Lesson 7 Structures and Processes of the Respiratory Syst
advertisement

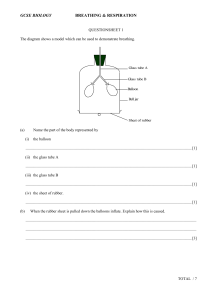
The human respiratory system has four important structural features that enable it to function properly: A thin permeable respiratory membrane through which diffusion can occur A large surface area for gas exchange A good supply of blood A breathing system for bringing oxygen-rich air to the respiratory membrane Ventilation: the process in more complex organisms that ensures a flow of oxygen-rich air to the lungs. (aka: breathing) Gas Exchange: the processes whereby the body cells obtain oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide. (aka: diffusion of gases) CILIA (in pink) MUCUS CELLS (in red) The oil in the machine of our body We make about 1 – 1.5 litres per day When sick, consistency changes (or from dehydration) Allergies (and some infections) cause leakage of mucus producing cells Green colour can be from neutrophils (most abundant white blood cell in humans) Alveoli (air sacs) High Surface area Air is 37oC and moist Membrane is one cell thick Passive Transport. Breathing is based on negative pressure http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CBv2Bqq AydE Pleura space (area between visceral and parietal pleura) is filled with fluid to minimize friction If air is introduced into the pleural cavity (ie: through a stabbing or broken rib), the membranes separate. This causes the lung to collapse in a condition called pneumothorax. If pneumothorax occurs, the lung cannot inflate because nothing is pulling on it to increase its volume and reduce its air pressure. This leads to difficulty breathing. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=isZzZ4TMnY TOTAL LUNG CAPCITY: TIDAL VOLUME: The maximum volume of air that can be inhaled The volume of air inhaled or exhaled during a during a single breath. normal, involuntary breath. It's about 0.5L in the average adult or 10% of the total lung capacity. INSPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME: EXPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME: The amount of additional air that can be The volume of additional air that can be inhaled after a normal inhalation. exhaled after a normal exhalation. RESIDUAL VOLUME: The volume of air that remains in the lungs after a forced exhalation. The residual volume of air prevents the lungs from collapsing. VITAL CAPACITY: The maximum amount of air that can be inhaled or exhaled. During periods of high demand for oxygen the reserve volumes decrease and tidal volume increases. The maximum tidal volume is the vital capacity. Vital capacity is about 4.4L to 4.8L in males and 3.4L to 3.8L in females. Physical activity depends on the energy released during aerobic cellular respiration which depends on the rate of oxygen delivery a high maximum rate of oxygen usage indicates an efficient respiratory system. The rate of oxygen usage can be calculated using a spirometer. VO2: It is an estimated or measured value representing the rate at which oxygen is used in the body. It is measured in millilitres per kilogram per minute (mL/kg/min) VO2max: The maximum rate at which oxygen can be used in an individual. It is the maximum amount of oxygen that an individual can use during sustained, intense physical activity. It is also measured in mL/kg/min. EPO -- a hormone naturally produced by human kidneys to stimulate red blood cell production http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_3HVzBM FcD8 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7dG4b7Pz -J4