Water and the Fitness of The Environment
advertisement
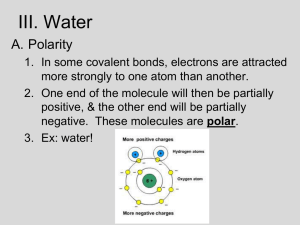
Water and the Fitness of The Environment Polarity Effect on Environment Effect on Living Things Water as a Solvent pH and Living Things Polarity Opposite ends of the water molecule have opposite charges Oxygen region has a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atoms have a partial positive charge Two water molecules are held together by a hydrogen bond which gives water some of its unique properties Hydrogen Bonding and Water’s Properties Water molecules attract one another and “stick” together and this gives water the property of Cohesion. Cohesion helps in: the transport of water against the force of gravity in plants Hydrogen bonding also results in Adhesion Adhesion results in water sticking to the sides of the tube-like cells in plants, helping them rise as a unit to the leaves. Effects on the Environment Water absorbs and releases heat to moderate the temperature of Earth’s environment. This makes areas of the earth more habitable than they otherwise would be without this property. This results from its relatively high Specific Heat, or the amount of heat that must be absorbed or lost for one gram of that substance to raise its temperature 1oC. Its temperature changes less than other substances when it absorbs or loses a given amount of heat. (It absorbs or loses a relatively large amount of heat for each degree it goes up or down.) Effects on The Environment 2 Many areas near ocean waters can sustain populations because their coastal areas are much warmer than interior areas at that latitude. Ocean temperatures remain much more stable than land temperatures which allows for diverse marine life to thrive. Effects on The Environment 3 Water also has a high Heat of Vaporization or quantity of heat a liquid must absorb for 1 gram of it to be converted to a gas. This evaporation causes the surface of the liquid to cool causing something called Evaporative cooling. This contributes to the stability of temperature in lakes and ponds . Effects on The Environment 4 Water actually loses density when it takes solid form. As water becomes a solid crystal the hydrogen atoms become locked a bit further apart which results in it becoming 10% less dense than it is as a liquid. This allows life to continue at depth in lakes and ponds through the winter. Effects on Living Things Evaporative cooling allows animals to cool their body temperature in warmer climates, preventing them from overheating. Cohesion and adhesion allow water to flow against the force of gravity in plants. Water is an important part of animal and plant tissues and allows substances to be dissolved in and move with it. Water as a Solvent Water is a solvent or a dissolving agent due to its polarity It dissolves many things but is not a “universal solvent” See example in your text pages 45-6 Negatively charged part of the water molecule attracts positive ions and vice versa-Water forms a hydration shell around each dissolved ion Substances that have a love for water are called hydrophilic and those that seem to repel water are called hydrophobic Solute Concentrations Solute concentrations are important as controllers of what goes into and out of cells. Molarity is a measure of solute concentration based on moles of solute per liter of solution. To obtain one mole of a substance you measure out its molecular weight in grams. Remember that one mole is equal to 6.02 X 1023 molecules pH and living things 1 Remember that acids are solutions that increase the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution and bases reduce the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution, usually by accepting hydrogen ions. The concentration of hydrogen ions in pure water is 10-7M at 25oC Therefore water has a pH of 7 because the pH is the negative log of the concentration of hydrogen ions in any solution. pH and Living Things 2 In addition remember that the product of hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions in a solution is always 10-14 Most living things exist in a very narrow pH range, usually from 5-7. Buffers are substances that minimize changes in pH to maintain a favorable pH range (see examples page 48-9). pH and Living Things 3 Acid rain or acid precipitation seriously affects plants because pH affects the solubility of minerals in the soil necessary for plants. If the pH does not allow soil and water to combine to dissolve needed minerals, trees and plants are stressed and can die easily.