Lab #2 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water Objective
advertisement

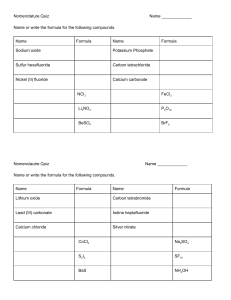
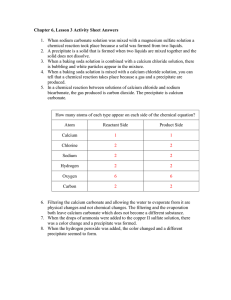
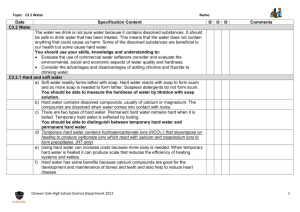
Lab #2 - Gravimetric Analysis of Calcium and Hard Water Objective: Determine the parts per million (mg/L), of calcium carbonate in a sample of hard water. Background: Tap water contains ions that can bind to soap molecules, rendering the soaps ineffective. Water containing these interfering ions is called hard water. The main source of hardness in our water is calcium ions. You must determine the hardness of our water in parts per million (mg/L) of calcium carbonate in a 20 mL sample of water. CaCO3(s) ↔ Ca2+(aq) + CO32-(aq) The reaction above is an equilibrium reaction in which limestone rock (calcium carbonate) is dissolved into the groundwater supply. You will be able to use Le Chatelier's principle to determine the amount of calcium carbonate dissolved in the water. Your group must figure out a way to shift the equilibrium far to the left to make all of the dissolved calcium carbonate a solid (precipitate). By weighing the resulting precipitate, the parts per million can be determined.