Goal Setting
advertisement

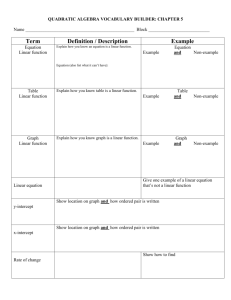
Goal Setting • A statement of something a person needs or wants to do related to finances/money Financial Goals SMART GOALS • Need to have a definite end • Non-example: I want to save more money. • Example: I want to have $100 in my savings account. S- Specific • Need to have a way to tell if progress has been made • Non-example: I want to be a better student. • Example: I want to improve my GPA by .2 points. M- Measurable • Need to use action words to describe • Non-example: I want to be employed. • Example: I want to apply for jobs. A- Action-oriented • Need to be able to be reached • Non-example: I want to earn $1 million by Christmas. • Example: I want to earn $500 working a seasonal job by Christmas. R- Realistic • Goals should be achievable in a reasonable amount of time • Non-example: I want to be a millionaire some day. • Example: I want to save up enough money for my first year of college by the end of the school year. T- Timely TIME FRAMES • Goals that can be accomplished in a few hours or days • Example: Earning an “A” on a test. Short-term • Goals that can be accomplished in one to six months • Example: Achieving a 4.0 for the semester Intermediate-term • Goals that are accomplished in six or more months • Example: Graduating from high school Long-term WHAT KIND OF GOAL? • Save up $100 to buy a new bike in the next two months. Intermediate-term • Be on time to your next class. Short-term • Save enough for retirement to live off the interest. Long-term • Passing all your classes at midterms Intermediate-term • Find a job in the next month. Intermediate-term • Save the money to take a family vacation to DisneyWorld Long-term • Prepare a rough draft of a 10-page research paper. Intermediate-term • Entering the career of your choice. Long-term • Beat a stage or level on a video game. Short-term • Read a book over the weekend Short-term • Read 15 books this year Long-term • Graduating from college with a degree in nuclear engineering Long-term • Do your homework for tomorrow Short-term • Save your change from today in your piggy bank Short-term • Save $20 a week until Hanukkah Intermediate-term WHY WE MAKE OUR FINANCIAL DECISIONS • • • • • They Need It They Want It Advertising/Marketing Peer Pressure Emotional Shopping Reasons People Buy Things SO HOW DO WE KNOW WHAT TO BUY? Decision making- The process of considering and analyzing information in order to make a choice. • Scarcity- the conflict that arises because people have unlimited wants and limited resources • Which means? • We can’t have everything we want • Opportunity Cost- the highest valued alternative one must give up to pursue a decision Economic Concept Needs Wants • Goods that are necessary to live • Ex: Food, water, shelter, transportation • Supplementary goods that might improve quality of life • Ex: fancy car, brand name clothing, new iPod • The beliefs and principles a person considers important, correct, and desirable. Values • What do you value? ADVERTISING • Helps consumers become aware of your product • Example: Why It Works • Uses suggestion- a psychological concept involving association of two ideas • Appeals to emotion • Example: Have a celebrity endorse a product. If you like the celebrity, you have good feelings toward the product. Why It Works • Uses repetition to help consumers remember the product • Example: Geico can help you do what? Why It Works • Plays on societal trends in order to target the appropriate audience • Example: Michael Phelps sponsoring products right after he won gold medals in Beijing. Why It Works EXAMPLES OF ADVERTISING Sketcher’s Ad from last superbowl CONSEQUENCES Pros Cons • You get what you want • Immediate gratification • Excessive debt • Less money for needs • More worry about how to pay for things • Impulse buying • Bankruptcy(?) Possible Consequences of Emotional Buying (Instant Gratification) Pros Cons • Security • Ability to afford needs • Ability to achieve goals • Less worry • Delayed gratification • Lifestyle change (?) Possible Consequences of Financial Planning (Delayed Gratification) • Legal inability to pay debts • Chapter 7- Liquidation- works to eliminate (wipe off the record) existing debt by getting rid of all assets • Chapter 13- Reorganization- court approves a repayment plan that does not require the person to give up their assets as long as they have steady income Bankruptcy • Harder to get loans after filing for bankruptcy • Interest rates are much higher on loans • Some debt cannot be eliminated through bankruptcy (i.e. back taxes, alimony, student loans, child support, and debts incurred through fraud) Why it’s not good CREATING A FINANCIAL PLAN A blueprint or plan for managing all aspects of a person’s money. 1. Determine the current financial situation 2. Develop financial goals 3. Identify all options 4. Evaluate alternatives 5. Create and use a financial plan of action 6. Review and revise the plan Steps • Greg currently has $100 in his checking account. He works a part-time job and makes about $100 a week. He is trying to save up to go on trip to Europe this summer that costs $2000, but he is not very good at financial planning. • What are some possible options? • Which option should he choose? • How would he implement this plan? • How might the plan change? Example- Identify the steps