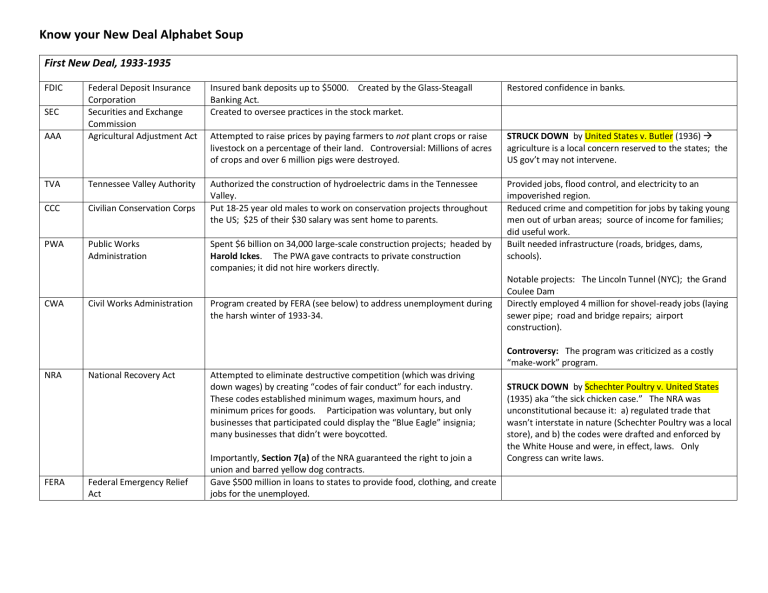
Know your New Deal Alphabet Soup First New Deal, 1933-1935 FDIC Insured bank deposits up to $5000. Created by the Glass-Steagall Banking Act. Created to oversee practices in the stock market. Restored confidence in banks. AAA Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Securities and Exchange Commission Agricultural Adjustment Act Attempted to raise prices by paying farmers to not plant crops or raise livestock on a percentage of their land. Controversial: Millions of acres of crops and over 6 million pigs were destroyed. STRUCK DOWN by United States v. Butler (1936) agriculture is a local concern reserved to the states; the US gov’t may not intervene. TVA Tennessee Valley Authority CCC Civilian Conservation Corps Authorized the construction of hydroelectric dams in the Tennessee Valley. Put 18-25 year old males to work on conservation projects throughout the US; $25 of their $30 salary was sent home to parents. PWA Public Works Administration Provided jobs, flood control, and electricity to an impoverished region. Reduced crime and competition for jobs by taking young men out of urban areas; source of income for families; did useful work. Built needed infrastructure (roads, bridges, dams, schools). SEC CWA Civil Works Administration Spent $6 billion on 34,000 large-scale construction projects; headed by Harold Ickes. The PWA gave contracts to private construction companies; it did not hire workers directly. Program created by FERA (see below) to address unemployment during the harsh winter of 1933-34. Notable projects: The Lincoln Tunnel (NYC); the Grand Coulee Dam Directly employed 4 million for shovel-ready jobs (laying sewer pipe; road and bridge repairs; airport construction). Controversy: The program was criticized as a costly “make-work” program. NRA FERA National Recovery Act Federal Emergency Relief Act Attempted to eliminate destructive competition (which was driving down wages) by creating “codes of fair conduct” for each industry. These codes established minimum wages, maximum hours, and minimum prices for goods. Participation was voluntary, but only businesses that participated could display the “Blue Eagle” insignia; many businesses that didn’t were boycotted. Importantly, Section 7(a) of the NRA guaranteed the right to join a union and barred yellow dog contracts. Gave $500 million in loans to states to provide food, clothing, and create jobs for the unemployed. STRUCK DOWN by Schechter Poultry v. United States (1935) aka “the sick chicken case.” The NRA was unconstitutional because it: a) regulated trade that wasn’t interstate in nature (Schechter Poultry was a local store), and b) the codes were drafted and enforced by the White House and were, in effect, laws. Only Congress can write laws. Second New Deal - 1935-1938 WPA Works Progress Administration Implemented to address continuing unemployment in 1935 (ahead of the 1936 election!); spent $11 billion; employed 8 million. Headed by Harry Hopkins, the WPA was more controversial than the PWA because it hired workers directly. NYA NLRB National Youth Administration National Labor Relations Board Social Security Act Fair Labor Standards Act REA Rural Electrification Administration “A New Deal for the Arts” -- In addition to construction jobs, the WPA also included the WPA Theater Project ; WPA Writer’s Project; WPA Artists project, which employed those in the arts economy to write, act, put on production, paint murals on public buildings, etc. Offered “work-study” programs for youth age 16-24 through their schools. Created by the Wagner Act, the NLRB was an agency that was created to hear complaints about unfair labor practices, oversee union elections. In essence, it created a special administrative court (complete with its own judges) for labor disputes. Provided: - Old-age insurance for retirees over 65 and their spouses. Workers and employers would contribute equally through payroll taxes. - Unemployment compensation. Paid by a new tax on employers. - Disability insurance to aid families. Paid by federal funds given to states. Replaced the NRA Codes. Created maximum hours (44 hrs per week; later 40); barred child labor; established a minimum wage. Aimed to bring electricity to rural areas. In 1935, only 12.6% of farms had electricity. By 1949, 90% did. A few notable projects: John Steinbeck’s novels Of Mice and Men and The Grapes of Wrath. The WPA Slave Narratives – journalists recorded interviews with hundreds of former slaves. Mary McLeod Bethune was appointed head of the NYA’s Division of Negro Affairs to ensure funding for training programs for African-American youth. For example, she successfully pushed for a new Civilian Pilot Training Program to be extended to African-American schools; as a result Tuskegee Institute became a center for training pilots and would later develop the famed Tuskegee Airmen. Bethune was the first black head of a federal agency and an influential member of Roosevelt’s “Black Cabinet” Restored the organized-labor provisions of the NRA, which had been struck down by the Schechter Case in 1935. Designed to create a “social safety net.” Unemployment insurance would reduce the overall economic shock of downturns by maintaining some income for those looking for work.






