Notes Outline L37,L38 -R38
advertisement

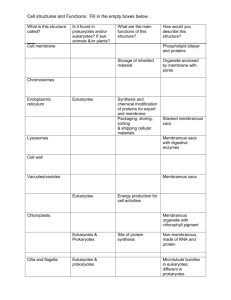
The Microbial World and You Microorganisms __________________________________________________________________ How are microbes named and classified? Linnaeus established __________________________________________________________________ Each organism has two names: __________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Are “Latinized” and used worldwide. May be descriptive or honor a scientist. Scientific Names Staphylococcus aureus Describes the clustered arrangement of the cells (staphylo-) and the golden color of the colonies (aur-). Escherichia coli Honors the discoverer, Theodor Escherich, and describes the bacterium’s habitat– the large intestine or colon Taxonomy What is systematics? Study of phylogenetic relationships Phylogenetics = ___________________________________________________________ Taxonomy = _____________________________________________________________ Also a way of organizing/ classifying Taxa (taxon—singular) How are prokaryotes classified? Divides prokaryotes into (based on rRNA sequences) __________________________ __________________________ Who is Carl Woese? 1978: created current classification scheme Three domains __________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ Eukarya __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ What is the taxonomy of organisms? _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ How are eukaryotes classified? Endosymbiotic theory Numerous kingdoms, including Protista Fungi Plantae Animalia What about viruses—How are they classified? Not included in three domains, which are ____________ ___________ and ______ Why not? Viral species: population of viruses with similar characteristics A closer look at the microbes What are bacteria? Simple, single-celled Prokaryotes ______________________________________________________________ Come in different shapes ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ Peptidoglycan cell wall Binary fission Some have flagella What are archaea? Also prokaryotes ________________________________________________________________________ Live in extreme conditions __________________________________________________________________ Hyperthermophiles Methanogens ________________________________________________________________________ What are fungi? Eukaryotes Have a true nucleus ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Includes Molds Mushrooms Yeasts Slime molds Sexual and asexual reproduction What are protozoa? Eukaryotes ________________________________________________________________________ May be motile via pseudopods, cilia, or flagella What are algae? Eukaryotes Cellulose cell walls ________________________________________________________________________ Produce molecular oxygen and organic compounds What are viruses? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Coat may be enclosed in a lipid envelope. Viruses are replicated only when they are in a living host cell. What are multicellular animal parasites? Eukaryote ________________________________________________________________________ Parasitic flatworms and round worms are called ________________________________. Microscopic stages in life cycles. What are infectious diseases? When a pathogen overcomes the host’s resistance, disease results. Emerging infectious diseases (EID): ___________________________________________. West Nile Virus Bovine spongiform encephalopathy Ebola hemorrhagic fever Hantavirus AIDS Anthrax