Document Based Question (*DBQ*)
advertisement

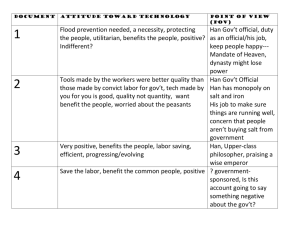
Document Based Question (“DBQ”) What is a DBQ? On the AP Exam, the Document Based Question is: 1. An evaluation of your ability to formulate and support an answer based on evidence from the documents. 2. A determination of your ability to analyze primary source documents including analysis of the point of view of the author of the primary source. 3. A measurement of your ability to determine similarities and differences among a number of primary sources. 4. An assessment of your ability to identify a missing “voice” or source based on your reading of the documents or primary sources. Primary Source Analysis Partner Question: What is a primary source? Examples of Primary Sources Primary Source Analysis The purpose of analyzing primary sources in AP World History is: • To “act” like “real” historians • To gather evidence on which to base an argument • To understand historical trends and points of view DBQ Essay – How do I write it? 1. Carefully read the essay prompt as well as any historical background information you are given. 2. Read and analyze the documents carefully. 3. Respond to the essay prompt based on the evidence you find in the documents. 4. Group documents based on content and/or different points of view. 5. Write a clear thesis that addresses the essay prompt. 6. Identify a “missing” perspective/voice/source based on missing evidence and/or point of view Document-Based Question Rubric • This is an “asset-based” rubric. • In other words, you can only “get” or earn points. Points cannot be “taken away” or lost. • Two parts to the rubric: • BASIC CORE • EXPANDED CORE • You can only get “expanded core” points if you earn all “basic core” points. • All AP World History essays are graded on a 0 to 9 point scale (well technically there is also a “dash (-)” score but that’s if you don’t make ANY attempt to write an essay.) The Rubric – How to Get Those Points! Basic Core • Thesis- 1 point • Has a clear thesis statement in the first paragraph that addresses all parts of the question • May be one or multiple sentences • Addresses ALL the Documents/Understands the Documents 1 point • Address all documents • Demonstrate understanding of the document by using the documents to address the essay questions • Listing the documents separately or as a group DOES NOT demonstrate understanding • Quoting a document does not demonstrate understanding • Supports thesis with appropriate evidence from all documents 2 points • Evidence from all documents that address the question • Analyzes point of view in at least three documents 1 point • Explain why an author has a particular point of view, or what informs the author’s point of view • Explain tone, intended audience, or intended outcome • Analyzes documents by grouping them in three ways 1point • Explicitly addresses the question by grouping documents based on analysis of content and/or points of view • Identifies and explains the need for additional documents 1 point • Must identify an appropriate additional document or source • Explain how the document or source will contribute to the analysis • What points of view are missing and why are they needed • Expanded Core 2 points • Only possible after achieving Basic Core (7 points) • Great thesis, great analysis, POV in all documents, additional groupings, subgroupings, outside historical content, clear and comprehensive conclusion More things to know . . . You will: • Use all the documents to support your thesis and address the essay prompt • Use parenthetical documentation • Ex: “AP World History is the best class (Doc 1)!” • Not just summarize or paraphrase the documents • Understand that ALL documents are relevant and should be used. • Be able to read and analyze between 6 – 12 documents within a 10 minute reading period Most important thing to know… Point of View Analysis is most likely the hardest point to earn on the DBQ rubric! Point of View Analysis • For the purpose of the AP World History exam DBQ question Point of View Analysis means: “WHY DOES THE PERSON SAY WHAT THEY SAY?” SPAR-tan • You will attempt point of view analysis using the ideas behind the acronym: SPAR-tan SPAR-tan •S = Speaker •P = Purpose •A = Audience •R = Result Speaker • Does the person say what they say because of: • • • • • • • • • Their background? Their social status? Their gender? Their nationality? Their religious or philosophical beliefs? Their occupation or position? Their level of education? The time period in which they live or write? Historical events or trends happening or have occurred in the past? Purpose • Does the speaker have: • A desire to inform based on biased information? • An interest in advocating for a certain action to be taken? • An interest in preventing a certain action to be taken? • A potential benefit for writing what he/she wrote? • A desire to avoid a potential punishment or adverse outcome? Audience • Is the speaker writing for a particular: • Person • Group of people • Why is the speaker writing for this particular person or group of people? • Promotion? • Advocacy? • Popularity? • Warning? • Criticize or admonish? • To admonish = to express disapproval Result • Does the speaker have an intended outcome? • What outcome does the speaker want to happen? • How does the speaker want the outcome to happen? • Why does the speaker want the outcome to happen? Second most important thing to know… •Identifying and justifying an additional document nd is the 2 hardest point to earn on the DBQ rubric! An Additional Document… • Can be from a point of view which is missing from the documents. • Can be point of view which is missing from one of your groupings. • Can contain evidence which is missing from the documents. An Additional Document… • May come from: • • • • • A member of a gender missing from the documents A member of a social class missing from the documents A member of a nationality missing from the documents A member of an occupation missing from the documents A member of a religion or philosophy missing from the documents • A member of a similar gender/social class/occupation/religion/philosophy but from a different area of the world not mentioned in the documents An Additional Document… • The most important piece of information needed when including an additional document is: WHY IS THIS INFORMATION FROM THIS MISSING SOURCE IMPORTANT TO HAVE OR KNOW? OR WHY IS THE ADDITIONAL DOCUMENT NEEDED? A note about the groupings of documents: • Grouping of documents can be based on: • Evidence in the documents that supports your thesis • Evidence in the documents that addresses the prompt • Similar points of view or bias found in the documents or their sources • Avoid: • Grouping documents based on the REALLY obvious (“These documents are all by men.”) • Grouping documents as being “positive,” “negative,” “neutral,” “indifferent”, or “not relevant” Let’s try to analyze some documents! Using your document packet and the DBQ organizer, you will analyze each of the documents from a past AP World History exam. World History Section II Part A Suggested writing time – 40 minutes Percent of Section II score – 33 1/3 Directions: the following question is based on the accompanying Documents 18. The documents have been edited for the purpose of this exercise. Write your answer on the lined pages of the Section II free-response booklet. This question is designed to test your ability to work with and understand historical documents. Write an essay that: •Has a relevant thesis and supports that thesis with evidence from the documents •Uses all of the documents •Analyzes the documents by grouping them in as many ways as possible. Does not simply summarize the documents individually •Takes into account the sources of the documents and analyzes the authors’ point of view •Explains the need for at least one additional type of document 1. Using the documents, analyze Han and Roman attitudes toward technology. Identify one additional type of document and explain briefly how it would help your analysis. •Attitude – how do they feel about technology Document 1 Source: Han government official, writing to local officials concerning flood prevention, early second century BCE I request that you establish water conservation offices in each district and staff them with people who are experienced in the ways of water. There should be one high official and one deputy with just enough workers to meet the need. For the area on both sides of each river select one person as chief hydraulic engineer. Order inspections of the waterways, the walls of the cities and their suburbs, the dikes and rivers, canals and pools, and government buildings and cottages, and supply enough workers to those who are to carry out the repair work in each district. • Han government official • Importance of water, waterways, and other engineering needs • Government authority over development of these needs; seen as the proper scope of government to regulate • Attitude – technology is essential part of the empire and requires government intervention Document 2 Source: Huan Guan, Han government official, Discourses on Salt and Iron, first century BCE In earlier times workers were allowed to do both foundry work and salt-boiling as long as they reported the work and paid a tax. Tools manufactured by individual families to do this work were well-made. Today the iron tools that workers are required to use are produced by the state using convict labor; these tools are often crude and not very functional. In previous times the tools manufactured by workers for their own use and for sale were of excellent quality. Now that the state has monopolized the salt and iron trades, most of the tools provided to the workers are hard and brittle and the responsible government officials are often not available to take complaints. Good implements are hard to come by. Salt and iron are now sold at very high prices by the state and many common people cannot afford to buy either. Some of the poorest peasants now have no choice but to till the soil with wooden plows and cannot afford salt to season their food. • Han government official • Government created sub-standard tools due to monopoly • As a government official, Huan Guan implies that good government should correct the situation • Misinterpreted as negative about technology, rather he is negative towards the government’s role • Attitude – technology is essential part of peasant production, responsibility of the government to support Document 3 Source: Huan Tan, upper-class Han philosopher, New Discourses, about 20 CE Fuxi* invented the pestle and mortar. Later on, the pestle and the mortar were cleverly improved in such a way that the whole weight of the body could be used, thus increasing the efficiency ten times. Later, water power was also applied, and the benefit was increased a hundredfold. *Fuxi is a mythological wise emperor. • Listing Fuxi as mythical emperor and inventor of pestle and mortar • Listing of progress of technology after emperor’s first invention • Misinterpreted Fuxi as author • Attitude – technology is a “gift” from enlightened emperors; Confucian benevolence through progress Document 4 Source: History of the Early Han Dynasty (government sponsored history), about 200CE Tu Shih was appointed governor of Nanyang (about 31ce). He was a generous man and his policies were peaceful. He destroyed evil-doers and established the dignity of his office. Good at planning, Tu Shih loved the common people and wished to save their labor. He invented a water-powered blowing-engine for the casting of iron agricultural implements that allowed people to enjoy great benefit for little labor. His invention has been widely adopted and used. • Governor of province, Tu Shih, was peaceful, destroyed evildoers, planner, and loved common people • Developed labor-saving device, water-powered blowingengine, to facilitate cast-iron agricultural implements • Attitude- technology is a “gift” from enlightened leadership; Confucian benevolence and harmony Document 5 Source: Cicero, upper-class Roman political leader, On Duty, first century BCE Now, as to which crafts and other means of earning a living are suitable for a gentleman to practice and which are degrading, we have been taught more or less the following: Vulgar and unbecoming to a gentleman are all the jobs hired workers take on, whose labor is purchased rather than their skill. All craftsmen spend their time in vulgar occupations; no workshop can have anything enlightening about it. • Those who work with their hands are “vulgar” or common; gentlemen do not work with their hands • Craftsmen and “hired workers” are not fit occupations for gentlemen • Attitude – technology is necessary, but not enlightened or fit for enlightened minds Document 6 Source: Plutarch, Greek-born Roman citizen and high official, describing second-century bce Roman political leader Gaius Gracchus, first century CE He was especially anxious about road building, paying attention to utility as well as to that which was beneficial to grace and beauty. For the roads were carried straight through the country without wavering, and were paved with quarried stone, and made solid with masses of tightly packed sand. Hollows were filled up and bridges were built across whatever wintry streams or ravines cut the roads. And both sides were an equal and parallel height with the result that the road for its entire course had a level and beautiful appearance. Besides these things, he measured the whole road mile by mile and set up stone columns as distance indicators. He also placed other stones on either side of the road at lesser intervals so that it would be easier for those who had horses to mount them from the stones without requiring a groom to help. • Regarding Roman leader Gaius Gracchus’ road building enterprises • Glowing report of roads and amenities encouraged by Gracchus for imperial good; no mention of populace • Attitude – technology has a practical/pragmatic side, but also one of aesthetics Document 7 Source: Seneca, upper-class Roman philosopher and adviser to Emperor Nero, first century CE I do not believe that tools for the crafts were invented by wise men. The question of whether the hammer or the tongs came first does not seem important to me. Both were invented by someone with a mind that was nimble and sharp, but not great or elevated. • Individual technology’s creator and creation is less important than its use • Differentiation between those who work with hands and those who work with their mind • Attitude – technology is necessary and takes “smarts”, but not enlightened Document 8 Source: Frontinus, Roman general, governor of Britain, and water commissioner for the city of Rome, first century CE All the aqueducts reach the city at different elevations. Six of these streams flow into covered containers, where they lose their sediment. Their volume is measured by means of calibrated scales. The abundance of water is sufficient not only for public and private uses and applications but truly even for pleasure. The water is distributed to various regions inside and outside the city, to basins, fountains and public buildings, and to multiple public uses. Compare such numerous and indispensable structures carrying so much water with the idle pyramids, or the useless but famous works of the Greeks. • Glowing report of aqueducts and their uses in the city of Rome • Attitude – emphasizes the practical and aesthetic nature of Roman technology over Egyptian or Greek Thesis – 1 point • The thesis must include both Han and Roman attitudes toward technology with correct qualification of each empire. • The thesis does NOT have to include a comparison of Han and Roman attitudes. • “The Han dynasty emphasized efficiency in their tools, as well as using technology to prevent natural disasters. The Romans, however, marveled at their civilization’s advancements; yet refused to glorify those who work with tools and crafts.” • “Throughout China there was a majority appreciation of technology advancement with a few against it, while in the Roman empire, the view were split between support and pessimism.” • “Han China’s attitude toward manufacturing and labor was more open and positive than the Romans who had a more systematic and classdivided society, therefore causing general attitudes of labor and technology to be low.” Grouping in 3 ways – 1 point • Explicitly address the question (attitude) by grouping in three ways, ie. type(s) of technology, views on technology, role(s) of government with respect to technology, by class, philosophers vs. officials • NOTE: the Han documents (Docs 1-4) and / or the Roman documents (5-8) will NOT count as groupings, BUT noting Han or Roman officials and Han or Roman upper classes as groups is acceptable. • Common Groupings: Docs 1 & 4 (positive uses of technology related to water), Docs 3 & 4 (enlightened leaders supporting technology), Docs 5 & 7 (negative Roman attitudes toward technology), Docs 6 & 8 (positive Roman attitudes toward technology) Additional document – 1 point • Identify an appropriate additional type of document or source and explain how the document or source will contribute to an analysis of Han and Roman attitudes toward technology. • Missing POVs • Documents by women to explore whether there are similarities or differences in Han/Roman attitudes according to gender (Did women feel the same about technology that men did?) • Documents by workers to explore attitudes of those classes who might be most affected by various technologies or those classes who would do the physical implementation of a new technology • Documents regarding the economic effects of technologies to help explain the positive/negative attitudes • “This is only the opinion of the upper-class (referring to Docs 5 & 7). An additional document explaining the view of a craftsman about new tools would provide a balance of opinions.” • “After seeing the opinions of high government officials and upperclass philosophers, it was made clear that the opinion of a common worker or civilian may have been helpful on the level of technology required to sustain a healthy society.” Sample Paragraph • Controlling water was important in both the Han dynasty and the Roman Empire (Docs 1 and 8). Han officials in the second century believed water conservation offices and hydraulic engineers should work together to prevent flooding (Doc 1). The writer requested the establishment of “water conservation offices in each district”, and “ inspections of waterways, walls”, etc along with necessary repairs (Doc 1). The Romans also used water engineering, aqueducts, to supply the cities with water (Doc 8). Frontinus bragged about the abundance of water for “public and private uses (Doc 8).” Both the Roman and the Han official want to use technology to control water for the benefit of the citizens. As a water commissioner, the writer of document 8 only talks about the positives of the water system, perhaps as a way of making himself look good in the eyes of his superiors. An additional document from a common citizen of Rome describing how aqueducts positively affect their life would support Frontinus, who only provides an official government point of view.