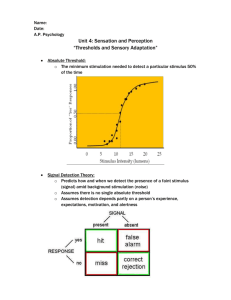
Performance Management (Best Practices)
advertisement

Performance Management (Best Practices) REF:www.cisco.com Document ID 15115 Introduction • Performance Management involves optimization of network response time and management of consistency and quality of individual and overall network services – Need to measure the user/application response time Performance management issues • • • • User performance Application performance Capacity planning Proactive fault management • It is important to note that with newer application like video and voice performance management is the key success Critical success factors (1/2) • Gather a baseline for both network and application data • Perform a what-if analysis on network and application • Perform exception reporting for capacity issues • Determine the network management overhead for all proposed or potential network management services Critical success factors (2/2) • Analyze the capacity information • Periodically review capacity information for both network and applications as well as baselining and exception • Have upgrade or tuning procedures set up to handle capacity issues on both a reactive and long-term basis Performance management process flow (1/3) Develop a network management concept of operation Measure Performance Perform a Proactive Fault Analysis Performance management process flow (1/3) • 1 develop a network management concept of operation – Define the required features : Services, Scalability and Availability objectives – Define availability and network management objectives – Define performance SLAs and Metrics – Define SLA Performance management process flow (2/3) • 2 Measure Performance – Gather network baseline data – Measure availability – Measure response time – Measure accuracy – Measure utilization – Capacity planning Performance management process flow (3/3) • 3 perform a proactive fault analysis – Use threshold for proactive fault management – Network management implementation – Network operation metrics Performance management process flow Develop a network management concept of operation Measure Performance Perform a Proactive Fault Analysis Develop a network management concept of operation (1/3) • The purpose is to describe the overall desired system characteristics from an operational standpoint • The use of this document is to coordinate the overall business goals of network operation, engineering, design other business units and the end users. Define the required features: Services, Scalability objectives (1/2) • Define services :to understand applications, basic traffic flows, users and site counts and require network services (create model of your network) • Create solution scalability objectives: to help network engineers design networks that meet future growth requirement and not experience resource constraint. – media capacity, number of routes and etc Define the required features: Services, Scalability objectives (2/2) • These are the standard performance goals: – Response time – Utilization – Throughput – Capacity (maximum throughput rate) Define availability and network management objectives (1/2) • Availability objectives define the level of services (service level requirements) – define different class of service for a particular organization – Higher availability objective might necessitate increased redundancy and support procedures Define availability and network management objectives (2/2) • Define manageability objectives to ensure that overall network management does not lack management functionality – Must understand the process and tools for organization – Uncover all important MIB or network tool information Define performance SLAs and Metrics • The performance SLAs should include the average expected volume of traffic, peak volume of traffic, average response time and maximum response time allowed Define SLAs • SLA (Service Level Agreement) - enterprise • SLM (Service Level Management) – service provider • SLM include definitions for problem types and severity and help desk responsibilities – Escalation path, time before escalation at each tier support level – Time to start work on the problem – Time to close target based on priority – Service to provide in the area of capacity planning, hardware replacement Performance management process flow Develop a network management concept of operation Measure Performance Perform a Proactive Fault Analysis Measure Performance • Gather Network Baseline data – Perform a baseline of the network before and after a new solution deployment – A typical router/switch baseline report includes capacity issues related to CPU, memory, buffer, link/media utilization, throughput – Application baseline: bandwidth used by app per time period Measure availability • Availability is the the measure of time for which a network system or application is available to a user – Coordinate the help desk phone calls with the statistics collected from managed devices – Check scheduled outages – Etc Measure Response Time • Network response time is the time required to • • • travel between two points Simple level – pings from the network management station to key points I the network. (not accuracy) Server-centric polling : SAA (Service Assurance Agent) on router (Cisco) to measure response time to a destination device Generate traffic that resembles the particular application or technology of interest Measure accuracy • Accuracy is the measure of interface traffic that does not result in error and can be expressed in term of percentage • Accuracy = 100 – error rate • Error rate = ifInErrors * 100 / (ifInUcastPkts + IfInNUcastPkts) Measure Utilization (1) • Utilization measure the use of a particular resource over time • Percentage in which the usage of a resource is compared with its maximum operational capacity • High utilization is not necessarily bad • Sudden jump in utilization can indicate unnormal condition Measure Utilization (2) • Input utilization = ifInOctets *8*100/(time in second)*ifSpeed • Output Utilization ifOutOctets *8*100/(time in second)*ifSpeed Capacity planning • The following are potential areas for concern: – CPU – Backplane or I/O – Memory – Interface and pip sizes – Queuing, latency and jitter – Speed and distance – Application characteristics Performance management process flow Develop a network management concept of operation Measure Performance Perform a Proactive Fault Analysis Perform a Proactive fault analysis • One method to perform fault management is through the use of RMON alarms and event groups • Distributed management system that enables polling at a local level with aggregation of data at a manager to manager Use threshold for proactive fault management (1/2) • Threshold is the point of interest in specific data stream and generate event when threshold is triggered • 2 classes of threshold for numeric data – Continuous threshold apply to continuous or time series data such as data stored in SNMP counter or gauges – Discrete threshold apply to enumerated objects or discrete numeric data such as Boolean objects Use threshold for proactive fault management (2/2) • 2 different forms of continuous threshold – Absolute :use with gauges – Relative (delta): use with counter • Step to determine threshold – 1 select the objects – 2 select the devices and interfaces – 3 determine the threshold values for each object or interface – 4 determine the severity for the event generated by each threshold Network management implementation • The organization should have an implemented network management system. • SNMP/RMON or other network management system tools Network operation metrics (1/2) • Number of problems that occurs by call priority • Minimum, maximum and average time to close in each priority • Breakdown of problems by problem type (hardware, software crash, configuration, power user error) Network operation metrics (2/2) • Breakdown of time to close for each problem type • Availability by availability or SLA • How often you met or missed SLA requirements Performance Management Indicator Indicators for performance management (1/3) • Performance indicators provide mechanism by • • which an organization can measure critical success factors. They are the followings: Document the network management business objectives • Create detailed and measurable service level objectives Indicators for performance management (2/3) • Provide documentation the service level agreement (SLA) with charts or graphs that show the success or failure of how these agreements are met over the time • Collect a list of the variables for the baseline such as polling interval, network management overhead incurred, possible trigger threshold – whether the variable is used as a trigger for a trap, and trending analysis used against each variable Indicators for performance management (3/3) • Have a periodic meeting that reviews the analysis of the baseline and trends. • Have a what−if analysis methodology documented. – This should include modeling and verification where applicable • When thresholds are exceed, develop documentation on the methodology used to increase network resources. – One item to document is the time line required to put in additional WAN bandwidth and a cost table Document the network management business objectives (1/3) • This document is the organization network management strategy and should coordinate the overall business goals of network operations, engineering, design, other business units and the end users. • It enable the organization to form the long range planning activities for network management and operation. Document the network management business objectives (2/3) • Identify a comprehensive plan with achievable goals • Identify each business service/application that require network support • Identify those performance-based metric needed to measure service Document the network management business objectives (3/3) • Plan the collection and distribution of the performance metric • Identify the support needed for network evaluation and user feedback • Have documented, detailed and measurable SLA objectives Document the Service Level Agreements • Before document the SLA, you must define the service level objectives metrics • This document should be available to users for evaluation to provide feedback for variables needed to maintain the service agreement level • SLAs are living agreement – What works today might become obsolete tomorrow Create a list of variables for the baseline • This list includes items such as – polling interval – Network management overhead incurred – Possible trigger thresholds – Trending analysis used against each variable – Router health – Switch health – Routing information – Utilization – delay Reviews the baseline and trends • Network management personnel should conduct meeting periodically (operational and planning) • Also include the review of SLA Document a what-if analysis methodology • A what-if analysis involves modeling and verification of solutions. • It includes the major questions, the methodology, data sets and configuration file • The main point is that he what-if analysis is an experiment hat someone else should be able to recreate with the information provided in the document Document the methodology used to increase network performance • This document includes additional WAN • • bandwidth and a cost table that helps increase the bandwidth for a particular type of link It helps the organization realize how much time and money it costs to increase the bandwidth Periodic review this document to ensure that it remain up to date Configuration Management (Best Practice) Ref.: www.cisco.com Document ID 15111 High Level process flow for Configuration Management Start Create Standards Implement Standards Maintain Documentation Validate and Audit Standards NO Improve ? YES Review Standards Create Standards (1) • Create Standards helps reduce network complexity, the amount of unplanned downtime and exposure to network impact events Create Standards (2) • Following standards for optimal network consistency – Software version control and management – IP addressing standard and management – Naming convention and Domain Name System/ DHCP assignment – Standard Configuration and Descriptors – Configuration Upgrade procedure – Solution Templates Software Version Control and Management (1) • Software version control is the practice of deploying consistent software versions on similar network devices • Limit amount of software defects and interoperability issues • Reduce the risk of unexpected behavior – With user interfaces – Feature behavior / upgrade behavior Software Version Control and Management (2) • Following steps for Software version control – Determine device classifications based on chassis, stability and new feature requirements – Target individual software versions for similar-device classification – Test, validate and pilot chosen software versions – Document successful version as standard for similardevice classification – Consistently deploy or upgrade all similar devices to standard software version IP Address Standards and Management (1) • IP address management is the process of allocating, recycling and documenting IP address and subnets in a network • It reduces the opportunity for overlapping or duplicate subnets, wasted IP address space, complexity IP Address Standards and Management (2) • We should standard subnet size for standard application – – – – Subnet Subnet Subnet Subnet size size size size of of of of building WAN link Branch site Loopback • The subnet block should promote IP summarization • (contiguous IP ) Create standards for IP assignment – Router should be the first available address – Switch may be the next available address – Dynamic address should be followed by fixed address • Finally document standard you developed and IP allocation Naming Convention and DNS/DHCP Assignment (1) • Consistent, structure use of naming conventions and DNS for devices helps – Create a consistent point to routers for all network management information related to a device – Reduce the opportunity for duplicate IP address – Creates simple identification of a device showing location, device type and purpose – Improve inventory management by providing a simpler method to identify network devices Naming Convention and DNS/DHCP Assignment (2) • On router, it is strongly recommended to use loopback interface as the primary management interface • Loopback interface can be used for trap, SNMP and syslog • Individual interface can have name convention that identifies the device, location, purpose and interface Naming Convention and DNS/DHCP Assignment (3) • It is also recommended to identify DHCP ranges and adding them to the DNS including location of the user • Example: “dhcp-bldg-c21-10” to “dhcpbldg-c21-253” which identifies IP address in building C, second floor wiring closet 1 Standard Configuration and Descriptors (1) • Standard Configuration applies to protocol and • • media configuration as well as global configuration command Descriptors are interface commands used to describe an interface It is recommended to create standard configurations for each device classification – Router , LAN switch, WAN Switch, ATM switch Standard Configuration and Descriptors (2) • Each standard configuration contain the global, media, • and protocol configuration command Global configuration – Password, vty, banners – SNMP configuration, Network Time Protocol (NTP) • Media configuration – ATM, Frame Relay, Fast Ethernet configuration • Protocol Configuration – Routing protocol – Access control list – QoS configuration Standard Configuration and Descriptors (3) • Descriptors are developed by creating a standard format that applies to each interface • The descriptor includes – the purpose and location of the interface – Other devices and location connected to the interface – Circuit identifier Standard Configuration and Descriptors (4) • It is recommended – to keep standard configuration parameters in a standard configuration file – downloading the file to each new device prior to protocol and interface configuration • We should document the standard configuration • file including an explanation of each global configuration parameter and why it is important RME (Cisco Resource Manager Essentials) Configuration Upgrade Procedure (1) • Upgrade procedures ensure that software and • hardware upgrades occur smoothly with minimal downtime Upgrade procedures include – – – – – vendor verification Vendor installing references such as release notes Upgrade methodologies or steps Configuration guideline Testing requirement Solution Templates (1) • Solution templates are used to define modular • • network solutions A network module may be a wiring closet, a WAN field office or an access concentrator It is used to ensure that similar deployment can be carried out in exactly the same way – can reduce risk level to the organization Solution Templates (2) • Specific details of the solution template – Hardware and hardware modules including memory, flash, power and card layouts – Logical topology including port assignment – Software versions including firmware versions – All non-standard, non-devices specific configuration, VLAN configuration, access lists, switching paths, spanning tree parameters and etc – Out of band management requirement – Cable requirement – Installation requirement including environmental, power and rack location Maintain Documentation (1) Start Create Standards Implement Standards Maintain Documentation Validate and Audit Standards NO Improve ? YES Review Standards Maintain Documentation (2) • It is recommended to use the following network documentation critical success factor – Current device , link and end user inventory – Configuration version control system – TACACS (Terminal Access Controller AccessControl System) configuration log – Network topology documentation Validate and Audit Standards (1) Start Create Standards Implement Standards Maintain Documentation Validate and Audit Standards NO Improve ? YES Review Standards Validate and Audit Standards (2) • We can use configuration management performance indicators to measure configuration management success • Configuration management performance indicators – Configuration integrity checks – Devices, protocol and media audits – Standards and documentation review Configuration integrity checks • It should evaluate the overall configuration of the network its complexity and consistency and potential issues • For cisco network, it is recommended to use Netsys configuration validating tool. Device, Protocol and Media Audits • It is used to check consistency in software versions, hardware devices and modules, protocol and media and naming convention • Ciscowork RME is a configuration tool that can audit and report on hardware versions modules and software versions Standards and Documentation review • It is done to ensure that the information is accurate and up • • to date The audit should include reviewing current documentation recommending changes or additions and approving new standards Following documents should be reviewed on a quarterly basis – – – – – – – Standard configuration definition Solution templates including recommended hardware configuration Current standard software versions Upgrade procedures for all devices and software version Topology documentation Current templates IP address management