CAPTURING SOLAR ENERGY: LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTIONS
advertisement

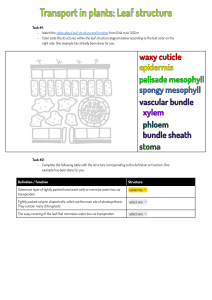
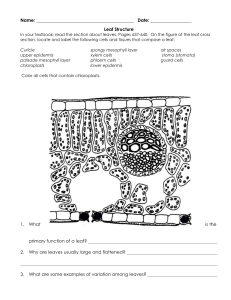
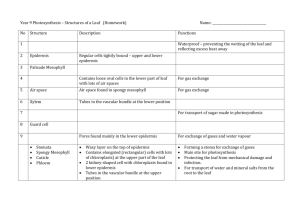
CAPTURING SOLAR ENERGY: LIGHT DEPENDENT REACTIONS PLANT STRUCTURE LEAVES: the photosynthetic organ of plants - Carry out photosynthesis - 3 types of tissue a) Epidermis (upper and lower) b) Mesophyll c) Vascular Bundles PLANT STRUCTURE LEAVES PLANT STRUCTURE a) EPIDERMIS - Single layer of cells at the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf - Main function: protect inner layers from dessication, bacterial invasion, and mechanical injury - Cells have thick walls made of cutin and lack chloroplasts PLANT STRUCTURE a) EPIDERMIS - Contain stomates on underside of leaf - Function: passageway for oxygen, carbon dioxide and water - Opening regulated by pair of guard cells - Movement of water controlled by active transport of K+ - Guard cells actively take up K+ - Open stomata: light stimulates K+ pump - Closed stomata: high CO2 within leaf and low water PLANT STRUCTURE a) EPIDERMIS PLANT STRUCTURE b) MESOPHYLL - Tissue between two epidermal layers - Composed of palisade cells and spongy cells - Packed with chloroplasts, site of photosynthesis PLANT STRUCTURE c) VASCULAR BUNDLES: Xylem: transport water and dissolved minerals upwards into mesophyll - dead vessels and tracheids Phloem: conduct dissolved food material (products of photosynthesis) downwards to lower parts of plant - live sieve tubes and companion cells PLANT STRUCTURE c) VASCULAR BUNDLES: