File
advertisement

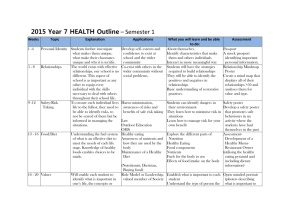
2. Success and Failure of Dieting STARTER – 5 mins 1. What is a diet 2. What are the different types of diets? Discuss, pair, share HOT QUESTION Learning Objectives •ALL will understand what a diet is and what reasons people have for going on a diet •ALL will be able to give reasons why diets succeed and fail •MOST will be able to describe research which demonstrates success and failure of dieting Learning outcomes • You will read dieting case studies and answer questions • You will take notes on Ao1 points about dieting • You will create your own case study using the theories covered in this lesson. Why does dieting often not work? • 89% of women in Britain have been on some form of diet (Klesges et al 1987) • Millions of pounds are spent each year on the diet industry • Why do diets not always work? • What makes a successful dieter? • Discuss in 3’s AO1 What is success? • Wing and Hill (2001) defined success as ‘successful long-term weight loss maintenance, involving the intentional loss of at least 10% of initial body weight and keeping it off for at least a year’ Case studies • In 3 groups read your case study and discuss and answer the questions. • Prepare to feedback on your answers. Oprah Winfrey • Oprah is a famous American talk show host who has always publically struggled with her weight. She recently started the ‘slim fast’ diet that involves dramatically cutting back on the amount of food she eats replacing each meal with milk shake. Throughout a 6 week period Oprah struggled to resist eating snacks and food other than the milkshakes that weren’t allowed on the diet and often relapsed. After this time she weighed herself and became frustrated that her weight had actually increased compared with her friend Rachael who rather than using a restriction diet simply tried to eat healthy balanced meals. Restraint Theory AO1 • Herman and Mack (1975) suggest attempting not to eat increases the probability of eating. Boundaries model AO1 • This explains how dieting leads to overeating. • Hunger usually keeps intake of food above a safe minimum. • Satiety keeps intake below a safe maximum level. Herman and Polivy (1984) Normal Eater TOO little Normal eating range Satiety Hunger Dieter TOO much Normal eating range (larger) Hunger Diet boundary Satiety • Dieter have a larger range between hunger and satiety because it takes longer to feel hungry and more food to satisfy them • Restrained eaters have a target or boundary they try to stick to but this doesn’t make them full so they keep eating! Peter Kay Peter Kay is a famous comedian who is currently very over weight and struggling to lose it! He has tried different diets including the Atkins diet, detox diet and weight watchers but has found none of them work very well. Peter finds that every time he tries to restrict his favourite foods like doner kebabs he ends up thinking about them all the time. This just gets worse and worse the longer he stays on a diet. After several weeks on his last attempt to lose weight peter ended up going out with some friends to the pub for a few drinks finally ending up the kebab house devouring a doner. Role of denial AO1 • Cognitive Psychology has shown if you try to suppress a thought on a regular basis you end up thinking about it more! • Wegnar et al (1987) demonstrated this. • Ask 1 group of PP’s not to think about a white bear and 1 group to think about it • Both groups instructed to ring a bell if they did. 1st group rang the bell more. • Theory of ironic processes of mental control Adele • Adele is a super star who has a world renowned voice. Adele has always struggled with her weight and has tried many different diets. The most successful type of dieting Adele has tried involved focusing on the different foods that formed her 3 meals a day. Her nutritionist has given Adele a diet plan with many different recipes to stop her becoming bored with the same old routine. This has proven to be quite successful and Adele enjoys shopping and preparing different ingredients written down on the plan for each meal that she has. Detail AO1 • Attention to WHAT we eat is the key to successful diet according to Redden (2008). • Focusing on the detail of meals stops people becoming bored of the diet/eating experience. • Gave 135 pp’s 22 jelly beans, one at a time. • When each bean was given out information was flashed on a computer screen. • Group 1 saw general info (Bean 6). Group 2 saw info on flavour. Group 1 got bored of eating quicker than group 2. Plenary • Design you own case study of someone on a diet. • Link the explanation of their success or failure on the diet to a theory we have covered. • Prepare to explain your case study.