Slide 1 - Images

Ch. 4 Arrangement of
Electrons in Atoms
4.1 Electromagnetic Spectrum
YouTube Notes
Light
Light behaves like a wave and particle!
Light as a Wave
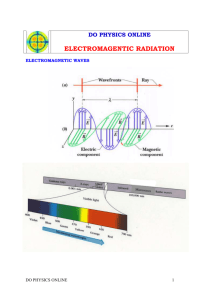
electromagnetic radiation :
form of energy that acts as a wave as it travels
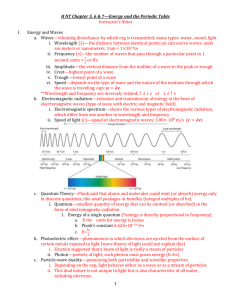
includes: visible light, X rays, ultraviolet and infrared light, microwaves, and radio waves
All forms are combined to form electromagnetic spectrum
Light as a Wave
Draw in your journal.
Speed of light: all form of EM radiation travel at a speed of 3.0 x
10 8 m/s
Light as a Wave c
wavelength: (λ) distance between points on adjacent waves; in nm
(10 9 nm = 1m) frequency: (ν) number of waves that passes a point in a second, in waves/second
Inversely proportional!
Example
1. Calculate the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation whose frequency is
7.5 x10² Hz.
Photoelectric Effect
when light is shone on a piece of metal, electrons can be emitted
Photoelectric Effect
Max Planck: a German physicist suggested that an object emits energy in the form of small packets of energy called quanta
quantum- the minimum amount of energy that can be gained or lost by an atom
Einstein later suggested that light can be viewed as stream of particles
photon- particle of EM radiation having no mass and carrying one quantum of energy
Energy of a quantum of radiation
(joules)
Light as a particle
E
h
Planck’s
Constant is equal to
6.626x10
-34 J*s
Frequency
Example
3. Determine the energy (in joules) of a photon whose frequency is 3.55 x 10 17 Hz.
Line-Emission Spectrum
ground state- lowest energy state of an atom
excited state- when an atom has higher potential energy than it has at ground state
Line-Emission Spectrum
line-emission spectrum- series of wavelengths of light created when visible portion of light from excited atoms is shined through a prism
When an excited atom falls back to ground state, it emits photon of radiation…we see this as different colors!
Flame Test Lab