water assignments
advertisement

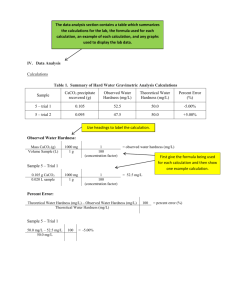
Nirma University Institute of Technology B.Tech (First Year) Subject: - Chemistry Chapter – Water Date of submission:Section: A Odd roll no. students attempt odd questions and even roll no. students attempt even questions 1. What is hardness of water? What is carbonate, non-carbonate and pseudohardness? 2. What do you mean by hardness? Explain different types of hardness? 3. Define degree of hardness. Name its units. Establish the relationship between them. 4. Why hardness is usually expressed in terms of equivalent amount of CaCO3? Give units of hardness and relation between them. 5. Name the chemical species formed after reaction of soap and hardness of water:(a) CaCO3 (b) Calcium stearate (c) CaSO4 (d) Calgon 6. Which of the following substances will (a) increase hardness (b) decreases hardness (c) have no effect on hard water containing : MgCl2, MgSO4, Ca(HCO3)2, CaSO4, CaCl2, KCl, NH4Cl, NH4OH, (NH4)2SO4, Ca(OH)2, Na2SO4, CaCO3, NaCl, NaOH, Na2CO3. 7. What is superfiltration or hyperfiltration? 8. Compare demineralization and electro dialysis process for water treatment. 9. What is alkalinity of water? Which ions are responsible for it? When P=M alkalinity is due to the presence of _____ ions. 10. Explain why HCO3¯ is usually more abundant ion in river water than in sea water. Alkalinity of natural water is due to the presence of:(a) HCO3¯ (b) SiO32- (c) HSiO3¯ (d) CO32- (e) all 11. Write balanced chemical equations for removal of SO42-from water using anion exchange resin R-Cl. 12. Write balanced chemical equations for conversion of NaCl to ZnCl2 using cation exchange resin. 13. Distilled water can be obtained by:(a) Permutit process (b) Boiling (c) Lime soda process (d) Ion exchange resin 14. Ionic and non-ionic impurities from water can be removed by:(a) Reverse osmosis (b) Electrolysis (c) Deionization (d) All 15. Which of the following is not used as a water softener for permanent hardness:(a) NaOH (b) Ca(OH)2 (c) Na2CO3 (d) Sodium hexa meta phosphate 16. Which of the following is not a coagulant:(a) FeSO4 (b) Al2 (SO4)3 (c) NaAlO2 (d) N2 H4 17. (a) Water containing dissolved salts with peculiar salty taste is called hard water (True or False) (b) Weakly basic anion exchangers can be regenerated with ________ or _______ or _______. 18. (a)Rain water is the purest form of natural water (True or False). (b) _________ is indicator used in EDTA method. 19. Compare Ion Exchange, Zeolite, Lime-Soda Process with respect to principle involved, advantages and limitations. 20. 11. (a) What are boiler scales? What are ill effects of scales? How can scale formation be prevented by: (i) phosphate conditioning, (ii) calgon conditioning? (b) Write short notes on : (i) Caustic embrittlement (ii) Priming and Foaming Section B 1. A zeolite bed was exhausted after removing completely the total hardness of 20000 liters of water. It required regeneration with 150 litres of a solution containing 100 mg/l of NaCl. Calculate the hardness of water. (Ans 641 mg/l) 2. The analytical report of a water sample is as under: Substance H2SO4 MgSO4 CaSO4 Concentration 49 240 136 (in mg/L) Mol. wt. 98 120 136 NaCl 25 58.5 3. A water sample contains 204 mg of CaSO4 per liter. Calculate the hardness in terms of CaCO3 equivalents. 4. 0.28 g of CaCO3 was dissolved in HCI and the solution was made to one litre with distilled water. 100 ml of the above solution required 28 ml of EDTA solution on titration. 100 ml of the hard water sample required 33 ml of the same EDTA solution on titration. After boiling 100ml of this water, cooling, filterning and then titration required 10 ml of EDTA solution. Calculate the temporary and permanent hardness of water. (Hardness ; Total = 330, Perm. = 100, Temp. = 230ppm) 5. A sample of water on analysis has been found to contain the following in ppm Ca(HCO3)2 = 12.5; CaCl2 = 8.2; MgSO4 = 2.6. Calculate the temporary and permanent hardness in degree French? 6. A standard hard water contains 1 5g of CaCO3 per jilter. 20 mL a this required 25mL of EDTA solution. 100 ml of sample water required 18 ml EDTA solution. The same sample after boiling required 12 mL EDTA solution. Calculate the temporary hardness of the given sample of water, in terms of ppm. 7. 100 ml of a water sample, on titration with N/5O H2SO4 gave a titre value of 5.8 ml to phenolphthalein end point and another 100 ml sample on titration with same acid gave atitre value of 11.6 ml to methyl orange end point. Calculate the alkalinity of the water sample in terms of CaCO3 and comment on the type of alkalinity present. 8. 100 ml of water sample, on titration with N/50 H2SO4 using phenolphthalein as indicator, gave the end point when 5 ml of acid were run down. Another lot of 100 ml of the sample also required 5 ml of the acid to obtain methyl-orange end point. What type of alkalinity is present in the sample and what is its magnitude? 9. The total hardness of 1,000 litres of water was completely removed by a zeolite softener. The zeolite softener required 30 litres of sodium chloride solution, containing 15 g/litre of NaCl for regeneration. Calculate the hardness of water. 10. 10,000 litres of hard water was softened by zeolite process. The zeolite required a total amount of 8 litres of NaCl solution containing 150 g/L of NaCI for regeneration. Calculate the hardness of water.