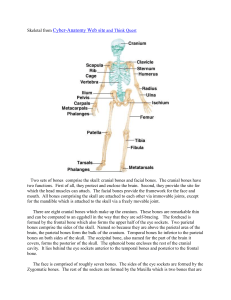
Skeletal organization
advertisement

Skeletal organization Ch. 7 Anatomy Part II Table 7.1, p. 141 Axial Skeleton Head, neck and trunk Appendicular Skeleton Upper and lower limbs 26 22 25 60 60 bones bones bones bones bones in in in in in vertebra skull ribs arms/hands legs/feet Skull drawing Did you hear about the latest pirate movie? Its rated “Arrrrrrrrrgh!” Skull: p. 142-147 At birth, babies’ skulls have soft spots (membranous areas) So they can pass thru birth canal easier More of a forehead than adults A chinese elephant man (from a tumor) Vertebral Column Fig. 7.15 contortionist - Google Video Ends with your sacrum and coccyx Sacrum-triangular, 5 fused vertebrae Coccyx-tailbone Ribs Fig. 7.19 Ribs 1st 7 rib pairs-true ribs Join to sternum Other 5 pairs-false ribs Do not reach sternum directly Last 2 pairs are floating ribs Shoulder area Clavicle (collar bone) is the bone most often broken Upper Limb Humerus, radius, ulna Fig. 7.25: wrist and hand bones Pelvic girdle Females usually have a wider pelvis Breakdancing Kid How to dance like a white guy. Lower limbs Femur, tibia and fibula in legs, with patella Foot bones Fig 7.31 Joints Joints Different types Fibrous-like a suture between skull bones Cartilagenous-ex. in vertebrae Synovial-ex. knee, finger Types of synovial joints (Table 7.4) Ball and socket-shoulder, hip Condyloid- like btw metacarpals and phalanges Gliding- wrist Hinge-elbow Pivot-proximal ends of radius and ulna Saddle-carpal and metacarpal of thumb Most information was taken from the textbook, Hole’s Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology. Pictures taken from google.com