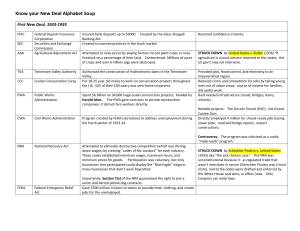
TheNewDeal - The Taft School | Haiku Learning

THE NEW DEAL
1933-1936
The Situation in 1933
• 13,000,000 unemployed
• 34,000,000 belonged to families with no full time wage earner (out of 125,000,000)
• Industrial production had fallen by 45% from 1929
• Homebuilding dropped 80% from 1929
• About 5,000 banks went under from ’29-32.
• By 1933, 11,000 of 25,000 banks had failed.
• GDP fell by 30%, the stock market by 90%
• By 1933, 25% of all workers and 37% of an non-farm workers were unemployed
• The income of the average family dropped 40%
The Banking Crisis
• 3/6/33 – Closes banks
• 3/9/33 – Emergency Banking Relief Act: All Federal
Reserve approved banks would be guaranteed cash flows from the Fed. Bank: bank runs end
• 6/16/33 – Glass-Steagall Act: Creates the Federal Deposit
Insurance Corporation to guarantee bank deposits.
Requires banks to separate their investment and commercial banking activities. (repealed in 1999)
The Hundred Day Congress
Financial Reform
• 4/5 – FDR orders US gold coins to be exchanged for paper dollars
• 4/19 – US abandons the gold standard
• This begins the era of a managed currency.
• 5/27 – Federal Securities
Act
Immediate Relief
• 3/31 - Unemployment Relief act creates the CCC
• 5/12 – Federal Emergency
Relief Administration created
CWA
•
•
5/12 – AAA created
5/18 – TVA created
•
•
6/13 – HOLC created
6/16 – NRA created (PWA)
The AAA
• Agricultural Adjustment Act
• Attempted to raise the price of farm goods by paying farmers not to farm. Instead, they would be paid “parity prices” – what the crop would have sold for.
• This was intended to end overproduction and put more wealth in farmers’ hands.
• Ruled unconstitutional in 1936.
• Congress replaced it with a conservation plan to pay parity prices if farmers planted soil conserving crops like alfalfa.
• The government has been very involved in agricultural production ever since.
The NRA
• All encompassing attempt to boost wages and production.
• Largely voluntary.
• Created a minimum wage and a maximum work week.
• Created the PWA to “prime the pump”
• Gave more bargaining power to unions
• Ruled unconstitutional in 1935.
• The Wagner Act and National Labor Relations Act was salvaged from the NRA to preserve union bargaining power.
• Industrial production did rise 55% in the two years the
NRA was operating.
Public Works
• CWA Immediate “make work”
• CCC – Young men sent to the woods to do conservation work (the beginnings of the American Army of WWII)
• TVA – Built 20 dams in the Tennessee River Valley, electrified the South.
• REA – Spread electric power lines through rural areas.
• PWA – Mostly larger scale public works projects (dams, bridges, hospitals, schools, warships)
• WPA – Mostly smaller scale projects like parks, poverty relief, roads and educational projects (writers, poets and artists)
Long Term Reform
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
6/6/34 – Securities Exchange Commission founded to investigate fraud on Wall Street.
6/12/34 – Reciprocal Trade Agreement allowed the
President to lower tariffs with other countries that did the same
6/18/34 – Indian Reorganization Act (Indian New Deal)
4/30/35 – Resettlement Administration moves farmers off poor lands
8/14/35 – Social Security Act
6/25/38 – Fair Labor Standard Act: Minimum wage created, overtime rules, no child labor
8/2/39 – Hatch Act prevents civil servants from campaigning
Social Security
• Covers old age, disability, and survivors (orphans) of those who die during their wage earning years.
• Originally included unemployment insurance (it was later moved into a separate program).
• At first, agricultural, domestic and government workers were exempted from the program.
• Few blacks and women benefitted at first.
• Money is withdrawn from paychecks (payroll tax) to pay for the program.
• Over time, it came to include almost everyone.
Recession of 1937
• Disputed causes.
• FDR bowed to pressure to balance the budget. He cut spending in the PWA and WPA.
• Also, Social Security taxes were being collected but benefits were not being paid out.
• The Federal Reserve also tightened the money supply.
• Overall constricting of demand.
• Unemployment went from 14% to 19%.
• Industrial production fell 37%
• FDR responded by putting more money into WPA and PWA.
• The economy recovered some, but would await WWII for a full recovery.
The Roosevelt Recession
Unemployment Government spending