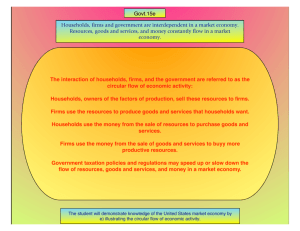
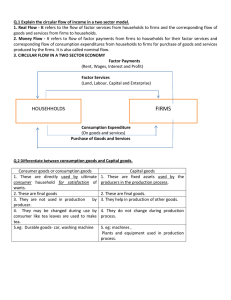
E160.S10.W02.1.EconomicCompetition
advertisement

Welcome to ECON 160 Principles of Microeconomics richard.tontz@csun.edu http://www.csun.edu/~rlt50610/ Aplia Course Key: 5TS6-7CEH-MEVL Econ 160 • The Economic System of Competition Review: Definitions • Good : is anything that an individual wants to have more of, at zero price. • Resource: Anything that can be used to produce goods. • Scarcity: A good is scarce if the amount desired at zero price is more than the amount available at zero price. Review:Assumptions • Humankind has unlimited wants • Our resources are limited • Scarcity : Individually, and as a Society, we do not have enough resources to produce all the things we want. Review:Implications of Scarcity • Choice: people must choose which goods to acquire. • Economic Cost: The Cost of any action, is the personal value of the next highest valued alternative given-up. • Competition: We are in a state of competition for the use of resources Forms of Competition in Society • Violence, or Threat of Violence • Social/Political : competition on the basis of some limited behavior or characteristic • Economic/Market: competition based on offering the highest value in exchange. Scarcity Society Choices • What to produce? Goal find the mixture of outputs that maximizes society’s value. • How to produce? Goal: find the optimal mix of inputs to maximize technical output. • For whom to produce? Who will get to consume the goods produced. What Economics Is About • Microeconomics: decisions of individuals and firms: what to buy and what to produce. • Macroeconomics: the whole economic system and the role of government. Mechanisms of Choice • Political: our representatives make choices • Economic/market: individuals and firms make choices based on relative prices about what to produce Ten Principles of Economics • Individual decision making • How people interact • The economy as a whole Individual Decision Making • • • • People Face Trade-offs: Choice Opportunity Cost Rational people think at the margins People respond to incentives How People Interact • Trade Makes everyone better off • The market system organizes production efficiently • Markets outcomes can sometimes be improved upon by Government The Economic/Market Form of Competition Circular Flow Diagram of the Exchange Economy Goods & Services Goods & Services Product Markets $'s $'s Revenue HOUSEHOLDS FIRMS $'s $'s Income Inputs Resources Resource Markets Economic Agents & Decision-making • Households: Decisions: What to sell? What to buy? Assume Maximize Utility • Firms: Decisions: What inputs to use? What to produce? Assume Maximize Profits. • Markets: Factor Markets, Product Markets Role of Money: The medium of exchange Definition of Money • Currency in Circulation: Currency outside of Banks in the hands of households,or firms • Checkable deposits in Banks, Savings & Loans, Credit Unions Assignments • Check Aplia for Assignment due Sunday Night • Read Chapter 3 • Check for new Classnotes & Powerpoints