INDONESIA POSITION, ROLE & STRATEGY IN

UMM TEAM – MALANG
JUNE - 2008
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
Country Description
Impact of Climate Change in Indonesia
Source of Green House Gasses
Working Group on Climate Change
Legal & Regulatory Framework
National Development Planning
Program for Mitigation
Technology Requirement
Financing the Climate Change Strategy
Energy status & Alternative Energy
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
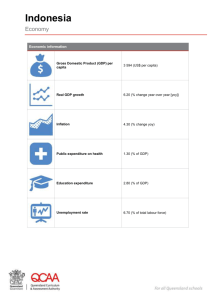
Indonesia is located in the tropical belt, is the largest and widest archipelago country in the world, consist of 17,508 big and small islands, there are 5 big islands : Sumatera, Java, Borneo,
Celebes and West Irian
There are two season in Indonesia , May to
October is dry season and October to April is rainy season
Second world’s longest coast line (81.000 km)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Based on demography survey in 2000, the total population was 206 million, representing the fourth largest country in the world
With the population growth rate was 1,49 percent.
Estimate population in 2006 was 220 million.
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Climate Change Effects
Sea Level Rise
Ocean Warming
Increased
Temperature
Increased Rainfall
Increased
Evaporation
Increased Tropical
Storms
Impacts on Indonesia
Disappearing Small Islands
Salt Water Intrusion
Decline in Fisheries Harvest
Loss of Biodiversity
Increased Fire Risk
Increased Disease Risk, Range
Floods and Land Slides
Changes in Planting Season
Drought, Food Security
Transport Vulnerability
Food and Water Scarcity
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Deforestation rate (2000 – 2005) -> 2,8 Million
Ha/year & Forest fire (West Borneo in 2006) -> loss of 91 Million USD (source: www.beritabumi.or.id
)
Flood (February 2007) result in 8 Billion USD loss
(source: www.detikfinance.com
)
Landslide -> 80 Million USD/year
Human health : Dengue, Malaria, Diarrhea
Rise of Sea Level
Drought (Cirebon District in 2006) result in loss of
8.6Million USD (source: http://greenpena.blogspot.com
)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
The disappearing of small Island -> within 2005 –
2007, 24 small islands disappear, the location:
3 island in Nanggroe Aceh Darussalam (NAD)
3 island in Papua
5 island in Riau
2 island in west sumatera
7 island in the coastal area of Jakarta
( source: Ministry of Oceanary & Fishery
)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
The availability of water is very dependent on the climate, due to the limited supply of water (only covers about 37% of urban population and 8% of rural population) causing people and industries use deep groundwater resources land subsidence that creates areas vulnerable to flood and salt water intrusion
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Jakarta
Coastal
Region in 2050
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
During El Nino years (1994, 1997,2002,
2003, 2004 and 2006) shown that 8 reservoirs in Java have produced electricity below normal capacities
During El Nino 1997 has caused serious problems to coral reef ecosystems where
90-95% of coral reefs at the depth of 25m have experienced coral bleaching
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Poorest nations and poor groups are likely to be hardest hit by the effects of climate change as they:
rely heavily on climate change-sensitive sectors (agriculture and fisheries)
Are less able to respond (lack of human, institution and financial capacity)
Achievement of the National Development goals and
Millennium Development Goals (MDG) – see table
Changes in mean climate, variability, extreme events and sea level rise
Impact on poverty and national development planning targets
Impact on the eight MDG
Increased temperature and changes in precipitation reduce agricultural and natural resources
Lowered industrial output and labour productivity, high inequality, impacts on trade, and fiscal and macro-economic growth, and povertyreducing effects
Change in precipitation, run-off and variability leads to greater water stress
Increased incidence or intensity of climate related disasters lead to damage to assets and infrafstructure
Reduced productivity and security of poor people’s livelihood assets, and reduced access for the poor to their livelihood assets
Temperature, water and vegetation changes contribute to increase prevalence of disease
Less effective coping strategies among the poor, and increased vulnerability of poor people
1.
2.
3.
Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger
Food security jeopardized, more intense disasters threaten livelihood
Achieve universal primary education
More vulnerable livelihoods means more children engaged in employment; infrastructure damage from disasters
Promote gender equality and empower women
Women make up twothirds of world’s poor and are more adversely impacted by disasters.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Reduce child mortality
Children more vulnerable to malaria and other diseases, which are spread more widely by climate change
Improve maternal health
Pregnant woman particularly susceptible to malaria
Combat HIV/ AIDS, malaria and other diseases
Increase prevalence of mosquito-bone diseases
Ensure environmental sustainability
Climate change indication of unsustainable practices. Move toward more energy-efficient model of consumption
Promote global Partnerships
Wider forums must acknowledge the role of climate change in impacting MDGs
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Based on Workshop on Climate Change and Health in South East Asian Countries :
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Transportation
Industry
Forestry
Agriculture
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
EXISTING INDONESIAN WORKING GROUP ON
CLIMATE CHANGE
Mitigation Adaption Post Kyoto Transfer of Technology Financial Mech.
Forestry Energy
Energy: Industry Transportation Agriculture Forestry Ocean Waste
Working Group on Climate Change Activities: to undertake qualitative policies and measures that lead to the our response to Climate change, i.e. to stabilize concentration of GHGs at the safe level.
Working Group of Transfer of Technology Activities: to further derivation and enrichment the previous project and to prioritize technology needs, and capacity building to assess technology needs, modalities to acquire and absorb them.
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Ministry of Environments
Ministry of Research and Technology
Agency for the Assessment and
Application of Technology (BPPT)
Governments Departments: Energy &
Mineral Resources, Forestry, Agriculture, etc.
Meteorology and Geophysical Agency
Indonesia State Electricity Company
Private Sectors
Universities
NGOs
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Presidential Rule No.5, 2006 regarding National
Energy Policy, asp. on energy mix by the year
2025
Presidential Decree No.10, 2005 on energy efficiency
Presidential Decree no. 1, 2006 regarding
Biofuel Utilization Program
Act No. 6/1994 which stipulate the ratification of
UNFCCC
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Act No. 23/1997 regarding Environmental
Management
Ministrial Decree of Forestry No. 14/04 regarding Afforestation/Refforestation Project
Ministrial Decree of Environment no. 53/03 regarding Ministry of Environment as National
Committe of Climate Change
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Ministrial Decree of Environment no. 206/05 regarding Ministry of Environment as the
Indonesia DNA
Government Regulation no. 4/2001 concerning
Controlling Environmental Damages and or
Pollution Associated with Forest and Land Fire
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
LEGAL & REGULATORY FRAMEWORK FOR INDONESIA POWER SECTOR, INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT & IMPLEMENTATION
DESCRIPTION PT. PLN (PERSERO) INDONESIA POWER SECTOR LEGAL & REGULATORY FRAMEWORK
INFRASTRUCTURE
DEVELOPMENT LEGAL &
REGULATORY FRAMEWORK
POLICY,
STRATEGY,
NATIONAL
TARGET, AND
NATIONAL PLAN
DERIVATION
ARTICLE 5
POINT 1&2
ARTICLE 5
POINT 1
ELECTRICITY LAW
(GOVERNMENT OF INDONESIA LAW NO. 15 / 1985)
<A>
INFLUENCED BY
NATIONAL
ELECTRICITY
GENERAL PLAN 2006-
2026
( MEMR DECREE NO.
2270K/31/MEM/2006)
<C>
ARTICLE 2
POINT 2
MODIFICATION OF
GOVERNMENT REGULATION
NO 10/1989 SUBJECT,
SUPPLY AND UTILIZATION OF
ELECTRICITY
(GOVERNMENT REGULATION
NO.3/2005)
<B>
NATIONAL ENERGY POLICY
(PRESIDENTIAL REGULATION NO.5/2006)
<D>
ASSIGNMENT TO PLN FOR ACCELERATION OF
COAL FIRED POWER PLANTS DEVELOPMENT
(PRESIDENTIAL REGULATION NO. 71/2006)
<E>
COAL FIRED
POWER PLANT
CRASH
PROGRAM ESTABLISHMENT OF COORDINATION TEAM
FOR POWER PLANTS DEVELOPMENT.
(PRESIDENTIAL REGULATION NO,72/2006)
<F>
COOPERATION
BETWEEN
GOVERNMENT AND
ENTERPRISES FOR
DEVELOPMENT OF
INFRASTRUCTURE
(PRESIDENTIAL
REGULATION NO67/
2005)
<P>
CONSIDERING
SUPPLY AND UTILIZATION OF BIOFUEL AS
ALTERNATIVE FUEL
(PRESIDENTIAL INSTRUCTION NO.1/2006)
<G>
LIQUEFIED COAL’S SUPPLY AND ITS
UTILIZATION
(PRESIDENTIAL INSTRUCTION NO.2/2006)
<H>
RENEWABLE
ENERGY
IMPLEMENTING
RULES,
PROCEDURES
AND PLAN
·
·
SUPPLY AND DEMAND
BALANCE
INVESTMENT
REQUIRMENT
PROJECT LIST
·
LEGALIZATION OF
MODIFIED PLN ELECTRICITY
SUPPLY GENERAL PLAN/
RUPTL 2006-2015
(MEMR DECREE NO. 2923K/
30/MEM/2006)
<I>
POWER PURCHASE AND TRANSMISSION RENTAL
PROCEDURE OF POWER
PURCHASE AND/OR
TRANSMISSION RENTAL
ELECTRICITY SUPPLY
FOR PUBLIC
(MEMR REGULATION
NO.001/2006)
<J>
GUIDELINES OF THE
ISSUANCE OF
ELECTRICITY BUSINESS
LICENSE FOR
TRANSMISSION
TRANSPROVINCE OR
CONNECTED TO NATIONAL
GRID
(MEMR REGULATION NO.
010/2005)
<L>
CRITICAL AREA
LIST OF POWER
SYSTEMS (AREAS)
IN CRITICAL
CONDITION
(EMERGENCY
CONDITION)
(MEMR REGULATION
NO. 206-12/40/600.2/
2006)
<M>
LIST OF POWER
SYSTEMS (AREAS)
IN CRITICAL
CONDITION
(EMERGENCY
CONDITION)
(MEMR
REGULATION NO.
482-12/40/600.2/
2006)
<N>
RENEWABLE ENERGY
MEDIUM SCALE
MEDIUM SCALE OF
RENEWABLE ENERGY
POWER PLANT
(MEMR REGULATION
NO. 002/2006)
<O>
RISK
MANAGEMENT
GUIDELINES FOR
INFRASTRUCTURE
DEVELOPMENT
(MINISTRY OF
FINANCE
REGULATION
NO.38/PMK.01/2006)
<Q>
IMPLEMEN-
TATION
POJECT DEVELOPMENT
AND IMPLEMENTATION
TO OBTAIN GOVERNMENT
SUPPORT/ GUARANTEE
Minyak
Bumi
51.66%
PRIMARY ENERGY MIX 2005
Panas Bumi
1.32%
Tenaga Air
3.11%
Gas Bumi
28.57% t
1
?
NATIONAL ENERGY TRAJECTORY
• Enhancing energy security & mitigating CO2 emissions: to secure strategic reserve, to improve efficiency in energy production & use, to increase reliance on non fossil fuels and to sustain the domestic supply of oil/gas (slower growth in fossil fuel-demand in oil/gas imports and in emissions).
• Proposed energy technology use, diffusion and deployment, increasing clean energy technologies.
• Energy infrastructures and its time frame.
• Etc.
Presidential Rule
No. 5/2006
Batubara
15.34% t
2
?
t
3
?
THE NATIONAL ENERGY ISSUES
What is the
Sustainable
Road Map? t
25
National Energy Mix Target 2025
(PERPRES NO. 5/2006)
Minyak Bumi 20%
≤
Gas Bumi
30%
Bahan Bakar Nabati
(Biofuel) 5%
Others
≥
≥
Batubara 33%
≥
Surya, Angin 5%
Batubara yang
Liquefaction) 2%
≥
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Integrating Climate Change to National
Development Planning Process
INPUT DOCS
BRIDGING DOCS
Strategic Nat. Res & Env.
Assessment (SNREA) for 2010-2014 NMTDP
2010-2014
National Mid-Term
Development Plan
(NMDPT)
National
Communication,
National Sector
Strategy, etc.
Climate
Change
Program
MID TERM
DEVELOPMENT
PLAN
2004-2009
GOV WORK
PLAN
2008
GOV WORK
PLAN
2009
GOV WORK
PLAN
2010
MID TERM
DEVELOPMENT PLAN
2010-2014
GOV WORK
PLAN
2011
GOV WORK
PLAN
2012
GOV WORK
PLAN
2013
GOV WORK
PLAN
2014
GOV
FUNDING
LOAN
FUNDING
GRANT
COMM/
PRIVATE/
NGO/CSR
CDM
DEBT
SWAP
INDONESIA
“NATIONAL ACTION PLAN
IN FACING CLIMATE
CHANGE”
MINISTRY OF ENVIROMENT
“The Strategy of Carbon
Absorption Potential
Improvement and Strategy of Carbon Emission
Reduction”
MINISTRY OF SOCIAL
WELFARE
CLIMATE CHANGE NATIONAL
ACTION PLAN
LIVING DOCUMENT
1.
2.
3.
NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PLANNING AGENCY
BAPPENAS
“NATIONAL DEVELOPMENT PLANNING RESPONSE TO
CLIMATE CHANGE”
Agriculture
Coastal and Small Island
Health
4.
Transportation
5.
Public Works
6.
Human Settlements
7.
Energy and Mining
8.
Forestry
9.
Environmental
10. Technology
11. Rehabilitation & Revilitation Peat
Land
12. Mainstreaming Decentralized
Disaster Risk Reduction
INTERNATIONAL
WORLD
IMPLEMENTATION
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
What is national development plan?
Process to make development plans consist of long-term development plan, medium-term development plan and annual development plan which will be implemented by state institutions, private sector and community in all level of regions
Current regulations applied for development planning:
Law No. 25/2004 about Development Planning
Presidential Regulation No. 7/2005 about Medium-term National
Development Planning 2004-2009
Other national development plan policy relates to Climate Change:
Millennium Development Goals (do not have legal status)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Environmental Policies are aimed to:
1.
To mainstreaming sustainable development principles into alldevelopment aspects;
2.
3.
4.
5.
Improve coordination among environmental institutions in nantional and local level;
Increase the law enforcement effort to the poluters;
Increase the capacity of environmental institutions in national and local level;
Improve the awareness of community on environmental issues and support community active participation to monitor environmental quality;
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Among 15 environmental policy objectives, 3 objectives
(No.5-7) are related to climate change issues :
1.
Improve urban air quality especially in Jakarta,
Surabaya,Bandung, and Medan, supported by improvement of environmentally sound of transportation system and management;
2.
3.
Reduction of ODS (Ozone Depleting Substances) gradually until 2010;
Improve national capacity in adapting climate change issues into development aspects;
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Target 9 : Integrate the principles of sustainable development into country policies and programmes and reverse the loss of environmental resources
Target 10 : Halve, by 2015, the proportion of people without sustainable access to safe dringking water and basic sanitation
Target 11 : By 2020, to have achieved a significant improvement in the lives of slum dwellers
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
To integrate the agenda of climate change adaptation to the National Development
Strategy such as: Mid-Term & Long-Term Development Plan;
To re-observe and re-adjust initiative or program to be resilience to the climate change;
To Institutionalize the climate information usage to enable climate risk mitigation and management;
To encourage local government to integrate the climate risk consideration into their local development planning;
To strengthen information and knowledge to reduce climate risk in recent and in the future;
To ascertained of the availability of internal resources and funding for adaptation program and maximalize the utilization of available international funding;
To choose for no-regret option, which is taking the adaptation act regardless for example the non-occurence of climate change;
To encourage the establishment of national dialog to accelerate the implementation process of climate change adaptation agenda in Indonesia.
1. Toward Green Indonesia (MIH) &
Aforestation (National forest and land rehabilitation)
2. Water Conservation (Watershed
Management, Well Absorption, Reservoir)
3. Forest Fire Master Plan Poverty Derivation
Education for Farmer (for not doing land clearing by land burning such as: government will supply fertilizer and contribute good quality seed)
4. Flood Management
5. Reconstruction/redesign of irrigation
Agriculture
6. Encouraging CDM Project increase by sectoral approach
7. Mixed Energy Policies
8. Free tax for clean technology equipments
9. Energy Efficiency in the government buildings
10. Air Pollution Control for Transportation
11. Self Sufficient Energy Village Program
ADAPTATION
1. Encourage MGA (Meteorological and Geophysical Agency) to have station monitoring for weather forecast More Accurate and Realistic
Number
2. Identify the vulnerable sectors affected by climate change.
3. Public Participation.
4. Mainstreaming Adaptation Issue into related policies sector; for reviewing the 5--years Strategy Programme.
5. Draft National Strategy on
Adaptation to Climate Change
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
The immediate objective:
to enable Indonesia to identify national technology needs,
capacity building to asses international technology availability, and
modalities to acquire and absorb the appropriate technology.
Sectors in Existing Indonesian TNA
Energy Sector
Energy Industry
Industry Sector
Household and Commercial Sector
Transportation sector
Non-Energy Sector
Agriculture and Livestock
Forestry
(Existing Indonesian TNA submited to UNFCCC on 2001)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
MODALITIES OF TECHNOLOGY TRANSFER
Institutional Establishment
Regulation Development
▪ Procedure of Transferring Technology
▪ The Role of Decentralization
▪ System & Procedure Establishment
Financial Arrangement
Foreign Direct Investment
Official Development Assistance
The Global Environmental Facility
Clean Development Mechanism
Multilateral & Bilateral Agencies
Regional Development Banks
Etc.
(Existing Indonesian TNA submited to UNFCCC on 2001)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Criteria for prioritizing technology needs
Utilization of local resources
Rational utilization of resources
Socio-economic important
GHG reduction potential
Investment cost
Social acceptance
Minimum impact on environment
Methods for prioritization of technology needs
Cost–benefit and risk–benefit analyses
(Existing Indonesian TNA submited to UNFCCC on 2001)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Indonesia listed barriers and measures sector-wise. Types of barriers to technology transfer identified are:
Economic / market
Information/awareness
Policy
Regulatory
Institutional
Human
Technical
Infrastructure
Indonesia expressed concern about the high investment costs of selected mitigation options, which could translate into higher product prices and loss of competitiveness in the case of the energy sector. However, it identified barriers only in the transport, forestry and agriculture sectors.
(Existing Indonesian TNA submited to UNFCCC on 2001)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
High Efficiency Power Generation: Clean Coal Technology, CHP Technology, etc.
Energy Efficiency in Industrial sector (cement, iron & steel, pulp & paper, fertilizer, textile, mining, lime calcination, chemical, etc.)
Energy Efficiency in Industrial Equipments (Industrial process, electrical motor, boiler, compressor, furnace, Refrigeration, heater, room conditioning, cooling tower, electrical system, combustion, pump, lighting, steam distribution, waste heat recovery, etc.
Energy consumption efficiency in transportation including using gas for vehicles including improvement of public transportation
Carbon Capture Sequestration (CCS)
Cleaner Production Technology for Industry
Renewable Energy: Biomass, Wind, Solar, Ocean, Geothermal, Hydro electric, etc.
Climate modification technology
Climate monitoring & reporting system
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Avoiding forest burning, avoiding deforestation, forest conservation and reforestation, etc.
Composting of agricultural waste, manure management, etc.
Landfill management to avoid methane release
Ocean Sequestration
Technology for water resources management
Industrial waste water treatment
Industrial solid waste treatment (recovery, composting of palm free fruit bunch.
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Indonesia is already responding to this challenge in anticipation of the future consequences.
In 2007 and 2008, central government spending on environmental programs over 2006 levels to 6 trilion rupiah was doubled.
At the regional level, we have also nearly doubled spending to 6 trillion Rupiah on reforestration and special funds for environment and conservation.
Together, these funds amount to USD 1.4 billion spent on environment management, conservation and forest restoration.
In 2005, Indonesia also instituted a large increase in fuel prices by reducing subsidies that will encourage energy efficiency , while protecting the poor .
53
Indonesia
(RPJP, RPJM,
RKP)
Climate
Change
Joint
Programs
Donor
(Country Strategy/
Program)
The support of developed countries on Climate Change Program all over the world should be in addition to their commitment to support MDG’s achievement through ODA(0.7 % GNP)
54
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
F i n a n c i n g
Bilateral
JBIC
DFID
AusAID
DANIDA
Netherlands
EC
GTZ
Norway
CIDA
Sweden
Multilateral
Wolrd Bank
ADB
UNDP
O t h e r s
Int’l trust funds: GEF,
Adaptation funds, CIF
Private Sectors
M e c h a n i s m s
G-to-G
Bilateral
Multilateral
Loan
Grant
CC Trust Fund
Trust tee
Management
GoI host
TA & financial & management support
Mitigation & Adaptation
Climate-Proof Economy
Policy Re-orientation
Community-Based Programs
Awareness raising
Training/Workshops
Capacity Building
Small-scale Investment
Piloting
Execution of Policy/Strategy
Policy Implementation
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
UNFCCC Convention
Article 11: grant and/or concession…
Prefer to have ODA+
Paris Declaration
ownership, donor harmonisation, governance,…
In line with national interest and financing regulation:
Long-term and Mid-term National Development Goals
State Law No. 17/2003 about State Finance and Foreign Loan and Grant
Regulation (Government Regulation No.2/2007)
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Non-UNFCCC mechanism:
Grant from Bilateral Countries or Multilateral Institutions (ODA and
ODA+)
Foreign Loan (ODA and ODA+):
▪ Program Loan: only for budget/fiscal deficit
▪ Sectoral Loan: emphasizing co-benefit approach between development and climate change
▪ Trust Fund (both International and national)
UNFCCC mechanism:
Global Environmental Facility (GEF)
Special Climate Change Fund (SCCF)
Adaptation Fund (AF)
Up-coming Reduction Emission from Deforestation and
Degradation (REDD) mechanism
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
CDM investment through Bilateral, Multilateral and
Unilateral sources
PRIVATE SECTOR:
We should also look to encourage greater levels of private sector involvement in mitigating and adapting strategies.
Government can use fiscal instrument to encourage private sector to invest in environmental friendly technology
Grant
Debt swap
Trust Fund
Soft Loan - concession
59
Steering Committee/Ministers
Policy Report
Program Steering
Committee
Chair: GoI
Co-chair: Representative of Donor
Sub
Group/Issue
Sub
Group/Issue
Sub
Group/Issue:
Climate
Change Program
Dialogue
Ministries/Agencies/
Local Governments/
SOEs
Funding
Multi Donor
Trust Fund
(MOU GOI-Donors)
Bilateral/
Multilateral
Donors
60
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Indonesia Energy Projection
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Gas
Coal
Thermal
Other
Oil
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Gas
Coal
Oil
Wind
Wind
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
Presidential Decreed No. 1 / 2006
Regarding
Supply & Usage of Bio Fuel as Alternative Energy
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role
4 – Indonesia Position & Role