Do Now: Which new deal program did you think was the best and
advertisement

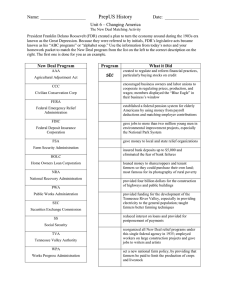
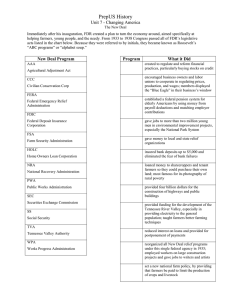
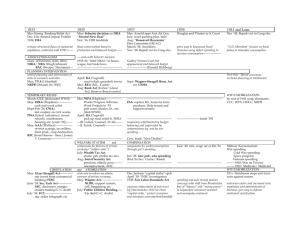
Do Now: Which new deal program did you think was the best and why? (Base these off the presentations from yesterday) Objectives: Students will be able to...(1) Describe the function of the major New Deal programs (2) analyze the info and form opinions on it's success Homework: Continue Reading Through Chapter on your Own • An impressive 15 acts of legislation were passed early on in FDR’s presidency • Born out of a divided administration (Many opinion) The Hundred Days Refresh • Declared a Bank Holiday right when he took office • Emergency Banking Relief Act passed after just 38 mins! • FDR then addressed 60 Million people in Fireside Chat • Following day the deposits outweighed withdrawals Step 1: Fix the Banks! • Advisors to FDR wanted him to go further to Trust-bust and create fair competition • Securities Act of 1933 – This created the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) • The Glass-Steagall Act – This created the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) Regulating Banks & Brokers • Advisors believed that struggles came from low prices and high production • Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA) – Government paid farmers NOT to grow certain crops • Had to destroy crops already planted • By 1936 farm surplus had ended and food prices rose (Hard Criticism • Large farmers did better than small ones because they had one crop vs. many • African American became homeless and jobless when landlords chose to shut down their land Step 2: Managing Farms & Industry • Americans were in debt – cut back spending • Home Owners Loan Corporation (HOLC) – Government bought loans and restructured with longer terms less interest • 1 out of 5 mortgages were helped • Still foreclosed if people lost jobs • Farm Credit Administration (FCA) – Similar program for farmers Step 3: Debt Relief • Didn’t want to simply GIVE money to the unemployed • Thought people could build morale and develop skills Step 4: Spending and Relief Programs • Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) – Gave men 18-25 conservationist jobs • Planting Trees, fighting forest fires, and building reservoirs • Public Works and Emergency Relief – Created FERA (Led by Harry Hopkins) • Public Works Administration (PWA) – Created construction projects, like highways, dams, sewers, water-works, schools, etc. • Indirect Hiring • Civil Works Administration (CWA) – Similar to PWA but employees hired directly ($1 Billion Spent) • Direct Hiring • Became alarmed at the spending and shut down program Programs • These programs did not restore prosperity • His actions inspired hope and optimism • Faith in nation had returned • Why do you think faith returned??? First Term Thoughts Do Now: Grab a worksheet from Mr. Collison and fill in the first part of the chart with a partner Objectives: Students will be able to...(1) analyze an image for key information (2) describe the second New Deal (3) compare and contrast the two New Deals Homework: Guided reading sheet for 23-4 The Second New Deal • Who opposed the New Deal? • Why did they oppose it? • What is deficit spending? • What comparisons can you make to our current economy? Opponents of the New Deal • People on the Right: • Thought he was putting too much regulations on Government • Deficit Spending – scared business leaders • Formed American Liberty League – Organized opposition to the New Deal • People on the Left: • Believed he had not gone far enough • Wanted more dramatic intervention Opposition from Right & Left • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V8iC1-eC3zo • Works Progress Administration (WPA) - Similar to PWA and CWA • $11 Billion Spent • Built: • 650,000 miles of highways, roads and streets • 125,000 public buildings • 8,000 parks • Improved: • 124,000 bridges • 853 airports Second New Deal Programs • Programs were taking longer to pass in congress. Why? • Supreme court struck down National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA) • Schechter vs. United States – “ The sick chicken” case • Schechter brothers violated chicken provision by selling diseased chickens and paying workers too little. • Supreme court ruled that Congress could not delegate powers to Executive Branch Supreme Court • National Labor Relations Board (Wagner Act): • The act guaranteed workers the right to organize unions and to bargain collectively • Set up binding arbitration – neutral party listens to both sides and decides on issues • Committee for Industrial Organization: Organization formed to help organize unions Industrial Unions • Sit-Down Strikes: Workers who stopped working but refused to leave plants • Flint, Michigan Auto-Plant: Union workers went on strike and it turned violent • Similar situations happened around the country Strikes • GOAL – To provide help for those unemployed through no fault of their own • People it helped: • • • • Elderly who stopped work after 65 Unemployed People with disabilities Poor families with young children • Critics didn’t like that the $$ came from payroll taxes on workers • Helped a lot of people initially, but left our the neediest of people at the time (Farmers and domestic workers) • 65 % African Americans fell in to this category Social Security Act • Using the chart on the back and the book, identify what those major programs accomplished, and who might have opposed them Your task….