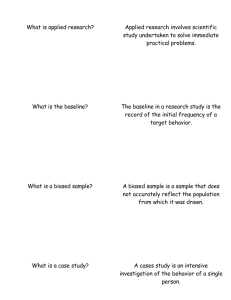
Unit 0: Science Practices Practice 1: Concept Application 1.A Apply psychological perspectives, theories, concepts and research findings to scenario. 1.B Explain how cultural norms, expectations and circumstances, as well as cognitive biases apply to behavior and mental processes. Practice 2: Research Methods and Design 2.A Determine the type of research design(s) used in a given study. 2.B. Evaluate the appropriate use of research design elements in experimental methodology. 2.C Evaluate the appropriate use of research design elements in non-experimental methodologies. 2.D Evaluate whether a scenario followed appropriate ethical procedures. Practice 3: Data Interpretation 3.A Identify psychology related concepts in descriptions or representations of data. 3.B Calculate and interpret measures of central tendency, variation, & percentile rank in a given data set. 3.C Interpret quantitative or qualitative inferential data from a given table, graph, chart, figure or diagram. Practice 4: Argumentation 4.A Propose a defensible claim 4.B Provide Reasoning that is grounded in scientifically derived evidence to support, refute, or modify an established or provided claim, policy, or norm Unit 0 – Science Practice Key terms Perspectives Biological/Neuroscience Evolutionary Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic Behavioral Humanistic Cognitive Social-Cultural Biopsychosocial Ethics IRB Informed consent Protect from harm Confidentiality Deception (Confederates) Debriefing Human and animal ethics Cognitive Biases Data interpretation Confirmation Bias Hindsight Bias Overconfidence Research Methods and Design Experiment o Independent, dependent variables o Random Assignment o Experimental and control group o placebo Non-experimental o Correlation Directionality problem Third- variable problem Correlation does not equal causation o Case study o Meta-analysis o Naturalistic observation Hypothesis Operational definitions Confounding variable v third variable Sample o Population o Representative sample o Random sample o Convenience sampling o Sampling bias o Sample size Generalizability Single blind v Double Blind Measurement tools Qualitative v Quantitative Peer Review and Replication Identify variables in charts/graphs Central tendency o Mean o Median o Mode o Range Normal Curve o Skew o Bimodal o Distribution of scores o Standard Deviation Scatterplot Correlation Coefficient Interpretation of results o Effect size o Statistical Significance