN port assignments (S2 and S3) (Vlan) A figure7 shows 2 pc under VLAN connected to router through Switch. The connectivity between switch and router in VLAN is called as VLAN trunk. 29 Figure 7 VTP VTP stands for VLAN trunking protocol. VTP is Cisco proprietary Layer 2 messaging protocol that manages the addition, deletion, and renaming of Virtual Local Area Networks on a network-wide basis. Cisco's VLAN Trunk Protocol reduces administration loads in a switched network. When a new VLAN is created on one of the VTP server, the VLAN is distributed through all switches in the domain. This reduces the need to configure the same VLAN everywhere. VTP provides the following benefits: VLAN configuration consistency across the network. Mapping scheme that allows a VLAN to be trunked over mixed Accurate tracking and monitoring of VLAN’s. Dynamic reporting of added VLAN’s across the network. Plug-and-play configuration when adding new VLANs in a VTP media. domain, also called a VLAN management domain. VTP domain consists of 30 trunked switches those are under the administrative responsibility of switches in server VTP mode. A switch can be in only one VTP domain with the same VTP domain name. The default VTP mode for the 2960 and 3560 switches is server mode. VLAN information is not propagated until a domain name is specified and trunks are set up between the devices. Trunk Configuration: Trunking is a process of connecting switches together so that they can send VLAN information between each other. A trunk port is a point-to-point connection between switches, a switch and a router, and switch and server. It carries the traffic of multiple VLANS. Configuration of trunk involves identifying trunk ports and selecting the encapsulation type. Identifying the trunk ports is a useful task in such a way that it eases VLAN configuration and administration. He remained that, all the uplink ports connecting access switches to distribution switches, distribution switches to core switches, edge switches to core switches and DMZ switches to core switches are set to be trunk ports. Ports on the 2960 and 3560 switches are set to dynamic auto by default. This means that they are willing to negotiate a trunk with the neighbor. However, if both sides are set to dynamic auto, the link will remain in access mode. Configuring one end of the trunk using the “switch port mode” trunk can do this command. On the 3560 switches, I also need to configure the trunk encapsulation with the “Switch port trunk 31 encapsulation” command .The 3560 switch can use either Inter-Switch Link (ISL) or 802.1Q encapsulation, whereas the 2960 switch only supports802.1Q DHCP: I spend some more time working on Dynamic host configuration protocol. DHCP is defined in RFC 2131 and is built around a client/server model—hosts requesting IP addresses use a DHCP client, whereas a DHCP server handles address assignment. Hosts can be manually configured to use a static IP address, subnet mask, default gateway address, and so on. That might be appropriate for some devices, such as servers, which would need stable and reserved addresses. For the majority of end user devices, static address assignment can become a huge administrative chore because DHCP is a dynamic mechanism. IP addresses are offered on a leased basis. Before the offered lease time expires, the client must try to renew its address; otherwise, that address may be offered up to a different client. DHCP Design Considerations: In ICAD, DHCP servers are the distribution switches. The distribution switches are configured as a DHCP server because DHCP is designed to work within a broadcast domain. They offer the client devices in the ICAD network IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway address. 32 DHCP excludes addresses within the IP subnet that should be reserved and not offered to clients. DHCP pool uses a text string pool-name to define the pool or scope of addresses that will be offered. Network: (Cisco, Building-Core-Networks-with-OSPF-IS-IS-BGP-and-MPLS, 2014) The command identifies the IP subnet and subnet mask of the address range. The subnet should be identical to the one configured on the Layer 3 interface. The DHCP lease time __________________ The DNS name of the university is _______________ The IP address for the DNS server is________________ Network Address Translation (Cisco, Building-Core-Networks-with-OSPF-IS-IS-BGPand-MPLS, 2014) (data-center-infrastructure-resource-guide.pdf, 2009) Moreover, another lesson I have learned during my internship period at ICAD Data center is that the internet is expanding at an exponential rate. As the amount of information and resources increases, it increasing the need of internet for even the smallest businesses and homes. Network Address Translation (NAT) is a method of connecting multiple computers to the Internet (or any other IP network) using one IP address. This allows home users and small businesses to connect their network to the Internet cheaply and efficiently. The incentive towards increasing use of NAT comes from a number of factors which are as follows: 33 A world shortage of IP addresses. Security needs. Ease and flexibility of network administration. The rest of the internship period was spend working on Microsoft server 2008 configuration like DNS, DHCP, IIS, Active directory and FTP server with my supervisor. In fact, it was a very important experience to me because it expanded my practical knowledge and helped me to develop new practical skills and abilities. Microsoft Window Server 2008 Active Directory Domain Services (Matthews, 2009) Active Directory domain services are used mainly to manage users and resource management across enterprise infrastructures spanning the physical subnets across the globe. Active Directory domain provides distributed database to store and manage application data, user data and computer data respectively. Active directory structure comprises of Single forest, multiple domains and child domains. Administrator can configure active directory domain based on the physical subnets. It is advisable to install directory server on the physical site. Active directory provides different security boundaries in the form of: a) Forest b) Domain c) Organizational 34 Units AD Functions: A UNIT AD plays two basic functions within a network: 1. A directory service containing a hierarchical listing of all the objects within the network, 2. An authentication and security service that controls and provides access to network resources. These two roles are different in nature but combine together to provide increased user capabilities while decreasing administrative overhead. The Active Directory itself is defined by a schema that indicates how each object is represented within the data store. For instance: A user object has a first name, last name, logon name, e-mail address, and password. Database schema refers to the structure of the database in the same way the Active Directory schema defines the Active Directory’s structure. Domain Name System (DNS) is a system for naming computers and network services that maps those names to network addresses and organizes them into a hierarchy of domains. DNS naming is used on TCP/IP networks, such as the Internet and most corporate networks. DNS naming locate computers and services by using user-friendly names. When a user enters the DNS name of a computer in an application, DNS look up for the name and provides other information that is related to the computer, such as its IP address or services that it provides for the network. This process is called name resolution. DNS naming system make it easier to use network resources by providing users with a way to refer to a computer or service by a name that is easy to remember. DNS looks up for that name and 35 provides the numeric address to those operating systems and applications that require to identify the computer on a network. PROCEDURES I HAVE BEEN FOLLOWING WHILE PERFORMING MY TASKS Procedures I have been using during my internship period in ICAD, main campus data center to perform my tasks are as following: (data-center-infrastructure-resourceguide.pdf, 2009) 1. Analyzing of each network hardware’s in data center. 2. Identified the three layer Campus hierarchical network model. 3. Analyze Cisco switch command. 4. Configuration of distribution layer switch. 5. Configuration of access layer switch. (data-center-infrastructure-resource-guide.pdf, 2009)In the first month of my internship program, it was all about studying technical details regarding the application of each network hardware infrastructure in the data center as well as identifying the three layers Campus hierarchical network model. While the procedures, which carried out during the second week, is from analyzing Cisco switch command to the study of VLAN, VTP, Trunk and configuration of distribution and access layer switch. 36 HOW GOOD I HAVE BEEN IN PERFORMING MY TASKS: During my internship program I work on my tasks with enthusiasm, as well as my supervisor is such a sincere man when I ask a question he answered courteously. All in all I did my task effectively and efficiently, and I was punctual and attentive while performing my tasks. CHALLENGES I HAVE FACED WHILE PERFORMING MY TASKS: I can truly say that during my internship with main campus data center that I was challenged, and through all those challenges I grew as a person as well as a student. Not only was the work that I was doing beneficial to get knowledge, but it also made me have to work hard to get it right knowledge. I learned how to configured distribution layer and access layer switch is new for me, how to multi-task and manage my time. THE OVERALL BENEFITS I GAINED FROM THE INTERNSHIP: One thing I have learned in a long life: “That all our science, measured against reality, is primitive and childlike—and yet is the most precious thing we have” ALBERT EINSTEIN PRACTICAL SKILL 37 The Internship provide an opportunity to connect classroom theory with current industry challenges, aware of latest technologies, and to converse and interact with a large pool of talented experienced department members which will provide a deeper insight to the overall operation, as well as provide a valuable pool of resources to assist in completion of internship program. This internship program was exactly what I needed to nurture the lack of practical skills I had. I would acquire practical experience to complement the theoretical content of my studies. THEORETICAL KNOWLEDGE During my internship period in the main campus data center, I gained theoretical knowledge. What I have been learned the course of data communication and computer networks in the classroom. I gained more knowledge about campus enterprise network, three Cisco hierarchy layers, the configuration of distribution and access switch and Microsoft window server 2008 DNS , DHCP ,IIS ,FTP and Active directory domain service. INTERPERSONAL COMMUNICATION SKILLS: (Ant0417, 2011) During my internship period the Interpersonal skills, which are the life skills I use every day to communicate and interact with other people-individually or in groups are good for me. Not only how I communicate with others, but also I got confidence and my ability to listen and understand. Through this internship, I found that I gained many new 38 skills, such as problem solving skill, diversity, effective communication, teamwork and service recovery, attention to detail, time management, personal empowerment, selfconfidence, responsibility and cultural sensitivity. My supervisor was so kind to answer with patience and teach me much that made this internship so enjoyable. I had gotten a wonderful internship that spent such a happy moment with all of them. Though, still have so much to learn, I think this challenge was what should include in my career. It will help me in future. TEAM PLAYING SKILLS In the section of the company I had been working, most of the time I had work with my supervisor though gained in terms of improving my team playing skill during my internship period in main campus ICT development office, data center is most valuable. LEADERSHIP SKILL (MTD, 2010) Leadership skills includes tool, behaviors, capabilities that a person needs in order to be successful at motivating and directing others, and the ability to help people grow in their own abilities. Well said by one of the famous writer: “the most successful leaders are those that drive other to active their own success”. I gained leadership skills from my supervisor during the internship period which include managing time, motivating individuals, giving feedback and building teams. 39 WORK ETHICS RELATED ISSUE An internship is an opportunity to learn the skills and behaviors along with the work values that are required for success in the workplace. Workplace ethics are established codes of conduct that reflect the values of the organization where you are working. I possess a willingness to work hard from my supervisor during my internship period. In addition to work hard, it’s important to work smartly. I acquired the most efficient way to complete tasks and finding ways to save time while completing daily assignments. It’s also important to care about my job and complete all projects while maintaining a positive attitude. ENTREPRENEURSHIP SKILL Entrepreneurship is the ability to create and build something from practically nothing. It is initiating, doing, achieving and building the organization, rather than just watching, analyzing or describing one. It is the ability of sensing an opportunity where others see chaos, contradiction and confusion. It is the ability to build a founding team to complement your own skills and talents. It is the know-how to find, marshal and control resources and to make sure you don’t go out of budget. Finally, it is the willingness to take calculated risks, both personal and financial, and then to do everything possible to get the odds in your favor.” 40 An entrepreneurship education program consists of wide-ranging subjects, and in every entrepreneurship education program, learning something at outside classroom like internship in a company plays an important role, as well as normal lectures in classroom. Of course, in this respect, the good relationship between educational institutions and business society is very important for the purpose of implementing an internship program as a part of curriculum. Interns gain firsthand understanding of entrepreneurship along with enhanced technical, professional, and communication skills. In this internship, I have gained self-confidence, information seeking, problem seeking and see sand acts on opportunities of business in networking. Though helping me to clarify my vision and decide whether or not to forge ahead with the idea. CONCLUSION After going through the whole period of internship as an intern, I’ve observed and learned so many professional activities. This internship was very fruitful to me because I had to cover many different fields. I also learnt new concepts and new ways of working. I also acquired practical experience to complement the theoretical content of my study for campus Cisco three-layer hierarchical model tasks and detailed configuration of each layers, wireless local area network (WLAN) and network security of data center. To conclude, I think that this internship was very beneficial to me as I learnt a lot, and it provide an opportunity to practically deal with technologies. 41 RECOMMENDATIONS The Data Center is the hub of the residential city computing resources, which are shared by the management and administrative communities. These facilities provide a secure, enterprise-wide, reliable, and redundant infrastructure for the delivery of missioncritical network systems with in premises. (Data, 2014) Some suggestions for the improvement of the situation are given below: Access Floors: One of the key predesigned considerations that affect almost every aspect of success within a data center environment is the access floor (raised floor). This infrastructure is every bit as important for cooling, equipment support, grounding, and electrical and communications connectivity as the building structure supporting it. Data center uses separate cluster so the building should be maintained in standard data center designed way. They should optimize the airflow and heat dissipation which will allow the computing equipment to run more efficiently, so the data center should be installed raised floor in standard way. Cable Management: All data cabling should be under the floor, both ends of the cable should be labeled and tagged for proper identification. 42 Hardware Management: The hardware is easily identifiable if data center hardware identification will be appropriate, fully qualified server names, and all equipment within the cabinets Protection: The data center should be protected in building grounding and lightning protection system. Retrieving Of Files: ICAD main office must configure FTP protocol for the retrieve of files based on FTP protocol. Antivirus: I strongly recommend that the ICAD should use licensed antivirus. Training Program: Training program should be started for all staff. 43 Bibliography pii/B978159749100650007X. (2007). Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from sciencedirect: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B978159749100650007X cisco1131g.pdf. (2008). Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from microtekno: http://www.microtekno.fr/destockage/pdf/cisco1131g.pdf data-center-infrastructure-resource-guide.pdf. (2009). Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from exocomm: http://exocomm.net/library/dc/data-center-infrastructure-resource-guide.pdf Ant0417. (2011). What_is_interpersonal_skills. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from anwers: http://www.answers.com/Q/What_is_interpersonal_skills Boger, P. (2010). cnp-switchlabmanual. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/lucnamthang/ccnp-switchlabmanual-17248202 Cisco. (2008). Campus_Network_for_High_Availability_Design_Guide.pdf. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from mars: http://mars.tekkom.dk/mediawiki/images/c/c3/Campus_Network_for_High_Availability _Design_Guide.pdf cisco. (2009). /CISCO%20-%20640-802-ccna.pdf. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from innos: http://innos.in/downloads/CISCO%20-%20640-802-ccna.pdf Cisco. (2009). 5500_wlanctrl_install_guide_ipland. Retrieved 4 23, 2015, from ipland: http://ipland.com.ua/modules/pages/doc/5500_wlanctrl_install_guide_ipland.pdf Cisco. (2011). 5500%20series%20corrected.pdf. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from skywire: http://skywire.com.au/user_files/File/5500%20series%20corrected.pdf Cisco. (2014). Building-Core-Networks-with-OSPF-IS-IS-BGP-and-MPLS. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from docstoc: http://www.docstoc.com/docs/142403262/Building-Core-Networks-withOSPF-IS-IS-BGP-and-MPLS Cisco. (2015). ASA5585S20-10K-K9. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from hardware: http://www.hardware.com/products/cisco/ASA5585S20-10K-K9 Data. (2014). data-centers/index.html. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from it.northwestern: http://www.it.northwestern.edu/data-centers/index.html DHCP. (n.d.). configure-dhcp-cisco-table1.jpg. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from tor: http://www.tor.eu/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/configure-dhcp-cisco-table1.jpg 44 HA_campus_DG. (n.d.). HA_campus_DG. Retrieved 4 23, 2015, from cisco: http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Campus/HA_campus_DG/ hacampusdg.html HP. (n.d.). dabs-electronics-uk-311.html?Fujitsu_Siemens_Base_Unit_FibreCat_SX80_ISCSI. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from dabs.s5.com.istemp.com: http://dabs.s5.com.istemp.com/electronics/dabs-electronics-uk311.html?Fujitsu_Siemens_Base_Unit_FibreCat_SX80_ISCSI Matthews, M. (2009). server-2008-a-beginners-guide-mgh. Retrieved from slideshare: http://www.slideshare.net/DibyanshuKumar/server-2008-a-beginners-guide-mgh MTD. (2010). leadership-skills.pdf. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from pbcoaching: http://www.pbcoaching.net/leadership-skills.pdf Switch. (n.d.). wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Switch.png. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from ebrahma: http://www.ebrahma.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Switch.png Vlan. (n.d.). 7xYi6R8wMQI/s1600/addresss+table.jpg. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from Blog: http://2.bp.blogspot.com/-vwhSLHKUhQ/UchLGtegm5I/AAAAAAAAAM0/7xYi6R8wMQI/s1600/addresss+table.jpg Wallace, M. W. (2009). chapter-1--understanding-network-security-principles.html?page=2. Retrieved from networkworld: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2268110/lanwan/chapter-1--understanding-network-security-principles.html?page=2 Webroot. (2001). ws-c6509-e. Retrieved 4 24, 2015, from netxg: http://www.netxg.com/content/ws-c6509-e 45