Final Exam Study Guide- Classification and Plants
advertisement

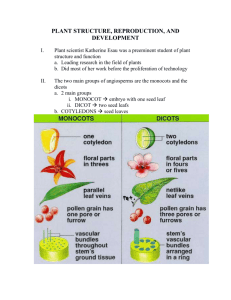
Biology Final Exam Study Guide- Units 1 and 2 Classification I. What is life? A-4.a: Describe the biological criteria that need to be met in order for an organism to be considered alive. 1. Complete the following table: Criteria to be considered living: Description of criteria II. Organization A-4.b: Define and provide examples of each level of organization. 2. List the levels of organization in order. III. Classification E-3.a: Explain how organisms are classified into a hierarchy of groups and subgroups based on similarities that reflect their evolutionary relationships. 3. How are organisms classified? _________________________________________________________ 4. How do scientists determine evolutionary relationships between organisms? _____________________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ E-3.b: List each of the major levels in the hierarchy of taxa: kingdom, phylum, etc. 5. List the major levels in the hierarchy of taxa in order. ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ E-3.e: Distinguish between and among viruses, bacteria, and protists, and give an example of each. E-3.f: Explain classification criteria for fungi, plants, and animals. 6. Create a concept map describing the different kingdoms. Include # and type of cells, and energy source. (Complete on a separate sheet of paper) IV. Animal Divisions E-3.g: Compare the major divisions of animals. 7. Complete the following table. Phylum Symmetry Digestion Skeleton Reproduction Example Porifera Cnideria Platyhelminthes Nemotode Mollusca Annelid Arthropod Echinoderm Chordata V. Binomial Nomenclature E-3.c: Explain the binomial nomenclature system. 8. Define binomial nomenclature. _________________________________________________________ 9. How are scientific names (binomial nomenclature) written? __________________________________ 10. What does the first word in a scientific name represent? ____________________________________ 11. What does the second word represent? _________________________________________________ Plants I. Flower Anatomy ACT: E-2.b: Explain the functions of unique plant structures, including the cell wall, chloroplasts, and critical parts of the flower and seed. Label the parts of the flower. Include the following: Stem, peduncle, sepals, petals, ovary, style, stigma, pistil (carpel), anther, filament, stamen, pollen, and ovule Describe the function of each part of the flower. 1. Stem: ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Peduncle: ________________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Sepals __________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Petals ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Ovary ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 6. Style ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Stigma __________________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Pistil ____________________________________________________________________________________________ 9. Anther __________________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Filament _________________________________________________________________________________________ 11. Stamen __________________________________________________________________________________________ 12. Pollen ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 13. Ovule ___________________________________________________________________________________________ II. Seed Anatomy ACT: E-2.b: Explain the functions of unique plant structures, including the cell wall, chloroplasts, and critical parts of the flower and seed. Draw and label the major structures of the seed. Include the following: Seed coat, micropyle, hilum, plant embryo, cotyledon Describe the function of the following seed parts. 1. Seed coat: _______________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Micropyle _______________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Hilum ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 4. Plant embryo _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Cotyledon _______________________________________________________________________________________ Compare monocots and dicots. _______________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ III. Plant Reproduction ACT: E-2.a: Describe the basic mechanisms of plant processes, especially movement of materials and plant reproduction. 1. Describe the difference between pollination, fertilization, and dispersal. _______________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Define germination: ______________________________________________________________ 3. Draw the plant reproduction cycle. Label with key steps and the following: a. Pollination b. Fertilization c. Dispersal IV. Plant Transport ACT: E-2.a: Describe the basic mechanisms of plant processes, especially movement of materials and plant reproduction. 1. 2. Describe the function of the following: a. Roots: ___________________________________________________________________________________ b. Leaves: __________________________________________________________________________________ c. Stem: ____________________________________________________________________________________ List the 3 main tissues of a plant: a. ______________________ b. ______________________ c. ______________________ 3. What covers the outer dermal tissue of a plant and helps to prevent water loss? _________________________________ 4. Describe the function of a guard cell. __________________________________________________________________ 5. Where are most guard cells located? ___________________________________________________________________ 6. What is a stomata? _________________________________________________________________________________ 7. If guard cells are full of water, they swell and the stomata ____________. If they have no water, they shrink and the stomata ______________. 8. 9. For each of the following conditions, determine if the stomata will be open or closed. a. Very hot, no water: _________________________________________________________________________ b. Sunny, photosynthesis is occurring: ____________________________________________________________ c. Night time: _______________________________________________________________________________ Describe the function of xylem and phloem. Make sure you know what they carry, and where they carry it! a. Xylem: ___________________________________________________________________________________ b. Phloem: __________________________________________________________________________________ 10. Where does most of the plant’s photosynthesis occur? _____________________________________________________ 11. Describe the following: a. Transpiration: _____________________________________________________________________________ b. Capillary action: ___________________________________________________________________________