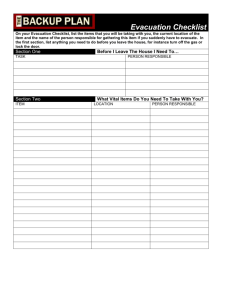
PPT Plan & conduct evacuation 270812
advertisement

PLAN AND CONDUCT AN EVACUATION OF PREMISES Unit Code: D1.HSS.CL4.10 Slide 1 Plan and conduct an evacuation of premises This unit comprises five Elements : Prepare evacuation policies and procedures Prepare for evacuation situations Update evacuation/Emergency Management Plans Conduct evacuations Review evacuation/Emergency Management Plan after actual implementation. Slide 2 Assessment Assessment for this unit may include: Oral questions Written questions Work projects Workplace observation of practical skills Practical exercises Formal report from employer or supervisor. Slide 3 Prepare evacuation policies and procedures Performance Criteria for this Element are: Involve relevant personnel in the planning process Identify the legal implications in relation to planning for an evacuation Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment (Continued) Slide 4 Prepare evacuation policies and procedures Develop a written set of evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of the evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Locate evacuation and Emergency Management Plan and floor plans in prominent and necessary positions. Slide 5 Involve relevant personnel in the planning process Evacuation and Emergency Management Plans (EMPs): Require proper planning Must address a variety of possible threats faced by the venue. Slide 6 Involve relevant personnel in the planning process In relation to EMPs: An evacuation plan is an EMP Not all emergencies will require an evacuation The purpose of an evacuation plan is to remove people from danger to a safe location ‘Relevant people’ should be involved in identifying the need for EMPs and in developing them. Slide 7 Involve relevant personnel in the planning process The following should be involved in identifying threats and developing appropriate EMPs: People with assigned emergency and evacuation responsibilities – Chief warden, area wardens, first aiders, communications officer Security staff (Continued) Slide 8 Involve relevant personnel in the planning process Building or centre management Maintenance department Fire services (Continued) Slide 9 Involve relevant personnel in the planning process Ambulance Supplementary emergency services – Civil Defence Police (Continued) Slide 10 Involve relevant personnel in the planning process Army bomb disposal units Anyone who could be expected to deal with an emergency – with a focus on night-time workers The Emergency Management Committee (EMC). Slide 11 Identify the legal implications in relation to planning for an evacuation Legal implications include Common law ‘duty of care’ requirements: • To prevent ‘foreseeable’ harm • All people in the property must have their safety and welfare protected • Anyone injured may sue the property under ‘negligence’. Slide 12 Identify the legal implications in relation to planning for an evacuation The legal system is divided into: Civil proceedings: • Person sues a person or business • Case decided ‘on the balance of probabilities’ Criminal proceedings: • Government against person or business • Decided on basis of ‘beyond all reasonable doubt’. Slide 13 Identify the legal implications in relation to planning for an evacuation Civil outcomes may include one or more of the following: Business must pay ‘damages’ Must make an apology Must do a nominated act Must refrain from doing a specified activity. Slide 14 Identify the legal implications in relation to planning for an evacuation If a person or business is found guilty of a crime, results may include: Warning Fine Gaol. Slide 15 Identify the legal implications in relation to planning for an evacuation OHS considerations: Provide specific safety and duty of care obligations on employers and venue Failure to comply can lead to criminal charges. Slide 16 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment A ‘risk’ or ‘threat’: Is anything with the potential to adversely impact on the safety of the people in the building The terms ‘risk’ and ‘threat’ can be seen to mean the same thing. Slide 17 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment You must take into account the following when identifying and determining risks/threats facing a business: Physical or geographical location Adjoining properties and businesses Local events (Continued) Slide 18 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment Size of the venue Activities taking place on the premises Number of people on-site Advice from authorities Legal liabilities. Slide 19 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment Risk analysis: Vital in risk identification Is the process of examining identified risk in order understand the totality of each risk in order to use this knowledge as the basis for calculating the risk level each risk presents to the business Is undertaken by the EMC Must be a thorough process Gives rise to disagreement over relevant and important issues. Slide 20 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment ‘Consequences’ and ‘likelihood’: Risk analysis combines: • Likelihood of a risk occurring, with • Consequences of the risk occurring The result: • Classifies the risk • Indicates action to be taken. Slide 21 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment Likelihood may be described as (for example): Almost certain Likely Likelihood Possible Very likely Unlikely (and will almost certainly happen Rare. Likely Consequence Major (e.g. death or disability) Serious (e.g. serious injury or lost time) Minor (e.g. first aid injury) Insignificant (e.g. incident but no injury) Extreme High High Medium High High Medium Medium Unlikely (but could happen at some time) High Medium Medium Low Very unlikely (and might happen only rarely) Medium Medium Low Low (and will probably happen at some time) Slide 22 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment Classification must be done on the basis of: Information about ‘context’ of each risk Personal and venue experience with each risk Previous history relating to the risk Occurrences in similar businesses Anticipated frequency of the ‘risk’. Slide 23 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment ‘Consequences’ of a risk may be labelled: Insignificant Minor Moderate Major Catastrophic. Consequence Likelihood Major (e.g. death or disability) Serious (e.g. serious injury or lost time) Minor (e.g. first aid injury) Insignificant (e.g. incident but no injury) Very likely (and will almost certainly happen Extreme High High Medium Likely (and will probably happen at some time) High High Medium Medium Unlikely (but could happen at some time) High Medium Medium Low Very unlikely (and might happen only rarely) Medium Medium Low Low Slide 24 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment Risk assessment matrix: Used to calculate and display ‘severity of consequences’ Shows rating for each risk in a standard form across the venue: • Numerical form (1 – 10) • Colours (Red = high risk level: Green = low risk level) • Word/letter form (L = Low risk; E = Extreme risk) Highest rated risks must be addressed first. Slide 25 Identify potential threats and risks facing the establishment EMPs should be prepared for: Fire Gas leak Bomb threat Suspicious package Robbery or armed hold-up Other? Slide 26 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMPs: Are the basis for practice and responses to emergencies Must be workplace based – for individual venues Must reflect planning that has been done Must be in writing. Slide 27 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans An emergency is: Unforeseen A threat Something demanding immediate attention. Slide 28 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Standard, non-negotiable requirements when an emergency arrives: Follow and implement workplace EMPs Saving people takes priority over saving property Never put yourself in harm’s way Get assistance; notify others immediately. Slide 29 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles of EMPs: Guide action to be taken Indicate sequence of actions Allocate roles and responsibilities to staff Provide contact details of key personnel and agencies Identify evacuation routes and assembly areas. All EMPs should be evaluated against these criteria. Slide 30 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans There are several topics to address to customise EMPs to the needs of individual workplaces – these include: Preparing site plans – a detailed and grid-referenced site plans showing layout of rooms and location of emergency equipment and support infrastructure Preparing floor plans – showing access points and differentiating between various access options (Continued) Slide 31 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Allocating positions, roles and responsibilities to individual staff for each EMP How people (‘head’) counts will be undertaken at evacuation assembly points to identify whether or not people are missing Providing for guest welfare in the immediate short-term (Continued) Slide 32 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Oraganising media liaison – to enable control of information being given out to the media Preparing flip cards – to optimise compliance with requirements of plans Determining special needs assistance and how it will be provided (Continued) Slide 33 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Obtaining MSDS for all on-site chemicals Preparing a ‘Bomb Threat’ checklist Developing ‘appropriate’ plans: • Addressing identified threats and risks • Allowing flexibility • Incorporating training & drills (Continued) Slide 34 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Creating warning and information protocols • Audible alarms • Public broadcast messages: Code red = Fire Code orange = Evacuation Code yellow = Explosion, person trapped, toxic emission Code purple = Bomb threat Code green = All clear. (Continued) Slide 35 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Creating emergency communications Identifying necessary staff training (Continued) Slide 36 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Planning for evacuations: • Immediate evacuations • Pre-warned evacuations Obtaining feedback from authorities on plans. Slide 37 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to terrorist attack: Notify security Evacuate Shut down power and equipment Notify adjacent properties Maintain communication Allow professionals to do their job. Slide 38 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to an immediate threat: Comply with what is being demanded Notify security Retreat Try to end the situation Note details of offender. Slide 39 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to an assault emergency: Call for internal assistance Give basic first aid Circulate description of attacker Provide location of attacker Implement ‘Respond to medical emergency’ EMP requirements. Slide 40 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to fire: Call emergency services Implement evacuation plan Notify neighbouring businesses and properties Close doors and windows Turn off air conditioning Fight fire – if safe & if trained. Slide 41 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to a gas leak emergency: Call emergency services Turn off or remove ignition sources Notify neighbours Evacuate Open windows & doors Turn off gas – if safe to do so. Slide 42 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to a medical emergency: Call an ambulance Never assume you know the cause Do not move the patient Do not ‘act in hope’ Keep public away Do not comment on the incident to anyone. Slide 43 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to a bomb threat: Stay calm Listen for background noise and caller clues Ask questions and record answers – see Bomb Threat Checklist Do not hang up Advise designated person quickly and quietly Initiate evacuation – never assume it was a hoax. Slide 44 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to a suspicious package: Decide quickly if it is a ‘suspicious package’ situation Do not touch it – leave it where it is Telephone police Move people away – initiate evacuation Turn off possible triggers. Slide 45 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to a hostage situation: Secure the area Notify designated workplace person Communicate information about the situation Implement evacuation Do not try to rescue hostages Never put yourself in danger. Slide 46 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to a chemical spill: Call emergency services and report the situation Provide as much detail as possible Implement evacuation Open windows and doors Prevent access to area Obtain MSDS Contain the spill – if possible, safe to do so. Slide 47 Develop written evacuation/Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to a deranged customer emergency: Attempt to control the situation yourself Be prepared to contact & involve Supervisor &/or Security Remove people to a safe area Restrict access to the area Protect property. Slide 48 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMP – Responding to armed robbery: Comply – do not stall; do not stare at offenders Try to remember offender details Call police as soon as safe and possible Do not talk to anyone – record pertinent details Gather witnesses Close venue. Slide 49 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans EMPs should identify ‘chain of command’ positions for: Chief Warden Deputy Chief Warden Communications Officer Floor or Area Wardens Wardens First Aid personnel Security. Slide 50 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles and responsibilities of Chief Warden: Determine emergency and the action to take Ensure emergency services have been notified Advise Area or Floor Wardens Initiate evacuation Monitor and coordinate responses Brief emergency services on arrival Cooperate with emergency services. Slide 51 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles and responsibilities of Deputy Chief Warden : Carry out duties of Chief Warden – when Chief Warden is absent Assist the Chief Warden as required – where Chief Warden is present. Slide 52 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles and responsibilities of Communications Officer: Ascertain details of emergency Notify relevant internal and external personnel Transmit instructions and directions Record action taken Detail progress of evacuation and responses including problems encountered. Slide 53 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles and responsibilities of Floor or Area Warden: Commence evacuation Implement emergency responses Communicate with Chief Warden Direct action of Wardens Advise Chief Warden of action taken Identify list of people on the premises Confirm evacuees. Slide 54 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles and responsibilities of Warden: Act as Area or Floor warden when required Search areas, rooms, departments Oversee and facilitate evacuation Assist special needs persons Control evacuation assembly area Undertake first attack response, where safe and trained to do so Slide 55 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles and responsibilities of First Aid providers: Report to Warden Assist Warden with mobility impaired and special needs people Render basic first aid Communicate with Area Warden on proposed action and issues arising Record first aid provided. Slide 56 Develop written evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Roles and responsibilities of Security staff: Work as directed by chain of command Close doors and windows; turn off power and gas Remove patrons Control crowds Meet and assist emergency services on arrival Protect assets. Slide 57 Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of plans Requirements of equipment to support EMP implementation: Must be suitable Must be sufficient Must be located at identified locations. Slide 58 Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of plans Possible equipment required: Fire detection devices Installation of devices and wiring to boards Fire protection equipment Fire-fighting equipment. Slide 59 Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of plans ‘Comms’ systems may require acquisition of: Internal communications system Portable comms units Megaphones. Slide 60 Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of plans Emergency lighting may include: Generator Emergency lights in nominated places Battery-powered lights Emergency ‘exit’ signs Emergency ‘evacuation route’ signs. Slide 61 Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of plans A Command or Control centre (or room) should contain: Landline telephone Mobile phones and two-way radios Torches Complete set of EMPs Fax and photocopier Whiteboard. Slide 62 Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of plans First aid requirements may include: Need to be able to deal with multiple casualties Oxygen Beds and cots Chemical showers Defibrillators. Slide 63 Acquire necessary equipment to support implementation of plans Personal protective equipment and clothing required may include: Helmets, masks and goggles Respirators and Breathing Apparatus Batons Gauntlets Steel-capped boots Fire-proof clothing. Slide 64 Locate plans in prominent and necessary positions Evacuation, floor and EMPs should be located: On each floor In every EMP folder In each staff room On the intranet In all Command and Control rooms With each of the emergency services (Continued) Slide 65 Locate plans in prominent and necessary positions With each EMC member With each Chain of Command member Within established in-house training materials So ‘Bomb Threat Checklists’ are provided at each telephone. Slide 66 Locate plans in prominent and necessary positions For guests: Include information in ‘Function kits’ & draft contracts Post information on website Put evacuation posters behind each guest room door Place warning notices in elevators Insert material in the in-room guest compendium. Slide 67 Summary – Element 1 When preparing evacuation policies and procedures: Identify and include relevant stakeholders including emergency services representatives Be aware of the legal obligations attaching to preparing effective plans to respond to foreseeable emergency situations Take time to identify all the threats, risks, hazards and dangers faced by the venue (Continued) Slide 68 Summary – Element 1 Determine ‘likelihood’ and ‘consequences’ for all identified risks and threats Calculate the severity of consequences for all identified risks Begin by preparing plans for the highest rated risk (Continued) Slide 69 Summary – Element 1 Develop written evacuation and emergency plans for all identified risks and threats Establish an internal chain of command (with roles and responsibilities) for staff to respond to emergencies Acquire the necessary resources (systems and equipment) to enable implementation of plans (Continued) Slide 70 Summary – Element 1 Distribute plans and related information throughout the venue for staff and guests Provide plans to emergency services for their information. Slide 71 Prepare for evacuation situations Performance Criteria for this Element are: Inform staff in relation to evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Test emergency and evacuation systems and equipment Train staff in emergency and evacuation procedures (Continued) Slide 72 Prepare for evacuation situations Undertake initial evacuation drill Undertake on-going evacuation drills. Slide 73 Inform staff in relation to evacuation plans and EMPs To ensure staff understand the evacuation/ plans and EMPs: Use dedicated sessions: • Staff information sessions • Staff briefings • Staff Question and Answer sessions • Feedback sessions (Continued) Slide 74 Inform staff in relation to evacuation plans and EMPs Inspect items • Tour of premises • Identify and explain what items can and cannot do • Handle, use and become familiar with items • Name parts of the item or equipment (Continued) Slide 75 Inform staff in relation to evacuation plans and EMPs Identify areas: Identify evacuation assembly areas – primary and secondary Describe factors likely to make evacuation assembly points unusable Tour venue to identify evacuation routes – primary and secondary. Slide 76 Test emergency and evacuation systems and equipment Systems, equipment and protocols that are part of an EMP must be tested: When installed On a regular, ongoing basis. Slide 77 Test emergency and evacuation systems and equipment Systems and equipment are tested to: Verify they work as expected Ensure they deliver the results required or expected Show staff how they work Identify where attention, service, replacement is required Discharge duty of care obligations. Slide 78 Test emergency and evacuation systems and equipment Always advise emergency services of intention to conduct workplace tests – tests can include: Testing communication systems and units Testing alarm systems Testing fire detection systems and equipment (Continued) Slide 79 Test emergency and evacuation systems and equipment Testing fire suppression & fire-fighting equipment Trialling evacuation routes Trialling evacuation assembly points. Slide 80 Train staff in emergency and evacuation procedures Staff training can include: In-house training: • May be mandatory • May be delivered by an external provider • Must include theory and practice • Must be competency-based (Continued) Slide 81 Train staff in emergency and evacuation procedures Off-site training: • Using an external, purpose-built facility Role plays: • To reflect workplace situations & scenarios to the best extent possible • At different times • Must feature a debriefing session. Slide 82 Train staff in emergency and evacuation procedures Chain of Command positions should receive specialist training – Chief Warden and Deputy Chief Warden: Decision making Leadership Communication Delegation Interacting with emergency services Knowledge of emergency services. Slide 83 Train staff in emergency and evacuation procedures Training for a Communications Officer may include: Operation of all communication equipment, systems and units Communications protocols Options for communicating in emergency situations Knowledge of constraints and limitations. Slide 84 Train staff in emergency and evacuation procedures Training for Wardens may feature: Knowledge about their roles and responsibilities Relationships with other chain of command personnel Venue knowledge Search and rescue skills. Slide 85 Train staff in emergency and evacuation procedures Training for First Aid providers should feature ‘advanced’ training : Treating burns Treating puncture wounds Dealing with stressed patients Operating a defibrillator Giving oxygen Working with emergency services. Slide 86 Undertake initial evacuation drill The ‘initial’ drill is vital to: Test the plan Trial evacuation routes Time the evacuation Enable staff practice/experience Discharge duty of care obligations Observe practice – to determine necessary changes. Slide 87 Undertake initial evacuation drill Requirements and concerns when conducting an initial drill: Advertise the drill to • Staff • Customers • Emergency services Scheduling – daylight; week day (Continued) Slide 88 Undertake initial evacuation drill Planning: • Training has been delivered to staff • Staff understand their responsibilities • A simple evacuation scenario is identified • The initial drill must focus on evacuation – not other responses allied to an evacuation (Continued) Slide 89 Undertake initial evacuation drill • Must include development of checklists – to assist observation and recording of action taken • Must appoint ‘observers’ – to help with analysis of the evacuation/drill • Must ensure the EMP as written is implemented – the aim is to test the plan, not to test the ability of staff to respond to ‘unforeseen circumstances’. Slide 90 Undertake on-going evacuation drills On-going drills must be conducted to: Discharge duty of care obligations Involve new staff Determine effectiveness of plans Identify workplace changes impacting on plans. Slide 91 Undertake on-going evacuation drills Keys in participating in drills: Attend all drills Take them seriously Follow EMP directions Use designated protective equipment and clothing Take notes. Slide 92 Undertake on-going evacuation drills On-going drills should address: Increasing complexity A variety of scenarios Changing basic aspects – time, day of the week (Continued) Slide 93 Undertake on-going evacuation drills Different sections of the building Involvement of all staff Conducting regular drills Adequate scheduling in advance of drills (Continued) Slide 94 Undertake on-going evacuation drills Liaison with emergency services Realism – to the greatest extent possible Use of observers A debriefing. Slide 95 Summary – Element 2 When preparing for evacuation situations: Inform staff about evacuation and EMPs using a variety of communication options focussing on the acquisition of knowledge and gaining of first-hand experience Trail established plans Test systems, technologies, equipment and protocols (Continued) Slide 96 Summary – Element 2 Record the outcomes from trials, tests and drills for use in debriefings and revisions to plans Train staff as required by the plans and supporting equipment, systems and protocols required to implement them Provide speciality training to individual staff as required by their role and position when an emergency and the need for evacuation occurs (Continued) Slide 97 Summary – Element 2 Schedule, plan and undertake an initial evacuation drill Revise plans and other arrangements on the basis of the outcome of the initial drill Schedule, plan and undertake ongoing evacuation drills varying the times, the focus, the parameters and the context of each. Slide 98 Update evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Performance Criteria for this Element are: Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel Inspect establishment to identify emerging factors that impact on the evacuation and Emergency Management Plans (Continued) Slide 99 Update evacuation and Emergency Management Plans Revise evacuation and Emergency Management Plans on the basis of feedback Disseminate revisions to evacuation and Emergency Management Plans. Slide 100 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel EMPs: Must be regarded as ‘living’ documents Require regular, organised communication between key personnel Rely on EMC to arrange necessary communication. Slide 101 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel Keys to effective communication: Hold regular (monthly, minimum), formal meetings: • Giving 2 weeks notice • Identifying date, time and venue • With an agenda • Minutes should be taken (Continued) Slide 102 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel Involve emergency services – as appropriate: • Advise them in advance • Encourage them to attend • Invite them to nominate items and issues for discussion and inclusion on the agenda (Continued) Slide 103 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel Determine who should attend • Wardens – all types • First aid; Comms; Security; Maintenance • Emergency services • Department heads • EMC members • Co-opted individuals (Continued) Slide 104 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel Allocate meeting roles: • Chairperson • Secretary • Communications officer (Continued) Slide 105 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel Record meetings: • Secretary takes ‘minutes’ • Minutes must be ‘passed’ at next meetings • Distribute to all attendees and stakeholders • File for future reference • File all documents presented to the meeting (Continued) Slide 106 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel Identify issues to be addressed – may include: • Reviews of drills • New threats and hazards • Draft responses to threats and hazards • Feedback from relevant personnel and stakeholders (Continued) Slide 107 Identify schedule for communication between relevant personnel New drills New equipment, systems and technology New or revised protocols to address changed circumstances Training Workplace inspections. Slide 108 Inspect to identify factors impacting on plans Physical inspections of the workplace are essential to identify changed conditions and threats. Inspections should involve: Management EMC OHS agencies Emergency services. Slide 109 Inspect to identify factors impacting on plans Planning inspections should address: Scheduling of inspections to reflect need Notification to participants Provision of relevant information Creation and distribution of checklists Determination of focus and scope. Slide 110 Inspect to identify factors impacting on plans When conducting the workplace inspection: Inspect all areas Address all identified requirements Inspect all evacuation routes Inspect all evacuation assembly areas (Continued) Slide 111 Inspect to identify factors impacting on plans Test systems and equipment Take notes and photographs of issues Hold a debriefing session. Slide 112 Revise plans on the basis of feedback EMPs must be revised when a need arises – this can be: After an actual workplace incident According to venue policies When ordered to do so (Continued) Slide 113 Revise plans on the basis of feedback After significant physical changes to the workplace Following analysis of drills To address significant changes to relevant workplace characteristics – practices, trade, facilities When a legitimate concern has been raised. Slide 114 Revise plans on the basis of feedback EMP revisions may address: New plans to address new threats Revised plans to address changed threats New protocols New signage and or maps (Continued) Slide 115 Revise plans on the basis of feedback Changes to roles and responsibilities New or revised evacuation routes and assembly points Different sequence of action to be taken New format for plans (Continued) Slide 116 Revise plans on the basis of feedback New, more or different equipment New or revised training and drills Revised budget New terminology Revised version control protocols. Slide 117 Disseminate revisions to plans Revisions to EMPs must be communicated to relevant others: Inserting revised pages into existing plans Updating EMP folders Changing workplace posters and signage Integrating changes into staff training (Continued) Slide 118 Disseminate revisions to plans Notifying emergency services Updating website and intranet Changing staff handbooks Updating policy and procedure manuals Holding staff meetings and briefings Slide 119 Summary – Element 3 When updating evacuation plans and EMPs: Develop a schedule of meetings between key emergency personnel Record the discussions and decisions of meetings of emergency personnel Develop a schedule for regular workplace inspections focussed on identifying issues impacting on or verifying emergency and evacuation plans (Continued) Slide 120 Summary – Element 3 Conduct scheduled workplace inspections using established checklists to guide activities and record findings Use feedback from stakeholders and results of workplace inspections to revise existing evacuation and emergency plans and create new ones, where required Communicate changes to plans and new plans to staff and guests Update and circulate evacuation and emergency plans to stakeholders. Slide 121 Conduct evacuations Performance Criteria for this Element are: Identify and assess need for evacuation Initiate evacuation in-line with evacuation plans and Emergency Management Plans (Continued) Slide 122 Conduct evacuations Implement evacuation in compliance with evacuation plans and Emergency Management Plans Respond to unforeseen circumstances and situations and hazards arising. Slide 123 Identify and assess need for evacuation Initiating an evacuation must be a reasoned decision: It is sometimes not an easy decision to make – important factors are: • Decide quickly • Err on the side of caution • Use common sense • Involve others in the decision. Slide 124 Identify and assess need for evacuation ‘Obvious’ decisions requiring evacuation are instances where people are at risk based on evidence at the time: Visible evidence Olfactory evidence Auditory evidence. Slide 125 Identify and assess need for evacuation When determining whether to initiate an evacuation in a situation where the decision is not obvious: Is there a genuine threat? Can you identify the cause? Can the threat be dealt with in-house? (Continued) Slide 126 Identify and assess need for evacuation Does there appear a need for emergency services to be involved? Are people under immediate threat or at immediate risk? Do things look as if they are going to get worse? What do other more experienced staff think? Slide 127 Identify and assess need for evacuation House protocol may require, at least, activation of a ‘warning alarm’ as soon as threat is detected. ‘Best advice’ is to activate this alarm if unsure, because: It notifies others and triggers a response It is not seen as over-reacting It can be easily upgraded It may be the most appropriate response in certain situations. Slide 128 Identify and assess need for evacuation Activate the ‘evacuate now’ alarm when: An obvious and credible threat has been identified The potential for greater impact from the cause exists You believe the situation cannot be contained in the immediate short-term. Slide 129 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans All EMPs must be implemented and followed when an emergency is identified – four basic requirements are: Activate ‘evacuate now’ alarm Notify emergency services Notify internal personnel Notify and assist patrons. Slide 130 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans Activating ‘evacuate alarm’ now may require: Pushing a button Breaking glass and following instructions Verbal notification to another person requesting they activate the alarm. Slide 131 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans Notifying emergency services: Never assume someone else has alerted the emergency services Plan and prepare: • Know your EMPs • Get advice from supervisor • Know where emergency telephone lists are • Pay attention to training and drills. Slide 132 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans When telephoning emergency services to report an emergency or to request assistance – call the emergency number: State you want to report an emergency Let the operator guide you regarding information required Speak clearly & calmly Do not hang up. Slide 133 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans Emergency services operators will want information about: Location of emergency Type of emergency Numbers involved and impacted Casualties and injuries. Never delay calling just because you do not have all the above information Slide 134 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans When reporting an emergency within your workplace: Follow house EMP protocols Identify self, position and location State you are reporting an emergency Describe the emergency (Continued) Slide 135 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans Give location of emergency Identify the extent of threat Identify numbers impacted Describe relevant factors State action you believe is needed Stay until told to hang-up and leave. Slide 136 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans Providing assistance to patrons during emergency may involve: Telephone designated numbers and rooms Visit nominated areas to verbally advise patrons Use a megaphone Knock on guest rooms doors Inspect and check nominated areas (Continued) Slide 137 Initiate evacuation in accordance with plans Escort individuals Show people where to go Assist special needs people Urge people to evacuate Tell people to leave personal property behind Place safety of people above protecting assets or saving pets. Slide 138 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Determine relevant environmental factors applying at the time of an emergency to help determine best response: Determine wind Verify threat type Identify location Count people involved Consider time, staff, venue resources. Slide 139 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans When implementing an evacuation plan or EMP: Safety of people must be the priority Plans must guide action Discharge assigned responsibilities (Continued) Slide 140 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Never make the situation worse Seek greatest good for greatest number Follow chain of command direction Help others Put on safety clothing and equipment. Slide 141 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Close down items, systems and equipment Apply skills to avoid panic and maintain calm: • Do not panic • Speak clearly with authority • Do not yell • Exude confidence (Continued) Slide 142 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Provide clear instructions: • Use simple words • Give brief commands • Use sign language • Repeat yourself • ‘Show and tell’ (Continued) Slide 143 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Secure premises – when safe and appropriate: • Remove property from threat • Rescue personal belongings • Prevent access to area • Stand guard (Continued) Slide 144 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Activate Command, Control and Communications room (CCC room): • Arrange furniture and equipment • Set up, test and verify systems • Distribute comms units • Advise emergency services of CCC room (Continued) Slide 145 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans • Capture required internal documentation • Contact relevant personnel • Record action • Plan responses (Continued) Slide 146 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Advise CCC room: • Report location • Advise action taken • Notify progress • Notify changed circumstances • Request assistance (Continued) Slide 147 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Provide first response: • When safe to do so • If trained • Avoid responses to designated situations (Continued) Slide 148 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Prepare for arrival of emergency services: • Remove vehicles • Remove obstructive items • Usher people away from arrival zone (Continued) Slide 149 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Assist emergency services on arrival: • Meet services on arrival • Provide relevant information and venue knowledge • Follow their directions • Assist and support their efforts • Get out of their way if you cannot help. Slide 150 Implement evacuation in compliance with plans Questioning CCC directions: Never blindly obey all directions given Explain reason for not complying or not wanting to comply Never put self or others at risk. Slide 151 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising You must notify ‘changed circumstances’ quickly to the chain of command - ‘changed circumstances’ include: Changed atmospheric conditions Numbers involved New threats Response results and failures Patron behavior. Slide 152 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising Responses to unforeseen circumstances: Do not put self in danger Use common sense Act swiftly Adapt existing EMPs Seek approval for proposed action Notify CCC about action. Please Note Slide 153 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising When responding to an emergency situation for which no EMP exists: Notify others including emergency services Assess situation Adapt existing EMP if possible Involve others Please Note (Continued) Slide 154 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising Prioritise the safety of people Contain the situation – as distinct from ‘responding’ to it Provide constant communication about the situation. Please Note Slide 155 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising If people are trapped and or injured: Do not make situation worse Communicate details to chain of command Reassure people Provide basic first aid Please Note (Continued) Slide 156 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising Secure the area Clear rubbish and debris Look for ‘live’ wires Never enter a confined space. Please Note Slide 157 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising When responding to a ‘falling debris’ situation: Advise chain of command about situation Retreat to safety Take shelter Prevent access Never risk personal safety. Please Note Slide 158 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising When faced by a ‘lack of information’ situation: Take action to get information: • Observe, listen, smell • Ask • Use observers • Monitor systems for information Use last known information as basis for response Pass on new information to chain of command. Slide 159 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising When faced with blocked (or unusable) evacuation routes: Remove obstructions – if safe, ask others to help Use secondary routes Advise chain of command Use your venue knowledge to determine an alternative. Slide 160 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising Where evacuation assembly points are unsafe: Using secondary points Escort evacuees Notify chain of command Reassure evacuees. Slide 161 Respond to unforeseen circumstances, situations and hazards arising When faced with a situation where systems or equipment do not operate as expected: Notify chain of command Seek replacement item Persist with what is available Leave the area if there is total failure of an item or a system. Slide 162 Summary – Element 4 When conducting evacuations: Determine type and extent of the emergency ‘Act quickly and make prompt decisions Be prepared to involve others in making an evacuation decision (Continued) Slide 163 Summary – Element 4 Always err on the side of caution Never put yourself in danger Notify emergency services and designated internal personnel (Continued) Slide 164 Summary – Element 4 Activate alarms Follow EMPs Put the safety of people above the security of property and assets (Continued) Slide 165 Summary – Element 4 Use common sense Discharge your responsibilities under the applicable EMP Assist others where possible (Continued) Slide 166 Summary – Element 4 Maintain constant communication with the chain of command Communicate changed, changing and unforeseen circumstances to chain of command. Slide 167 Review plans after actual implementation Performance Criteria for this Element are : Debrief with staff and wardens Debrief with emergency services Revise evacuation plans and EMPs on the basis of feedback (Continued) Slide 168 Review plans after actual implementation Disseminate revisions to evacuation plan and EMP Provide for amended training and drills on the basis of revised evacuation plan and EMP. Slide 169 Debrief with staff and wardens All emergency situations merit a debriefing. Debriefing must be planned: Identifying dates, time and venue Identifying participants – internal and external Preparing agenda (Continued) Slide 170 Debrief with staff and wardens Advising participants of need to attend Arranging the forum Reviewing on-site intelligence. Debriefing in session Slide 171 Debrief with staff and wardens The ‘right atmosphere’ must be created for debriefing sessions: Must be a search for truth Aim must be to determine cause, not allocate blame Must be a ‘no blame’ policy in effect Honesty must not equal loss of job. Slide 172 Debrief with staff and wardens Emergency situations can result in the need for an ‘Incident Report’ or similar to be completed by all staff who were involved in the incident. Reports can be: Verbal Written Combination of both. Slide 173 Debrief with staff and wardens Verbal incident reports: Staff answer questions put to them by management and EMC ‘Supposition’ must be avoided – facts only Are quick and relatively simple to implement Usually involve a site inspection May require a supporting written report. Slide 174 Debrief with staff and wardens Written ‘Incident Report’ forms may address: Facts of the emergency – date, time, location Names of those involved – staff, victims, casualties Cause Evaluation of response Suggestions for the future. Complete this report as soon as possible after the event. Slide 175 Debrief with staff and wardens Written incident reports may be needed to: Document the facts Comply with internal policy Support an insurance claim Learn from the incident. Slide 176 Debrief with staff and wardens Objective 1 = Define the situation: Describe it in detail Locate it Name those involved List resources deployed Identify causes Determine duration. Objective 1 Slide 177 Debrief with staff and wardens Objective 2 = Identify responses: First and follow-up responses Response to unforeseen circumstances Name of respondents Which alarms were activated and when What in the EMP worked well and what did not Environmental and situational factors impacting responses Communication undertaken. Objective 2 Slide 178 Debrief with staff and wardens Objective 3 = Evaluation of plans: Consider logistics Consider training and drills Consider ‘Command and control’ Consider factors impacting the incident Objective 3 (Continued) Slide 179 Debrief with staff and wardens Identify positive elements of the plans Identify aspects for revision Determine the extent to which the plan met the actual event or incident Determine why sub-standard performance occurred. Objective 3 Slide 180 Debrief with staff and wardens Objective 4 = identifying lessons learned, such as: Need to revise plans Need to develop new plans Need to alter training and drills Need to buy more/different resources Objective 4 (Continued) Slide 181 Debrief with staff and wardens Need for more or different workplace inspections Action or planning to prevent recurrence Need to change chain of command roles and responsibilities Need to amend evacuation routes and assembly points Suggestions to enhance or optimise response. Objective 4 A report is optional. Slide 182 Debrief with staff and wardens The staff-warden debriefing is not the forum to discuss: Individual performance and compliance with EMP requirements Recognition of effort and or achievement Legal issues (Continued) Slide 183 Debrief with staff & wardens Media attention Budget Loss of property Operational issues Insurance. Slide 184 Debrief with emergency services A debriefing must occur with emergency services after every evacuation or emergency ensuring: Truth and honesty from the venue All involved agencies are represented – single agency debriefings, or multiple agency debriefing? EMC members attend (Continued) Slide 185 Debrief with emergency services Findings from internal debriefing are available Reports from emergency services are available A tour of the site can be undertaken if required Coverage of the EMPs in place & used Responses by venue Initial notification of the incident to emergency services Feed back from emergency services on relevant topics. Slide 186 Debrief with emergency services Facts are compared with reports and internal debriefing Minutes and notes are taken Venue provides feedback to emergency services regarding their performance Coverage of how victims and casualties were treated A final report if prepared. Slide 187 Revise plans on the basis of feedback In relation to EMPs standard practice is: Revise EMPs on basis of feedback and reviews where there is a need to do so – never ignore the need for change Review regularly – every 12 months Review after significant workplace change Involve emergency services. Slide 188 Revise plans on the basis of feedback Before commencing revision of EMPs: Have a sound knowledge of the EMPs Gain a comprehensive knowledge of changed factors, conditions and other issues warranting a change in EMPs Know the amendments required by agencies, authorities or other stakeholders. Slide 189 Revise plans on the basis of feedback With EMPs, do not change what does not need changing – legitimate changes may relate to: Operational changes within plans ‘Cosmetic’ and ancillary changes to plans. Never ignore a legitimate need for change. Slide 190 Revise plans on the basis of feedback Operational changes to EMPs may include: More detail – to a variety of issues, such as: • Scope; purpose; action; logistics Additions, deletions and or amendments to steps, SOPs and or instructions Alterations to personnel and roles and responsibilities (Continued) Slide 191 Revise plans on the basis of feedback Integration of new or different equipment into plans New or revised evacuation routes New or revised evacuation assembly points Amendments to sequence of activities Provision of links to other EMPs. Slide 192 Revise plans on the basis of feedback ‘Cosmetic’ and ancillary changes to EMPs could include: Clearer layout Clearer fonts and larger font size Revisions to service and maintenance support Revision to membership of internal emergency groups or committees Re-scheduling of emergency group meetings Development of more and or different supporting materials. Slide 193 Revise plans on the basis of feedback Changes to EMPs may be subject to ‘version control’ protocols: To identify the version of the document being used To identify the date the document takes effect To identify who prepared the revised document To identify the file name for the update To indicate when the revision must be reviewed. Slide 194 Revise plans on the basis of feedback When updating EMPs remember to: Remove out-of-date pages when inserting new pages Double-check plans to ensure they are complete Archive all ‘out-of-date’ documents. File Identifier Name Date created Version no (eg V1) Date of next revision Version Control Slide 195 Disseminate revisions to plans Items potentially requiring revision and dissemination include: Site maps Site plans Training notes Evacuation-related public signage and posters (Continued) Slide 196 Disseminate revisions to plans Staff handbook Individual EMPs Website Intranet SOPs Checklists, forms, flip cards. Slide 197 Disseminate revisions to plans Distribution of EMPs: May be governed by a ‘distribution schedule’ May require distribution to: • Emergency services and nominated authorities • Head office • Insurers • Internal staff • Nominated physical locations. Slide 198 Disseminate revisions to plans Changes to EMPs should be accompanied by explanation: Why changes were necessary Who recommended the changes Of the details of the changes Of the impact of the changes Of timing Of support available to staff for the changes. Slide 199 Provide for amended training and drills on basis of revisions Amended training and drills: Are required to support all revised EMPs Should be recorded Can include on-site, one-off training Can feature external agencies or institutions May use ongoing, workplace training. Slide 200 Provide for amended training and drills on basis of revisions Drills following EMP revisions could require: Introduction of new drills into the established schedule for drills Amendment to scheduled drills A new focus for drills Involvement of different emergency services Observers A debriefing session. Slide 201 Summary – Element 5 When reviewing evacuation plans and EMPs after actual implementation: Require staff to complete internal reports regarding the emergency situation and use these as part of the basis for debriefing sessions Actively plan and prepare for the debriefing sessions – set dates and times, venue, invite participants, develop agenda Participate actively and honestly in all debriefing sessions (Continued) Slide 202 Summary – Element 5 Debrief with internal staff and external authorities, agencies and emergency services Record minutes of debriefing sessions Aim to identify causes and learn lessons for the future rather than allocate blame (Continued) Slide 203 Summary – Element 5 Review and revise evacuation plans and EMPs on the basis of feedback, direction and or recommendations and suggestions as a result of what happened during the actual incident Revise all items and documents supporting the evacuation plans and EMPs – EMPs are not independent, stand alone documents Advise stakeholders of changes to the evacuation & EMPs and explain why the changes were necessary (Continued) Slide 204 Summary – Element 5 Distribute hard copy revisions to identified internal and external stakeholders Provide supporting training and drills regarding changes to evacuation plans and EMPs. Slide 205