Communication & ICT - the Business Notes Wiki!
advertisement
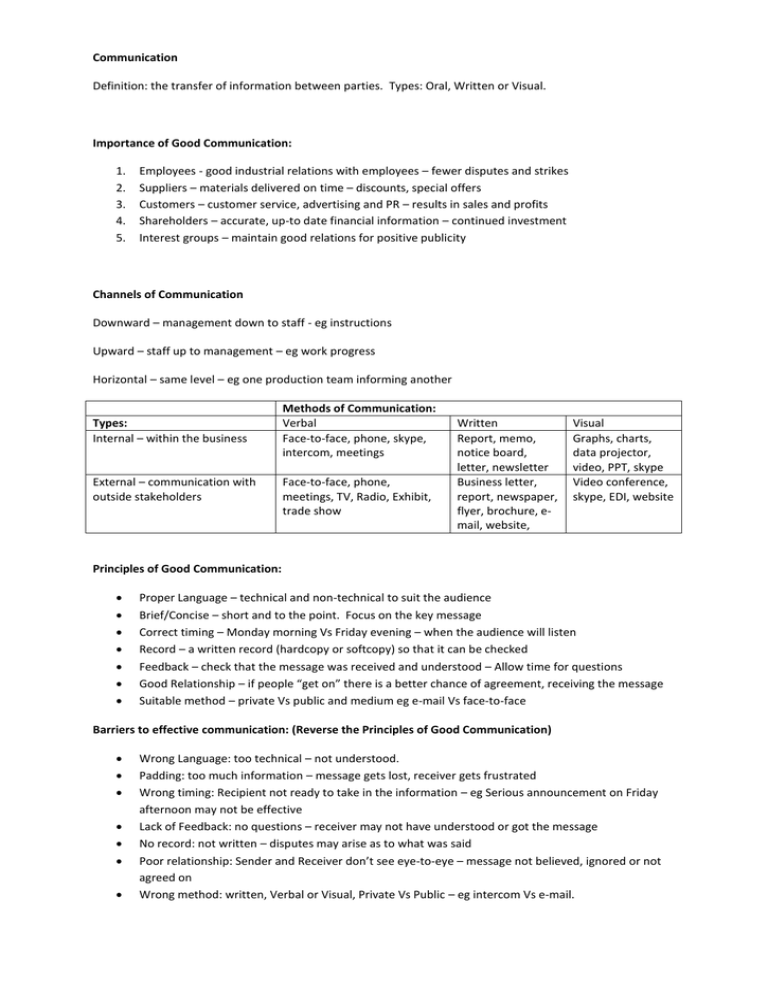
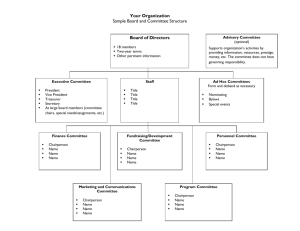
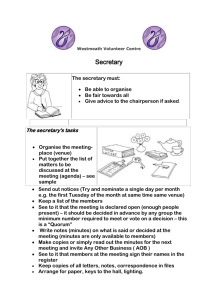
Communication Definition: the transfer of information between parties. Types: Oral, Written or Visual. Importance of Good Communication: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Employees - good industrial relations with employees – fewer disputes and strikes Suppliers – materials delivered on time – discounts, special offers Customers – customer service, advertising and PR – results in sales and profits Shareholders – accurate, up-to date financial information – continued investment Interest groups – maintain good relations for positive publicity Channels of Communication Downward – management down to staff - eg instructions Upward – staff up to management – eg work progress Horizontal – same level – eg one production team informing another Types: Internal – within the business External – communication with outside stakeholders Methods of Communication: Verbal Face-to-face, phone, skype, intercom, meetings Face-to-face, phone, meetings, TV, Radio, Exhibit, trade show Written Report, memo, notice board, letter, newsletter Business letter, report, newspaper, flyer, brochure, email, website, Visual Graphs, charts, data projector, video, PPT, skype Video conference, skype, EDI, website Principles of Good Communication: Proper Language – technical and non-technical to suit the audience Brief/Concise – short and to the point. Focus on the key message Correct timing – Monday morning Vs Friday evening – when the audience will listen Record – a written record (hardcopy or softcopy) so that it can be checked Feedback – check that the message was received and understood – Allow time for questions Good Relationship – if people “get on” there is a better chance of agreement, receiving the message Suitable method – private Vs public and medium eg e-mail Vs face-to-face Barriers to effective communication: (Reverse the Principles of Good Communication) Wrong Language: too technical – not understood. Padding: too much information – message gets lost, receiver gets frustrated Wrong timing: Recipient not ready to take in the information – eg Serious announcement on Friday afternoon may not be effective Lack of Feedback: no questions – receiver may not have understood or got the message No record: not written – disputes may arise as to what was said Poor relationship: Sender and Receiver don’t see eye-to-eye – message not believed, ignored or not agreed on Wrong method: written, Verbal or Visual, Private Vs Public – eg intercom Vs e-mail. Factors to consider when choosing a communication method: Cost: some methods are expensive and the business cost must be considered – eg skype Vs phone Urgency: If a message is urgent the speed of delivery must be considered – eg e-mail is quicker than snail mail Confidentiality: If a message is confidential then possibility of leaking a message must be avoided – eg intercom Vs face to face Record: if the message needs to be recorded then written or technology may be needed – eg verbal communication Vs Memo Feedback: if the sender needs feedback the method must facilitate that. Intercom Vs meetings Nature of the message: Complicated, technical, new, detailed – may need to be in written format for people to take time to study it. Legal Requirements: May require written form – eg written contract Types of Meetings Formal: regular meeting with notice and agenda Informal: unplanned, with no agenda Ad hoc meetings: a meeting that takes place at short notice Annual General Meeting: AGM: held once a year Extraordinary Meeting: EGM: Held in an emergency Notice: Time, Place & Date of next meeting Agenda: list of items for discussion at a meeting Quorum: the minimum number required to hold the meeting Motion: an item for discussion at a meeting Casting Vote: the chairperson has the deciding vote if there is equal votes for and against a motion Minutes: a written account of a meeting Chairperson Duties: Set the agenda with the secretary Open the meeting Ensure the quorum is present – minimum number of people required to attend Make apologies Minutes of last meeting are read and adopted Follow agenda Keep order Allow everyone a chance to speak Put motions to vote – exercise casting vote in a tie Arrange next meeting Secretary Duties: Set the agenda with the chairperson Send out the notice and agenda to those who should attend Read the minutes of the last meeting Read any correspondence Take written notes of the meeting Write up minutes of the meeting Arrange next meeting Business AGM Agenda: Minutes of Last Meeting Manager’s Report Accountant’s Report Election of Board of Management AOB Club AGM Agenda: Minutes of Last Meeting Chairperson’s Report Treasurer’s Report Election of Club Officers AOB Report: Detailed account with analysis, conclusions, recommendations Title: Report on Club Open Day Author: J. Bloggs, Chairperson Date: 12/1/2013 Aims: To report on the activities of the Club Open Day. To establish improvements that could be made. To identify if the open day was a success. Research: Methods used to gather data Findings: Open Day Activities Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats Conclusions: Improvements:………………………………… Was the open day a success? ………………. Recommendations: Actions to be taken based on findings A good reports is: Relevant Timely Clear Accurate Impartial Brief Purpose of a Report: Brings data together Allows expert analysis Enables informed decision making Letter: Business letter Sender Address Telephone Date Recipient Name Recipient Address Re: Dear Mr Giggs, Intro……………………….. Detail……………………… Conclusion…………….. Sincerely, _______________ J Bloggs Memo: a short note To: From: Date: Re: Dear staff, please note that……………………………………effective immediately. Sincerely, M Bloggs Charts: Bar Chart, Line chart, Bar Chart, Pictogram 2011 2012 2013 €,000 €,000 Shoe Shop Sales 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 14 Shoe Shop Sales 2011-2013 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 2013 2012 2011 Technology How technology can help business 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Automate repetitive processes – reduce staffing costs Facilitate reuse of data – improved information across business divisions Increase speed and efficiency of data processing – free up time for other activities Up-to-date information can facilitate quicker and better decision making – give competitive edge Create a modern and positive image – customers and staff happier Reduced Cost - Reduced and cost physical storage of paperwork – reduced cost of printing Uses of WWW for business 1. 2. 3. 4. Company website – advertising, providing information to customers, selling online Social networking – building up customer contacts, advertising, making business links, crowd sourcing Web – research, sourcing suppliers, markets, training online, online banking, Revenue ROS online Communication – Messaging, Skype, Webmail, video conferencing Opportunities for business online 1. 2. Selling online – e-business Global markets – access to markets worldwide Internet access Requirements The internet is a worldwide connection of computers 1. 2. Internet Provider – eircom, 3G, etc Browser – Firefox, Internet Explorer Problems of using email in Business 1. 2. 3. Junk Mail - Time consuming and expense in filtering Security – may not be secure Written form – some business situations require a printed form with signatures/dates TERMS IT – Information Technology EDI – Electronic Data Interchange – eg transmission of invoices between supplier and buyer ISDN – Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) is a set of communication standards for simultaneous digital transmission of voice, video, data, and other network servides Internet – a world wide connection of computer networks E-mail – electronic mail E-Commerce – electronic commerce, buying and selling online WWW – world wide web New Developments Paperless business – documentation stored, sent, received digitally Cashless trading – online money transfers, buying and selling Cloud computing – data stored in the web – eg google docs Online collaborations –eg crowd sourcing, groupon GPS tracking – eg sat nav, maps, Bluetooth – wireless connectivity Mobile apps