Barriers against Pathogens Handout - Grade-11
advertisement
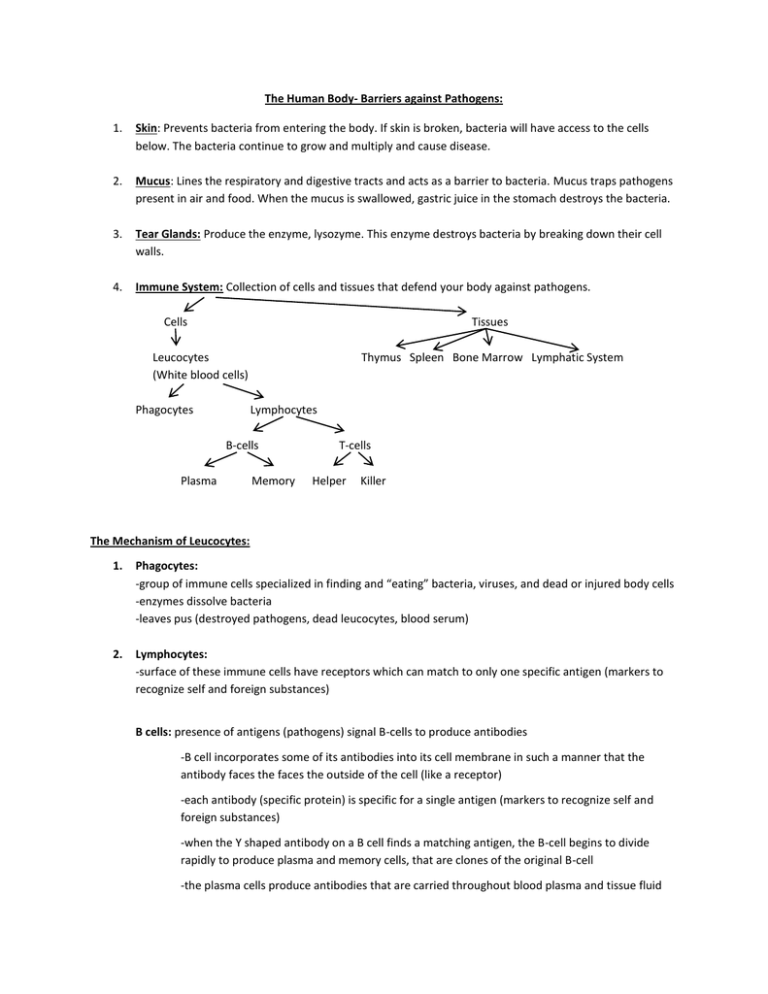
The Human Body- Barriers against Pathogens: 1. Skin: Prevents bacteria from entering the body. If skin is broken, bacteria will have access to the cells below. The bacteria continue to grow and multiply and cause disease. 2. Mucus: Lines the respiratory and digestive tracts and acts as a barrier to bacteria. Mucus traps pathogens present in air and food. When the mucus is swallowed, gastric juice in the stomach destroys the bacteria. 3. Tear Glands: Produce the enzyme, lysozyme. This enzyme destroys bacteria by breaking down their cell walls. 4. Immune System: Collection of cells and tissues that defend your body against pathogens. Cells Tissues Leucocytes (White blood cells) Phagocytes Thymus Spleen Bone Marrow Lymphatic System Lymphocytes B-cells Plasma Memory T-cells Helper Killer The Mechanism of Leucocytes: 1. Phagocytes: -group of immune cells specialized in finding and “eating” bacteria, viruses, and dead or injured body cells -enzymes dissolve bacteria -leaves pus (destroyed pathogens, dead leucocytes, blood serum) 2. Lymphocytes: -surface of these immune cells have receptors which can match to only one specific antigen (markers to recognize self and foreign substances) B cells: presence of antigens (pathogens) signal B-cells to produce antibodies -B cell incorporates some of its antibodies into its cell membrane in such a manner that the antibody faces the faces the outside of the cell (like a receptor) -each antibody (specific protein) is specific for a single antigen (markers to recognize self and foreign substances) -when the Y shaped antibody on a B cell finds a matching antigen, the B-cell begins to divide rapidly to produce plasma and memory cells, that are clones of the original B-cell -the plasma cells produce antibodies that are carried throughout blood plasma and tissue fluid -antibodies can then neutralize antigen molecules -the memory cells “remember” specific intruders -the second time a pathogen tries to invade the body, memory cells secrete large amounts of the antibody -very quickly, all the invading pathogens are destroyed -memory cells can give immunity to diseases T-cells: form clones after they attach to antigen. Like B-cells, they too form memory cells. -they respond to whole cells -come in two different types, helper cells and killer cells -Helper cells activate B cells and Killer T cells -Killer T cells attack cells of the body infected by pathogens, can also attack cancer cells