The New Deal
advertisement

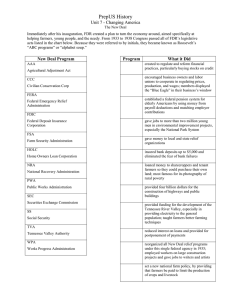
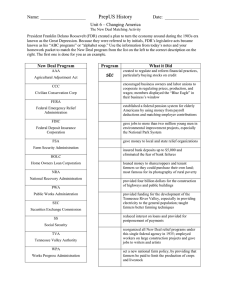
Restoring the Nation’s Hope 1933- presidential elections took place in November, but the Inauguration didn’t take place until April 4 months delay Hoover a “lame duck” Depression deepened Prompted Congress to pass the Twentieth Amendment which changed the date of the inaugural to January 20. Did not take place until the following election 2nd Bonus March on Washington Whitehouse provided campsites for the veterans Eleanor Roosevelt visited them demonstrating compassion and soothed popular fears about renewed radical agitation Inaugural Address- “The only thing we have to fear is fear itself” Fireside chats Referred to the relief, recovery, and reform programs of FDR’s administration that were aimed at combating the Great Depression Stabilizing Financial Institutions “Bank holiday”- closed banks for 4 days to inspect financial health 2/3 reopened Americans regained confidence in the banking system and began to put more money back into their accounts than they took out Glass-Steagall Banking Act of 1933created the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) to insure bank deposits Federal Securities Act- required companies to provide information about their finances if they offered stock for sale Securities and Exchange commission (SEC)- regulated the stock market Decreased the value of U.S. currency by taking it off the gold standard Hoped that this action would raise the prices of farm products and other goods Hoped that a devalued American currency would stimulate export trade Providing Relief and Creating Jobs Sent funds to local relief agencies Put federal money into public works programs, government-funded projects to build public facilities Civil Works Administration (CWA)- put unemployed to work building or improving roads, parks, airports, and other facilities Civilian conservation Corps (CCC)- put more than 2.5 million young, unmarried men to work maintaining forests, beaches, and parks Paid $30/month, allowed to live in camps free of charge and received food, medical care, and job training Indian Affairs used federal funds and native American workers to build schools, hospitals, and irrigation systems Regulating the Economy National Recovery Administration (NRA)balance the unstable economy through extensive planning Industry-wide codes to spell out fair business practices Regulated wages, restraining wage competition Controlled working conditions, production, and prices, and set a minimum wage Gave organized labor collective bargaining rights, which allowed workers to negotiate as a group with employers Public Works Administration (PWA)launched projects ranging from the Grand Coulee Dam to NYC’s Triborough Bridge to the causeway that connects Key West to the Florida mainland Assisting Homeowners and Farmers Home Owners’ Loan corporation (HOLC)- refinanced mortgages National Housing Act of 1934established the Federal Housing Administration (FHA)- government0wned corporation created to improve housing standards and conditions to insure mortgages and to stabilize the mortgage market Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA)- tried to raise farm prices through subsidies or government financial assistance Paid farmers not to raise certain crops and livestock- lower production would cause prices to rise Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA)- public works project that helped farmers and created jobs in one of the country’s least developed regions 1st President ever to appoint a woman to a Cabinet post Frances Perkins became Secretary of Labor and successfully pressed for laws that would help both wage earners ad the unemployed Hired African Americans in more than a hundred policymaking posts Mary McLeod Bethune held the highest position of any African American woman in the New Dealinfluential spokesperson for Af. Am. Concerns ▪ Advised FDR on programs that aided Af.Am. And in the process increased her level of influence Traveled widely for her husband, whose disability made traveling difficult Reported back on conditions in the country and on the effects of his program Sometimes took stands that embarrassed her FDR Controversial- some Americans though a First Lady should act only as a gracious hostess Many came to admire her for her political skills, her humanity, and her idealism Critics worried that New Deal agencies were giving increasing power to the federal government Supreme Court attacked FDR’s programs Declared the NIRA unconstitutional because it gave the Pres. Lawmaking powers and regulated local, rather than interstate, commerce Struck down the tax that funded AAA subsidies Called the Second New Deal or the Second Hundred Days Included more social welfare benefits, stricter controls over business, stronger support for unions, and higher taxes on the rich Works Progress Administration (WPA)provided work for more than 8 million citizens Built or improved tens of thousands of playgrounds, schools, hospitals, and airfields, and supported the creative work of many artists and writers National Youth Administration provided jobs, education, recreation, and counseling for young men and women ages 16-25 Resettlement Administration/Farm Security Administration (FSA)- loaned money to owners of small farms and helped resettle tenants and sharecroppers Rural electrification New Labor Legislation Wagner Act- legalized such union practices as collective bargaining and closed shops, which are workplaces open only union members. Also outlawed spying on union activities and blacklisting Be able to list 6 new deal agencies and their purpose.