Research in Psychology–Key Learning Goals
advertisement

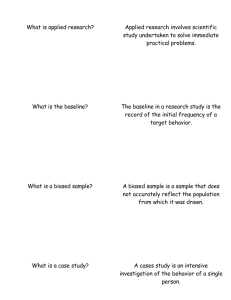
Research in Psychology–Key Learning Goals 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Explain science’s main assumption, and describe the goals of the scientific enterprise Clarify the relations among theory, hypotheses, and research Outline the steps in a scientific investigation Identify the advantages of the scientific approach Describe the experimental method, IV and DV, and experimental and control groups Explain how experiments can vary in format and design Describe the featured study on how expectations influence reactions to positive and negative outcomes Evaluate the major advantages and disadvantages of the experimental method Explain the role of naturalistic observation, case studies, and surveys in psychological research Evaluate the major advantages and disadvantages of descriptive/correlational research Describe three measures of central tendency and one measure of variability Distinguish between positive and negative correlations Discuss correlation in relation to prediction and causation Clarify the meaning of statistical significance Articulate the importance of replication in research Recognize sampling bias and placebo effects in research Recognize problems with self report data and experimenter bias in research Contrast the pros and cons of deception in research with human subjects Discuss the controversy about the use of animals as research subjects Summarize the major ethical principles governing psychological research Terms –Chapter 1 Hypothesis Theory Operational Definition Participants/Subjects Techniques Journal Peer Review Independent Variable Dependent Variable Control Group Extraneous Variables Random Assignment Naturalistic Observation Between Subjects Design Within Subjects Design Case Study Survey Descriptive Statistics Median Mode Variability Correlation Correlation Coefficient Negative Correlation Size/Strength of Correlation Statistical Significance p<.05 Sample Sampling Bias Placebo Effects Social Desirability Bias Double Blind Procedure (single blind not specifically mentioned) Internet Mediated Research Deception Abstract Introduction Results Discussion Anecdotal Evidence Naive Realism Data Collection Experiment Experimental Group Confounding Variables Reactivity Statistics Mean Standard Deviation Positive Correlation Inferential Statistics Replication Placebo Experimenter Bias Debriefing Methods References