Types of Checking Accounts
advertisement

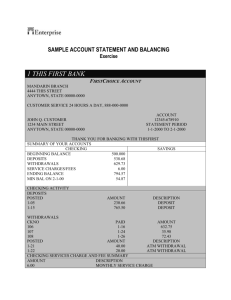
Banking and Checking Accounts Unit Unit Objectives: ~ To compute and compare earnings from simple and compound interest. ~ Calculating Interest Study Guide and Quiz ~ Introduction to Savings Accounts ~ Understand Checking Accounts - Types of Accounts - How to write checks - Filling in a registry ~ Checking Account Study Guide and Quiz ~ Checking Account Scavenger Hunt Key Terms: ~ Simple Interest: ~ Compound Interest: ~ Rate: ~ Savings Account: ~ Checking Account: Calculating Simple Interest *** The fees on some loans are computed by Simple Interest.*** RULE: I = PRT Example 1: Rich lends $400 to his cousin, who pays him a 7% simple interest each year. At the end of 3 years, the cousin pays back the loan. What is the total amount Rich collects? Step 1: Find the interest using I = PRT Step 2: Add the interest to the principal amount to find the total. Example 2: Find the simple interest earned and the total amount. Principal: $300 Rate: 5% Simple Interest : ______________ Time: 2 years Total = _______________ *** Complete pg 248 Exercise A, #2 – 10 EVEN!! Calculating Compound Interest People earn can earn compound interest for the money in their savings accounts We are still using I = PRT to calculate interest. Example 3: Kim deposits $100 into an account that earns 5% interest, compounded twice a year. Calculate the amount in the account after one year. Step 1: Compute the interest for the first 6 months. Step 2: Add the interest to the original deposit (or principal) to find the new principal. Step 3: Compute the interest for the second 6 months. Step 4: Add interest to the principal (from step 2) to find the new principal. (Interest compounded twice a year is said to be compounded semi annually) *** Let’s complete pg. 251 Exercise A Example 4: Compute the new principal at the end of one year when the interest is compounded quarterly. Principal: $100 First Quarter Third Quarter Rate of Interested: 5.5% Second Quarter Fourth Quarter New Principal at the end of 1 year: *** Let’s finish Exercise B on pg. 251 Introduction to Savings Accounts What is a savings account? What are the benefits of having a savings account? It's Safe: It Pays: Types of Savings Accounts There are many ways for you to save your money and earn interest. These are some of the most common accounts at banks and credit unions. After you have saved enough money, you may choose to invest with other types of financial services. Basic Savings Account Money Market Accounts Certificate of Deposit (CD) Savings Bonds Types of Checking Accounts Having a checking account at a bank or other financial institution allows you to write checks to pay for goods and services or to get cash. A check is a written order instructing your bank to pay money to someone or an entity. To use checks, you need to open a checking account and make regular deposits into that account. Banks offer several different types of checking accounts. Here are some of the most common checking options: • A basic checking • An interest bearing A joint checking What are the benefits of having a checking account? Checks How to Read a Check This information will be printed on your checks. 1. 2. Your Name Your Address City, State, Zip Code 1001 Date _____________ Pay to the order of ______________________________________ $ __________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ dollars Bank’s Name Address City, State, Zip Code For ____________________________________ 01234567 3. ____________________________________ 000000281609 1001 4. 5. 6. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. How to Write a Check This is the information you write on a check. Your Name Your Address City, State, Zip 1001 16-123/4567 Date ______1_____ Pay to the order of _____2_____________________________________ $ __3______________ 4__________________________________________________________________________ dollars Bank’s Name Address City, State, Zip For _5___________________________________ 1234567 6__________________________________ 0000000016093829387 1001 What to Write 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Filling in a Registry Keeping Track of Your Checks Your bank will give you a check register with your checks. Use the register to keep track of the checks you write. Example Use it to keep track of the deposits you make. Use it to keep track of how much money is in your account. Debits: ( - ) When you write a check, record it in your check register. Write the amount under the payment, or debit, column. Subtract this amount from your balance. If you pay a fee per check, remember to subtract that, too. Credits: ( + ) When you make a deposit, record it in your check register. Write the amount under the deposit, or credit, column. Add this amount to your balance. Check Register Check No. 3308 Date 6/10/06 6/12/06 3309 6/15/06 6/17/06 3310 6/17/06 Description of Transaction Northern Electrics May electric bill Deposit birthday money Anne’s Shoe Shop shoes for Jennifer ATM withdrawal lunch with Judy ReLini’s Salon hair color Payment (Debit) 83.46 Deposit (Credit) Fee .25 .25 20.00 1.00 29.00 .25 577.80 83.71 494.09 + 100.00 594.09 - 30.05 564.04 - 21.00 543.04 - 29.25 513.79 - 100.00 29.80 Balance Your Turn to Practice Write in these transactions on the check register. You pay 25¢ for each check. 1. On June 20 you make a deposit of $324.00. 2. On June 21 you write a check to The Gas Company for $34.02. 3. On June 28 you buy a video from Sam’s Videos for $20.43. What is your balance now? __________________________ *The following account begins with a balance of $297.15. Find the new balance after each transaction. Reading a Bank Statement 2D Student Handout - Reading a Bank Statement Topic 2: Money Management Name of Student ________________________ Reading a Bank Statement answer key Using the bank statement on the next page, answer the following questions: 1. What period does this statement cover? 12/20/99 - 1/18/00 2. What is the account number of this statement? 0471-678 3. How many deposits were made and what were the amounts? Three, for the amounts of $1200, $521.78, and $258.90 4. How many checks cleared and what was the total dollar amount of the checks that cleared? Six, for a total amount of $1590.25 5. Was there any ATM activity? If so, how many transactions were there, and what was the total amount? Yes—three for a total amount of $80.00 6. Was there any check card activity? If so, how many transactions were there, and what was the total amount? Yes—one for a total amount of $35.00 7. Were there any service charges? If so, what was the total amount? Yes—$3.50 8. What is the total of all withdrawals (checks, ATM transactions, check card transactions, service charges)? $1708.75 9. What is the new balance of the account? $883.97 10. Did check #182 clear? Yes 11. What was the amount of check #183? $217.54 12. Did check #185 clear? No 13. What was the amount of check #187? $53.97 Reconciling an Account Reconciling an Account (continued) Enter The New Balance shown on your statement $ ________ Add Any deposits or transfers listed $ ________ in your register that are not $ ________ shown on your statement $ ________ Total + $ ________ Calculate the subtotal $ ________ Subtract Your total outstanding checks and withdrawals - $ ________ Calculate the ending balance This amount should be the same as the current balance in your check register $ _______ Use the reconciliation worksheet above to answer the following questions: 1. What is the new balance shown on the statement? 2. What is the total amount of deposits listed in the check register but not shown on the statement? 3. What is the sum of the new balance and the deposits not shown on the statement? 4. What is the total amount of outstanding checks and withdrawals? 5. What is the ending balance? Name: Block: Date: