The MYP at SCJ- Student Quiz
advertisement

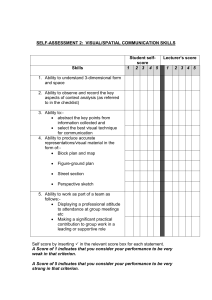
Let’s see how much you know… A. B. C. D. E. It creates rigorous course work for students in the state of Georgia. It allows Title I schools a way to offer college credit to their students The MYP is part of the No Child Left Behind initiative begun under President George W. Bush. The MYP is part of the Race to the Top initiative begun under President Barrack Obama. It allowed the children of military and other government employees overseas a to study a set curriculum. Why was the Middle Years Programme (MYP) originally created? E. It allowed the children of military and other government employees overseas a to study a set curriculum. 1858 Total Schools 141 Canadian Diploma Schools 58 PYP 146 MYP 141 DP 1 of 6 IBCC Schools in the USA 745 US Diploma Schools 26 Georgia Diploma Schools 3 Chatham County Diploma Schools 8 Caribbean Diploma Schools IB World-wide – 3295 schools in 141 countries 298 PYP 245 MYP 745 DP A. London, England, in 1902 B. Geneva, Switzerland, in 1968 C. New York, New York in 1973 D. Chicago, Illinois, in 1954 B. Geneva, Switzerland, in 1968 A. Grades K-5 (Ages 5-10) B. Grades 6-10 (Ages 10-16) C. Grades 9-10 (Ages 14-16) D. Grades 11-12 (Ages 16-18) B. Grades 6-10 (Ages 10-16) Knowledgeable Risk-takers Principled Communicators Balanced Thinkers Open-minded Inquirers Caring Reflective Language and Literature Language Acquisition Design Physical and Health Education Individuals and Societies Sciences Arts Mathematics Thinking Social Communication Self-Management Research Audience Boundaries Composition Expression Genre Innovation Interpretation Narrative Presentation Representation Style Visual Culture Adaptation Balance Choice Energy Environment Function Interaction Movement Perspectives Refinement Space Systems Adaptation Collaboration Ergonomics Evaluation Form Function Innovation Invention Markets and Trends Perspective Resources Sustainability Biology Balance Environment Transformation Consequences Energy Evidence Form Function Interaction Models Movement Patterns Physics Development Environment Transformation Consequences Energy Evidence Form Function Interaction Models Movement Patterns Chemistry Balance Conditions Transfer Consequences Energy Evidence Form Function Interaction Models Movement Patterns Change Equivalence Generalization Justification Measurement Model Pattern Quantity Representation Simplification Space System Economics Choice Consumption Equity Globalization Growth Model Poverty Power Resources Scarcity Sustainability Trade History Causality (Cause and Consequence) Civilization Conflict Cooperation Culture Governance Identity Ideology Innovation and Revolution Interdependence Perspective Significance Political Science/Civics/Government Authority Citizenship Conflict Cooperation Globalization Government Ideologies Integration Interdependence Leadership Power Rights Phases 1-2 Accent Audience Context Conventions Form Function Meaning Message Patterns Purpose Structure Word choice Phases 3-4 Audience Context Conventions Empathy Function Idiom Meaning Message Point of view Purpose Structure Word choice Phases 5-6 Argument Audience Bias Context Empathy Idiom Inference Point of view Purpose Stylistic choices Theme Voice Audience Imperatives Character Context Genres Intertextuality Point of View Purpose Self-expression Setting Structure Style Theme Criterion A Knowing and understanding Maximum 8 Criterion B Developing skills Maximum 8 Criterion C Thinking creatively Maximum 8 Criterion D Responding Maximum 8 Criterion A Knowing and understanding Maximum 8 Criterion B Planning for performance Maximum 8 Criterion C Applying and performing Maximum 8 Criterion D Reflecting and improving performance Maximum 8 Criterion A Inquiring and analysing Maximum 8 Criterion B Developing ideas Maximum 8 Criterion C Creating the solution Maximum 8 Criterion D Evaluating Maximum 8 Criterion A Knowing and understanding Maximum 8 Criterion B Inquiring and designing Maximum 8 Criterion C Processing and evaluating Maximum 8 Criterion D Reflecting on the impacts of science Maximum 8 Criterion A Knowing and understanding Maximum 8 Criterion B Investigating patterns Maximum 8 Criterion C Communicating Maximum 8 Criterion D Applying mathematics in real-life contexts Maximum 8 Criterion A Knowing and understanding Maximum 8 Criterion B Investigating Maximum 8 Criterion C Communicating Maximum 8 Criterion D Thinking critically Maximum 8 Criterion A Comprehending spoken and visual text Maximum 8 Criterion B Comprehending written and visual text Maximum 8 Criterion C Communicating in response to spoken, written and visual text Maximum 8 Criterion D Using language in spoken and written form Maximum 8 Criterion A Analysing Maximum 8 Criterion B Organizing Maximum 8 Criterion C Criterion D Using language Maximum 8 Producing text Maximum 8 A. B. C. D. E. Explain how the Key Concept was used in the unit Explain how the Related Concept was used in the unit Explain how the Global Context was used in the unit Describe how Approaches to Learning was applied Describe the unit’s assessment and the rubric criteria used to grade it