Leaf and Photosythesis
advertisement

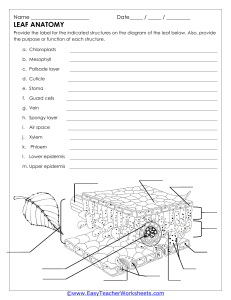
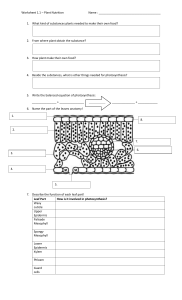
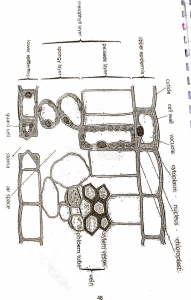
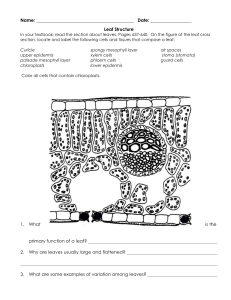
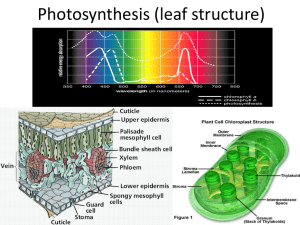
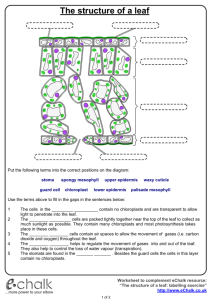
Year 9 Photosynthesis – Structures of a Leaf (Homework) No Structure Description 1 Functions Waterproof – preventing the wetting of the leaf and reflecting excess heat away 2 Epidermis 3 Palisade Mesophyll 4 Regular cells tightly bound – upper and lower epidermis Contains loose oval cells in the lower part of leaf with lots of air spaces For gas exchange For gas exchange 5 Air space Air space found in spongy mesophyll 6 Xylem Tubes in the vascular bundle at the lower position 7 8 Name: __________________________________ For transport of sugar made in photosynthesis Guard cell 9 Stomata Spongy Mesophyll Cuticle Phloem Pores found mainly in the lower epidermis For exchange of gases and water vapour Waxy layer on the top of epidermis Contains elongated (rectangular) cells with lots of chloroplasts) at the upper part of the leaf 2 kidney-shaped cell with chloroplasts found in lower epidermis Tubes in the vascular bundle at the upper position Forming a stoma for exchange of gases Main site for photosynthesis Protecting the leaf from mechanical damage and infection. For transport of water and mineral salts from the root to the leaf Use these words to label the diagram of a leaf : vein, petiole, mid-rib, blade For the internal structure of a leaf: guard cells, cuticle, vascular bundle, spongy mesophyll, , palisade mesophyll For the next 2 diagram on the right: Stoma, chloroplast, guard cell, epidermis cell, cytoplasm, nucleus Photosynthesis process: glucose, carbon dioxide, oxygen, sunlight, oxygen, water, chlorophyll