Continuity of life-forms
advertisement

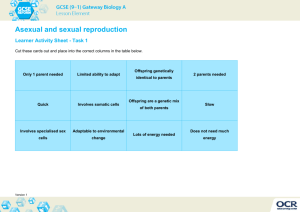
Continuity of life-forms B-5.2: Explain how genetic processes result in the continuity of life-forms over time. Continuity of life-forms Continuity of life-forms on Earth is based on an organism’s success in passing genes to the next generation Organisms from years ago resemble those alive today Because same genetic processes have passed along the genetic material of life (DNA!!!) Continuity of life-forms Most scientists attribute the continuity of life-forms over time to the genetic processes that all organisms share. All life on Earth, share at least the same 2 structures Nucleic acids (RNA or DNA) carry code for protein synthesis Proteins (all life composed of same 20 amino acids) Transcription and translation (nucleic acids coding for proteins) is same in all life on Earth Same sequence of nucleotides code for same specific amino acids Example: AUG always codes for methionine no matter the organism Passing Genetic information All organisms have reliable means of passing genetic information to offspring through reproduction Reproductive processes result in offspring receiving essentially the same genetic information as parents, can be some genetic variability Two types of reproductive processes Sexual reproduction Asexual reproduction Sexual Reproduction Uses meiosis to create gametes Fertilization results in embryo receiving alleles from each parent for each trait Offspring will express a combination of traits allowing for variation Sexual Reproduction and genetic variability Genetic variability through sexual reproduction, due to: Gene shuffling, Crossing over, Recombination of DNA, Mutations When gametes are produced, alleles are arranged in new ways in the offspring Sexual Reproduction and genetic variability Genetic changes result in transcription and translation of new/different proteins that will result different phenotypes of an individual organism Reproduction results in allele combinations producing traits that improve an organism’s chance of survival ensure the continuity of that life form over time. Sexual Reproduction and genetic variability Asexual Reproduction Involves only one parent Produces offspring that are for the most part genetically identical to parent Methods of asexual reproduction Asexual reproduction accomplished by cell division Binary fission (single-celled organisms) Mitosis (multi-celled organisms) Examples of asexual reproduction: budding, fragmentation, and vegetative propagation Asexual Reproduction and Genetic Variability Genetic variability in asexual reproduction can only occur in mutations in DNA passed from parent to offspring A way that organisms achieve variations as populations continue over time Pros and Cons of asexual reproduction Pro: reproduction rate is much higher than sexual reproduction Produces many offspring that are suited to continuing life in the present environment Con: genetically identical offspring respond to the environment in the same way If a population lacks traits that enable them to survive and reproduce, the entire population could die off Genetics of Evolution Genetic view of evolution includes the transfer of the genetic material through sexual and asexual reproduction. The continuity of a species is contingent upon these genetic processes If an organism can reproduce both sexually and asexually, they have an adaptive advantage for survival.