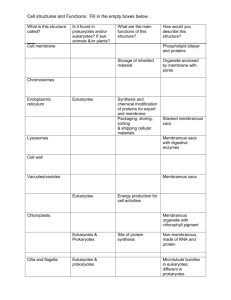
Microbial Structure
advertisement

Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes Computer Filename: pkvsek.ppt Hugh B. Fackrell 1 3/22/ Presentation Outline Major Groups of Organisms Classification of Organisms Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes 2 3/22/ Background Terms & Concepts Proteins Membranes (membr.ppt) Formation of lipid bilayers (membr.ppt) Prokaryotes Prokaryotes vs eukaryotes Evolution of eukaryotes 3 3/22/ Cell 4 Basic unit of all organisms in the various kingdoms Cell membrane Protoplasm Genetic information DNA & RNA 3/22/ Major Groups of Organisms Plants Animals Fungi Protista Prokaryotes Viruses 5 3/22/ Major Groups of Organisms Plants: – photosynthetic, inorganic food Animals: – non photosynthetic, organic food 6 3/22/ 1 of 2 Major Groups of Organisms Fungi: – non photosynthetic, organic food, – microscopic, filamentous Subgroups – Yeasts – True fungi 7 molds,rusts, smuts, mushrooms 3/22/ Protista Microscopic eukaryotes – Food organic or inorganic – Some photosynthetic Examples – Slime molds – Algae – Protozoa 8 3/22/ Prokaryotes Characteristics – No nucleus or nuclear membrane – Microscopic – Food organic or inorganic – Some photosynthetic Bacteria 9 Cyanobacteria Eubacteria Archaea (archaebacteria) 3/22/ Viruses Non cellular – Reproduce only in living host cells – Food from living cells – By infection only ONE nucleic acid – DNA viruses – RNA viruses 10 Protective protein coat 3/22/ Viroids 11 Special subgroup of viruses that lack the protective protein coat 3/22/ Prions Mad cow disease, scrapie “Infectious” proteins – genetically coded by animal 2 configurations of same protein – One form harmless – Second form pathologic – Pathological configuration acts as a template to convert harmless form 12 3/22/ Classification of Organisms From Fossil Record & Morphology – Five Kingdoms- plants, animals,fungi , protistia, prokaryotes – Prokaryotes - Eubacteria, Archeobacteria From Cellular organization – Three kingdoms- Eubacteria, Archaebacteria, Eukaryotes 13 3/22/ Empires Level of organization above the kingdom level Archaea (formerly Archaebacteria) Bacteria ( formerly Eubacteria) Eucarya (plants, animals, protista, fungi) 14 3/22/ Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes 15 Prokaryotes No nuclear membrane DNA in ONE molecule free in cytoplasm No membrane bound organelles No cytoskeleton Eukaryotes Nuclear membrane DNA organized in several molecules (chromosomes) Many different membrane bound organelles Cytoskeleton 3/22/ Prokaryotes (details) Size:1-10 m Flagella: simple, 2 proteins Capsule: extracellular polymer Cell wall: usual, complex Plasma membrane: no carbohydrates or sterols Ribosomes: small(70S) Cell division: binary fission 16 3/22/ Eukaryotes (details) Size:10-100 m Flagella: Complex, many microtublules Capsule: none Cell wall: if present chemically simple Plasma membrane:Sterols & carbohydrates Ribosomes: large (80S) in cytoplasm – small(70S) in organelles Cell division: mitosis 17 3/22/ Summary Simple cells Single circular chromosome 1-2 microns in size few internal compartments or organelles Complex Cell Wall common Cell wall unique 18 3/22/