1_3.3_Burning fuels - science
advertisement

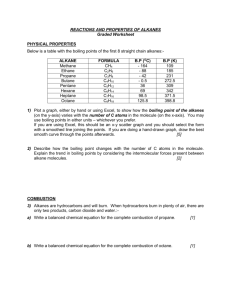
Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Prior Learning: Know what fractional distillation is & how it separates Keywords: Carbon monoxide, unburnt hydrocarbons, particles, sulfur compounds, sulfur dioxide GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Learning Objectives: Identify and explain • The combustion products formed from fuels. • That in a combustion reaction, the amount of oxygen available to react affects the products produced. • The pollutants produced when we burn fuels. I will be successful in this lesson if I can: • Write word equations for the complete combustion of hydrocarbons (Lvl C). • Describe differences between incomplete and complete combustion (Lvl C). • List pollutants formed when we burn fuels (Lvl C). • Complete balanced symbol equations for the complete and incomplete combustion of simple alkanes (Lvl A). • Explain how nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide and particulates are produced during the combustion process (Lvl A). GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula 1. Hydrocarbons contain 7. Carbon dioxide can be only hydrogen & carbon tested with a glowing splint 2. Fuels can only be 8. Oxygen can be tested hydrocarbons with limewater 3. A fuel is burned to 9. Water can be tested with release energy blue cobalt chloride paper 10. Sulfur dioxide can 4. beFuel is stored made by burning light energy 5. Combustion is a fossil fuels reduction reaction 6. When hydrocarbons burn in plenty of oxygen, carbon dioxide & water is made GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Combustion is the scientific word for burning and is a type of chemical reaction. I know… I know… BUT STILL You should have learnt this in Yr 7 Combustion is the reaction when a substance burns and reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light energy. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula When a substance burns, it is said to combust. Combustion is a rapid reaction between a substance and oxygen that releases heat and light energy. A fuel is a substance that reacts with oxygen (combusts) to release useful energy. Many fractions obtained from crude oil are used as fuels because they contain hydrocarbons that burn easily and release a large amount of useful energy. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula The natural gas, methane, is often burnt for cooking. Methane is made up of carbon and hydrogen. What is the chemical equation? What gas does methane react with when it burns? What substance will the carbon in methane change into when it burns in oxygen? What substance will the hydrogen in methane change into when it burns in oxygen? What is the word equation for the combustion of methane? CH4 methane 2O2 oxygen carbon CO2 dioxide 2H2O water GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Combustion demonstration How can we demonstrate combustion & the products of combustion with the provided equipment? GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Plenty of air is needed to provide enough oxygen for a hydrocarbon fuel to burn completely. The blue flame of a gas hob or a Bunsen burner is an example of complete combustion of a hydrocarbon (in this case, natural gas). What are the products of the complete combustion of a hydrocarbon? hydrocarbon + carbon oxygen dioxide + water GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula If there is a shortage of air (oxygen), incomplete combustion of hydrocarbons takes place. Instead of producing just carbon dioxide and water, incomplete combustion also produces carbon monoxide and/or carbon (soot). These form tiny particle in the air (particulates). It also releases less energy than complete combustion. Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas because it reduces the ability of blood to carry oxygen. Most fuels contain sulfur compounds. When the fuel burns, these sulfur compounds produce sulfur dioxide. GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula With the yellow bunsen flame the oxygen flow is restricted & With the blue combustion bunsen flame incomplete the oxygen flow is in a excess occurs. Therefore, lower & complete combustion occurs. temperature is achieved & Therefore, sootcombustion is producedis most efficient under these conditions, producing high temperatures & only carbon dioxide & water GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula 1. What type of chemical is propane? 2. How many carbons in its carbon chain? 3. What happens when there is plenty of oxygen? 4. What happens when there is a shortage of oxygen? DEMONSTRATION: ‘Burning Propane’ C1a 3.3 GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Propane is a hydrocarbon used in camping gas. What is the equation for its combustion? propane C3H8 + + carbon oxygen dioxide 5O2 3CO2 + + water 4H20 How would the equations change if butane was used? GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Complete these word (symbol) equations 1. Wax 2. Petrol 3. 4. CH4 6 CH4 oxygen Oxygen 2O2 8 8O2 Carbon dioxide carbon dioxide water Water carbon Carbon monoxide CO2 2H2O CO2 2 CO 12 H2O 3 C GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula In pairs, write a summary sentence about as many of these words as you can…. You will be asked to read out your sentences & copy down the correct ones •Combustion •Nitrogen oxide •Sulfur dioxide •Particulates GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula Learning Objectives: Identify and explain • The combustion products formed from fuels. • That in a combustion reaction, the amount of oxygen available to react affects the products produced. • The pollutants produced when we burn fuels. I will be successful in this lesson if I can: • Write word equations for the complete combustion of hydrocarbons (Lvl C). • Describe differences between incomplete and complete combustion (Lvl C). • List pollutants formed when we burn fuels (Lvl C). • Complete balanced symbol equations for the complete and incomplete combustion of simple alkanes (Lvl A). • Explain how nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide and particulates are produced during the combustion process (Lvl A). GCSE Core Chemistry Exam tip; You MUST be able to write equations for burning hydrocarbons. You should be able to write balanced symbol equations for the combustion of alkanes, given its formula GCSE Core Chemistry