Human Heredity - Ms. Zhong's Classes
advertisement

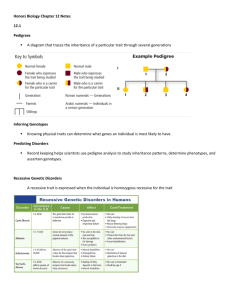
Human Heredity Human Chromosomes • A chromosome is a threadlike structure within the nucleus containing DNA: • To analyze chromosomes, - biologists photograph cells in mitosis, when the chromosomes are fully condensed and easy to see - The biologist then cut out the chromosomes from the photographs and group them together in pairs - A picture of chromosomes arranged in this is known as karyotype Human Chromosomes • A typical human body cell contains _______ chromosomes: - 2 of those 46 chromosomes are known as sex chromosomes: X and Y chromosome - The remaining 44 chromosomes are known as autosomal chromosomes, or autosomes - Male: 46 XY - Female: 46 XX Pedigree Chart • A pedigree chart shows the distribution of particular traits within a specific family group A half shaded circle or square indicates that a person is a carrier of the trait A circle represents female A completely shaded circle or square indicates that a person express that trait A square represents male A completely un-shaded circle or square indicates that a person neither express nor carry the trait Human Traits • Some human traits are almost impossible to associate with single genes: - Some traits are polygenic, meaning they are controlled by many genes: e.g. shape of your eyes or ears - Many traits are strongly influenced by environmental factors including nutrition and exercise: e.g. height Genetic Disorders • Many human genes have become known through the study of genetic disorders: -Disorders caused by recessive alleles: You need to inherit 2 copies of the recessive alleles to have these disorders - Disorders caused by dominant alleles: You only need to inherit 1 copy of the dominant alleles to have these disorders Recessive alleles disorder • Albinism: lack of pigment in skin, hair, and eyes (video) • Cystic fibrosis: Excess mucus in lungs, digestive tract and liver (video) • Galactosemia : Accumulation of galactose in tissues; mental retardation, eye and liver damage • Phenylketonuria (PKU): Accumulation of phenylalanine (an amino acid); lack of normal skin pigment, mental retardation (video) • Tay-Sachs disease: Lipid accumulation in brain cells; mental deficiency, blindness, death in early childhood (video) Dominant alleles Disorder • Achondroplasia: a form of dwarfism • Huntington's disease: Mental deterioration and uncontrollable movements, appears in middle age (video)