Electromagnetic Spectrum Webquest
advertisement

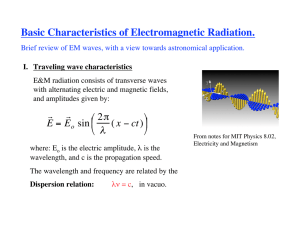
Electromagnetic Spectrum Webquest Task 1: Click on the NASA: Electromagnetic Link 1. When you tune your _____________, watch TV, send a _________ ____________, or pop popcorn in a _________________oven, you are using electromagnetic energy. 2. Electromagnetic energy travels in ______________ and spans a broad spectrum from very _____________ radio waves to very ______________ gamma rays. The human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. A radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x-ray machine uses yet another portion. Click on the: Anatomy of an Electromagnetic Wave (on the Right). 3. Electromagnetic waves differ from mechanical waves in that they do not require a___________________. 4. This means that electromagnetic waves can travel not only through air and solid materials, but also through the ___________________of space. Click on the: Wave Behaviors Link on the Right. 5. Reflection is when incident light (incoming light) hits an object and ____________ _______. Very smooth surfaces such as mirrors ______________ almost all incident light. 6. Absorption occurs when photons from incident light hit atoms and molecules and cause them to ______________. The more an object's molecules move and vibrate, the ________________ it becomes. 7. Diffraction is the bending and ________________ of waves around an obstacle. It is most pronounced when a light wave strikes an object with a size comparable to its own wavelength. An instrument called a spectrometer uses diffraction to separate light into a range of wavelengths—a __________________. In the case of visible light, the separation of wavelengths through diffraction results in a __________________. 8. Scattering occurs when light bounces off an object in a variety of ________________. 9. Refraction is when light waves change ______________ as they pass from one _____________ to another. Light travels slower in _______ than in a vacuum, and even slower in water. As light travels into a different medium, the change in speed bends the light. Click on the NASA: Electromagnetic Spectrum Diagram Link: 10. Fill-in the Table below using the diagram: Type or EM Radiation Radio Two examples: Microwave Infrared Visible Ultraviolet X-ray Gamma Ray 11. Which type of EM radiation has the longest wavelength?_______________________________ 12. Which type of EM radiation has the shortest wavelength?______________________________ 13. Which color of visible light has the shortest wavelength?__________________ 14. Which color has the longest wavelength?______________________ Go to the NASA: Diagram Link Look at the diagram of the EM Spectrum to answer the following question: 15. What two objects does the diagram compare the size or radio wave to? ____________________ __________________________ 16. What type of EM radiation has the highest frequency?_________________________ 17. What two types of radiation can penetrate Earth’s atmosphere? _____________________________ _______________________________ Click on the Hazards of EM Radiation Link: 18. List three hazards below: Post-Question: 19. Would we be able to survive without EM radiation? Explain your answer with information you learned from the webquest. (3-5 Sentences) Finished? Click on the Waves Quiz link and test yourself on your knowledge of the Parts of a Wave.