Comparative Respiratory Systems
advertisement

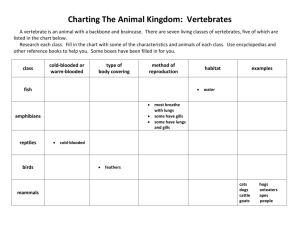
Comparative Respiratory Systems The function of animal respiratory systems is to… AND to… It’s all about DIFFUSION!!! Skin Diffusion (in Invertebrates) • • • • Thin layer of skin cells Moist/wet for gas diffusion Blood vessels close to the skin Gas exchange by diffusion • Oxygen in • Carbon Dioxide out • Example Organisms: • • • • • • Flat worms Round worms Segmented worms Jellies Sponges Mollusks • Bivalves • Snails • Cephalopods Gills (in Annelids) • Small thin branches • Lined with blood vessels • Gas exchange by diffusion • Oxygen in • Carbon Dioxide out • Example Organisms: • segmented worms • leaches • earthworms • Feathery structure just under the mantle (under the shell) • Lined with blood vessels • Gas exchange by diffusion • Oxygen in • Carbon Dioxide out • Example organisms: • Mollusks: • Bivalves (clams, mussels, etc.) • Gastropods (snails, slugs) • Cephalopods (octopus, squid, etc.) Mantle Cavity Gills (in Mollusks) • Spiracles • Holes along abdomen • How air gets into the body • Tracheal Tubes/Tracheoles • Tubes that carry air throughout body • Air Sacs • Reservoirs of air; push air through tracheal tubes when contracted • Gases are moved, to a large extent, by pumping actions of the body segments; no blood flow needed. Respiratory System (of Insects) Respiratory System (of Insects) • Hemolymph (i.e. arthropod blood) seeps into tracheoles in periods of low activity. • Fluid/gas interface gas exchange • Hemolymph pulled out of tracheoles in high activity • Gas exchange is nearer to cells • Respiratory system of insects is what restricts their body size. (i.e. this system is only efficient for small sizes up to diameter of 3 cm. Book Lung (in Arachnids) • Found inside an air-filled cavity (atrium) in underside of the abdomen. • Hemolymph (i.e. arthropod blood) flows between the layers of air pockets (lamellae) for gas exchange. • Stacks of alternating lamellae and tissue filled with hemolymph look similar to a folded book. Gills (in Fish) The Gills of a Tuna fish Gills (in Fish) • Gills have a highly-folded feathery structure • Gill filaments are hair-like projections • Filaments extend off 3-7 gill arches • Lined with capillaries (smallest blood vessels) • Counter current for efficient gas exchange • Operculum • Flap that covers/protects gills • Opens when water is pushed through gills • Buccal cavity (mouth) • Forces water past gills Amphibian Skin (only in water) & Gills (sometimes) Skin: similar to invertebrate structure and function Gills: similar to fish in structure and function Amphibian Lungs • Lungs • modified air sacs • Folded inner surface to… • Lined with small blood vessels • Gas exchange Avian (bird) Respiratory System • The Avian respiratory system is similar to that of Mammals, with two key differences: 1. Air sacs (9 of them) which expand on inhalation and contract on exhalation, allowing for… Avian (bird) Respiratory System 2. One-way flow: air moving through lungs is constant “fresh” air with higher O2 content. • Avian lungs are the only site of gas exchange, air sacs just move the air through the system. Mammalian Respiratory System • The nasal cavity is lined with hair to filter inhaled air; also warms and humidifies air. • Air is directed to alveoli (air sacs in the lungs) through branching network of tubes • Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles • Alveoli have very thin layer of cells (1 or 2 deep) with capillaries all around for maximized gas exchange. References • • • • • • • • • • • • http://www.bozemanscience.com/respiratory-system http://spice.duit.uwa.edu.au/samples/ast0842/specific/images/diving_animals/anatomy/snake_03.png http://aibara.tripod.com/rdiag.jpg https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=W7Efjt6UC1g http://media-2.web.britannica.com/eb-media/14/55014-004-B80B2BEF.jpg http://classconnection.s3.amazonaws.com/38/flashcards/1293038/png/fish_gills1336075212422.png http://www.amentsoc.org/insects/fact-files/respiration.html http://www.loganaskwhy.com/notes_reviews_handouts/Bio%20PPT%20Files/Chapter30LoganBio_files/slide 0052_image074.jpg http://www.brown.edu/Departments/Engineering/Courses/En123/MuscleExp/ImgSource/frog_gas_exchang e.gif http://www.paulnoll.com/Oregon/Birds/Avian-Respiratory.jpg http://science.kennesaw.edu/~jdirnber/Bio2108/Lecture/LecPhysio/42-25-BirdRespiratorySys-CL.jpg http://people.eku.edu/ritchisong/birdrespiration.html