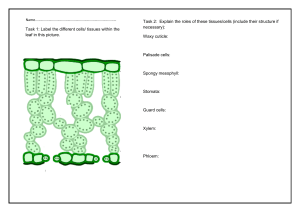
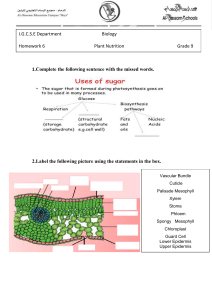
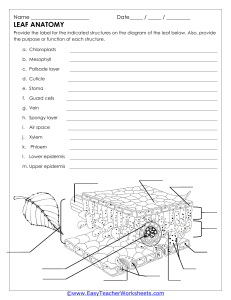
Plant Nutrition Photosynthesis def (photosynthesis) - Is a process in which plants synthesize carbohydrates from raw material using energy from light Raw Materials Water - Roots absorb water from the soil and transport it to the leaves through the xylem tissue. Minerals - Plants take in the minerals dissolved in water through active transport. Magnesium - Its a part of chlorophyll, its deficiency is called chlorosis. Nitrate - Helps in making protein (Growth of the plant) Carbon dioxide - Plants take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere through their stomata. Requirements Light energy - Sunlight or artificial light provides the energy for photosynthesis. (blue - red) Chlorophyll - It is the green pigment in the palisade mesophyll cells of the leaf. It traps light energy and passes it on to the raw materials. Products of Photosynthesis Glucose - It is the main product of photosynthesis. It is used by the plant in the following ways: It can be used as a substrate for respiration. It can be converted into starch and stored in tubers and seeds. It can be converted into cellulose and used in the formation of cell wall. It can be converted into fructose or sucrose and stored in sweet fruits. It can also be used in the production of nectar. Oxygen - It is the by product of photosynthesis. It is released into the atmosphere through the stomata. This oxygen is used by plants and animals for respiration. Site of Photosynthesis It takes place in the leaves of plants. It can also take place in the green stems, sepals and fruits. Leaf Structure Epidermis - It consists of a layer of cells arranged without any intercellular spaces. Both the upper and lower epidermis have stomata but the lower epidermis has more stomata than the upper epidermis to prevent the loss of water through evaporation. Cuticle - Waxy and waterproof layer which makes the leaf waterproof and prevents infections. Mesophyll tissue - They are of 2 types: Palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll. Palisade mesophyll - It is the upper portion of the mesophyll tissue, it comprises of 2-3 layers of closely packed rectangular cells which have abundant chlorophyll. Spongy mesophyll - It is the lower portion portion of the mesophyll tissue, it comprises of loosely packed circular cells with a lot of air cavities in between them. Vascular bundle - It contains xylem and phloem which conduct water and food. Structure of Stomata They are found in the epidermal layer of leaves, and other green parts of the plant. They help in the gaseous exchange between the plant and the atmosphere. Guard cells - They regulate the size of the pore. They have a thick inner wall and a thin outer wall. When they absorb water the thin outer wall expands pulling the inner wall along with it. This causes the stomata pore to expand. Subsidiary cells - They are soft allowing the guard cells to expand and contract without any air cavities in between.