Achieving Economic Stability
advertisement

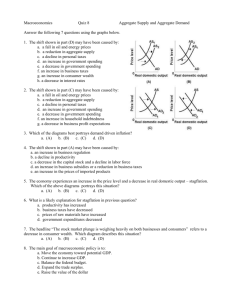
Achieving Economic Stability The Cost of Economic Instability • Forms of Economic instability – recession – High unemployment – Inflation • Stagflation: a period of stagnant growth combined with inflation – Experienced in 1970’s The Cost of Economic Instability • Economics Cost – GDP gap: measures the differences between the actual GDP and the GDP that could have been achieved had all the resources been fully employed The Cost of Economic Instability • The misery index: the sum of monthly inflation and unemployment rates • Uncertainty increases when GDP decreases Social Cost • Economic Instability – Results in wasted labor, capital, and natural resources – Can lead to political instability – Associated with: • Increased crime • Lower levels of police protection • Less willingness by companies to hire disadvantaged people Macroeconomic Equilibrium Aggregate Supply Total value of goods and services that all firms would produce in a specific period of time at various price level Aggregate Supply Curve • Shows the amount of real GDP that could be produced at various price levels Aggregate Supply Curve • Cost fall = ASC shifts to the right • Cost Rise = ASC shifts to the left Aggregate Demand Total quantity of goods and services demanded at different price levels Aggregate Demand Curve • Quantity of real GDP that would be purchased at various price levels Figure 16.4a Aggregate Demand Curve • shifts curve to the right – Decrease in savings, – expectations of strong economy, – increase in transfer payments financed through deficit spending, – reduction in taxes shifts curve to the right Figure 16.4b Aggregate Demand Curve • Shifts curve to the left – Increase in savings – Expectations of a weak economy – A decrease in transfer payments through deficit spending – An increase in taxes Figure 16.4b Macroeconomic Equilibrium Level of real GDP consistent with a given price level, as determined by the intersection of the aggregate supply and aggregate demand curves Macroeconomic Equilibrium • Achieved when aggregate supply equals aggregate demand • Does not provide exact predictions about the economy • Useful for analyzing macroeconomic trends Stabilization Policies Demand-Side Policies • Federal Policies designed to increase or decrease total demand in the economy by shifting the aggregate demand curve to the right or left • Fiscal Policy: the federal governments attempt to stabilize the economy through taxing and government spending Demand-Side Policies • John Maynard Keynes (1883-1946) was one of the most influential economists of the twentieth century. In addition to revolutionizing economic thinking about fiscal policy, he played a central role in the Bretton Woods Conference of 1944, which created the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank. • Keynesian Economics: a set of actions designed to lower unemployment by stimulating aggregate demand • Demand-Side Policies • Multiplier Effect: a change in investment spending will have a magnified effect on total spending • Accelerator effect: change in investment is caused by a change in overall spending, a downward economic spiral • According to Keynes: only the government is large enough to offset changes in investment spending Demand-Side Policies • Automatic stabilizers = unemployment insurance and federal – Increase government spending whenever changes in the economy threaten people’s income • Long Run: – All attempts by gov’t to increase aggregate demand merely increase the price level without increasing GDP Supply Side Policies • Reducing Taxes = increase in tax collections failed to materialize in the1980’s • Successful policies can shift aggregate supply – Moving economy into equilibrium • Seek to promote economic growth rather than economic stability Laffer curve Monetary Policies • Believe the money supply should be allowed to grow – Slow and steady – Trying to control inflation – Permit economic growth • Expanding the money supply cannot permanently affect rate of employment Economics and Politics Changing Nature of Economic Policy • Discretionary fiscal policy – Used less today – Has increased the use of monetary policy • Passive Fiscal Policy – Contribute to stability of the American Economy • Structural Fiscal Policy – Designed to strengthen the economy in the long run – Does not deal with unemployment or inflation Why Economist Differ? • Choose polices that reflect their sense of which economic problems are most critical • Affected by the economic conditions prevailing in their lifetimes Economic Politics • The Council for Economic Advisors – Advises the president of the United States on economic policy • Contribute to the understanding of economic activity • Help policy makers prevent another Great Depression, stimulate growth, help disadvantaged groups • Cannot help a country AVOID minor recessions