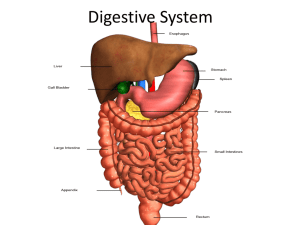
Pancreas, Liver, GB and Small and Large Intestine
advertisement

Pancreas, Liver, GB and Small and Large Intestine Pancreas • Found posterior to stomach • Extends across the abdomen • Only gland to produce enzymes to digest every type of food • Amylase – carbs • Lipase – fats • Proteinase - proteins • Secretes enzymes into the duodenum • Enzymes are mixed with an alkaline fluid that neutralizes the acidic chyme coming from stomach • When chyme enters the duodenum the hormone cholecystokinin is released to signal the release of pancreatic juice • Hormones also produced by the pancreas • Insulin • Glucagon Gallbladder • Pear shaped sac found in hollow of liver • Bile made by liver is stored in gallbladder • Bile storage sac (bile produced in liver) • Bile digests fatty food - bile goes into the duodenum from the gallbladder • Cholecystokinin signals the gallbladder to release bile • Gallstones are crystallized cholesterol which can cause blockages Liver • Largest gland in the body • Located on the right side of the body under the diaphragm • Consists of four lobes suspended from the diaphragm and abdominal wall by a ligament • Connected to the gallbladder via the common hepatic duct • Can regenerate if part of it is damaged or removed Metabolic Functions of the Liver • Store glycogen • Convert glycogen to glucose • Create new glucose Metabolism of Carbohydrates • Hyperglycemia—excessively high levels of glucose in the blood • Excess glucose is stored in body cells as glycogen • If blood glucose levels are still too high, excesses are converted to fat • Hypoglycemia—low levels of glucose in the blood • Liver breaks down stored glycogen and releases glucose into the blood Protein Metabolism • Proteins are conserved by body cells because they are used for most cellular structures • Amine groups are removed from proteins as ammonia • The rest of the protein molecule enters the Krebs cycle in mitochondria • The liver converts harmful ammonia to urea which can be eliminated in urine Fat Metabolism • Fats and fatty acids are picked up by the liver • Uses some fats to make ATP • The rest are broken down into simpler compounds and released into the blood • Body cells remove fat and cholesterol to build membranes and steroid hormones Fat Metabolism • Most cholesterol is produced in the liver (85%) and is not from diet (15%) • Cholesterol is not used to make ATP • Functions of cholesterol • Serves as a structural basis of steroid hormones and vitamin D • Is a major building block of plasma membranes Role of the Liver in Metabolism • Several roles in digestion • Manufactures bile • Plays a central role in carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism • Stores glycogen and vitamins • Produces cholesterol, blood proteins (albumin and clotting proteins) • Detoxifies drugs and alcohol • Decomposes red blood cells • Degrades hormones Bile • Produced by cells in the liver • Composition is • Yellow/green color – not an enzyme • Salt • Cholesterol • Electrolytes • Function— • emulsify fats by physically breaking large fat globules into smaller ones • Breakdown Red Blood cells Small Intestine • The body’s major digestive organ • Site of nutrient absorption into the blood • Muscular tube extending from the pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal valve • Suspended from the posterior abdominal wall by the mesentery Subdivisions of the Small Intestine • Duodenum • Attached to the stomach • Curves around the head of the pancreas • Finishes digestion – pancreas and GB attached Subdivisions of the Small Intestine • Jejunum • Attaches anteriorly to the duodenum • 2/5ths of absorption • Ileum • Extends from jejunum to large intestine • 3/5ths of absorption Small Intestine Anatomy • Villi – increase surface area • Villi—fingerlike structures formed by the mucosa • Microvilli—tiny projections of the plasma membrane (create a brush border appearance) • Circular folds (plicae circulares)—deep folds of mucosa and submucosa Small Intestine Physiology • All about absorption and transporting the nutrients to the blood stream • Peristalsis moves the chyme through the SI to the LI through the ileocecal sphincter Small Intestine Physiology • Mucus – secreted by cells for easy passage and to help absorption • Peptidase – breaks down protein • Sucrase – breaks down sugars • Lipase – splits fats Large Intestine • Larger in diameter, but shorter in length, than the small intestine • Frames the internal abdomen • Reabsorption of water and electrolytes Large Intestine Anatomy • Cecum—saclike first part of the large intestine – attached to SI by ileocecal valve • Appendix • No digestive purpose • lymphatic tissue that sometimes becomes inflamed (appendicitis) • Hangs from the cecum Large Intestine Anatomy • Colon • Ascending—travels up right side of abdomen • Transverse—travels across the abdominal cavity • Descending—travels down the left side • Sigmoid—enters the pelvis (S shaped) • Rectum and anal canal —also in pelvis Large Intestine Anatomy • Anus—opening of the large intestine • External anal sphincter—formed by skeletal muscle and under voluntary control • Internal involuntary sphincter—formed by smooth muscle • These sphincters are normally closed except during defecation Large Intestine Anatomy • No villi present • Banded muscles • Mucus – lubricate for feces passage • Haustra (pocketlike sacs) – pouches for holding fecal material Large Intestine Physiology • Little to no digestive function • Vitamin B and K – bacteria living in LI produce these vitamins • Reabsorb water, vitamins and minerals Large Intestine Physiology • Peristalsis and mixing occur 2-3 times a day • Mass Movement – movement of material happens in large sections that constrict at once • Defecation reflex – forces out rectum when sphincter relaxes