Topic 2: Cells

1.3 & 1.4 Cellular
Membranes
• What do you know?
• What questions do you have?
Read & Consider 1.3.1 – 1.3.3
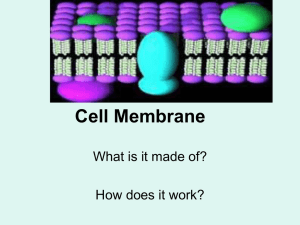
Cells are surrounded by water inside and out. Membrane behavior is dictated by interactions with water.
• Polar
• Nonpolar
academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu
The diagram should include:
Phospholipid bilayer
Cholesterol
Glycoproteins
Integral proteins
Peripheral proteins
Watch – History of Cell Membrane up to Gorter and
Grendel’s 1925 discovery
“ Insights into cell membranes via dish detergent ”
Davson and Danielli’s “Fat Sandwich Model” – accepted until 1972
Singer and Nicolson’s “Fluid Mosaic Model” – accepted today
• What do you know?
• What questions do you have?
• Compare and contrast diffusion and osmosis.
Read & Consider 1.4.1-1.4.2
Diffusion: passive movement of particles from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
Osmosis: passive movement of water molecules from a region of lower solute concentration to a region of higher concentration.
Isite.lps.org
Simple Diffusion –there is no expenditure of energy in moving the molecules across the membrane.
Facilitated Diffusion – larger molecules move passively through the membrane via channel proteins.
sjcabiology.wikispaces.com
Molecules moving from low to high concentration must be actively moved.
Video
A transport mechanism for the movement of large quantities.
Exocytosis: vesicle membrane fuses with the plasma membrane.
Endocytosis: a vesicle is formed by the in folding of the plasma membrane.
Material Transport
o Phospholipid molecules can change places in the horizontal plane (creates fluidity). o Molecule exchange in the vertical plane DOES
NOT occur (maintains integrity).
Video
Inner Life of a Cell
2007 – the President and Fellows of Harvard College
Tissue or organs to be used in medical procedures must be bathed in a solution with the same osmolarity as the cytoplasm to prevent osmosis. Complete the exploration phase for the lab with the following aim:
To determine the osmolarity of an unknown substance by bathing samples in hypotonic and hypertonic solutions.