safety tips in computer use - Singapore Manufacturing Federation
advertisement

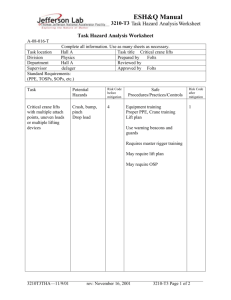
Our Project – Modification of Wind Sock Structure 3 Sep 2007 Team Details Team Name: Maintenance Team Team Members: Facilitator Mr Yeo Soo Hock HSE Manager Leader Mr Rajandran Senior Machinery Technician Members Mr Cheng Swee Guan Tong Hoi Site Manager Mr Jagan Penta Tong Hoi Site Supervisor Mr Kalaivanan K HSE Officer Mr Foo Seck Ket Lead Technician Team Meetings Team Participation % of Attendance 100% 90% 100% 100% 100% 80% 100% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Oct-06 Nov-06 Dec-06 Jan-07 Feb-07 Project Schedule Project Selection – Brainstorming Session Total 13 suggestions were contributed; only three were qualified to be safety & health related project. Three suggestions or safety concerns were as follows: – Problems/ Risks Involved When Changing of Wind Sock. – Problems/ Risks Involved Using Emergency Chlorine Shut-Off Valve. – Risks Involved Without Proper Access platform for operating valves Project Selection Matrix – Risk Assessment Safety & Health Problems/ Risks No of Potential Hazards Problems/ Risks Involved When Changing of Wind Sock Risk Level 10 Medium Risk Problems/ Risks Involved Using Emergency Chlorine Shut-Off Valve. 6 Medium Risk Risks Involved Without Proper Access Platform for Operating Valves 3 Low Risk SELECTED Risk Assessment – Before Implementation Infineum Singapore Risk Assessment Rev 2 Jun 06 Job/Tasks: Changing of Wind Socks on Top of Tank Tops Conducted by: Rajandran, Cheng, Jagan, Foo SK, Kalai Reviewed by: Yeo Soo Hock – HSE Manager Date of Conduct: 25 Oct 06 Remote A Occa B Freq C Major 1 Med risk Hi risk Hi risk Mod’ 2 Low risk Med risk Hi risk Minor 3 Low risk Low risk Med risk Facilitator S/N 1 (MOM Risk Matrix) Hazard Identification Man fall from height Existing Control Measures Risk Level Use safety harness Use man-cage with proper locking device Use crane (after verifying its safe for use) Ensure crane operator, lifting supervisor, rigger and fitters are competent for the job. Adhere to lifting procedures in HSE manual. Adhere to Permit-To-Work System Low Risk, A3 Supervisor at site to advise labourers and reduce the number of re-occurrences. Medium Risk, C3 Take breaks in-between. Take lots of water before and during work Try to reduce wasting time or delays. Low Risk, A3 Verify safe for use before commencement. Adhere to lifting procedures in HSE manual. Adhere to Permit-To-Work System Ensure ground is firm for lifting Medium Risk, B2 Verify safe for use before use Low Risk, A2 2 Manual handling (pull, push, stretching) 3 Excessive Exhaustion –Long hours (fatigue) 4. Crane failure – Crane topple 5. Lifting gear failure- load fall from height 6 Labourer not understanding hazard. Most of the Hazards were Due to Crane Operation Ensure workers are aware of hazards and competent for the work. Supervision at site is enforced Medium Risk, C3 7 Trip and fall Ensure only essential materials are brought up tank top. Ensure housekeeping. Low Risk, A2 8 Oil leak from crane Ensure oil is contained if any spill Low Risk, A2 9 Inhalation of vapour from tank hatch Stop work and inform Shift Superintendent. Low Risk, A2 10 Inclement weather Stop work if there is risk of lightning and strong wind. Low Risk, A3 Implementation Steps of Operation BEFORE Implementing Selected Solution. Step 1: Preparation Prepare manpower, accessories and crane service. Step 2: Administration Apply permits (cold work, lifting, road closure permits). Conduct tool box briefing. Inform control/guard room. Validate document Step 3: Site Inspection & LMRA Cordon off to prevent unnecessary entry. Conduct inspection with checklist Conduct LMRA (Last Minute Risk Assessment) Step 4: Trial Lift (w/o load) Ensure all measures taken prior to actual lift Step 5: Lifting and Change Wind Sock Commence lift and change wind sock Step 6. Completion Complete work and finish off all administrative work. Location of Windsocks – Before Implementation Above Pipe Rack Blending Process Unit Illustration of Changing Wind SockBefore Implementation Analytical Techniques – Root Cause Analysis Man Method 5 wind sock locations. Apply PTW (crane, road clearance and lifting permit). Barricading of road Machine High cost 1 crane driver, Set-up of crane Long hours for labour Use of 1 lifting sup, and prep for 1 rigger & Fatigue Manual man-cage operation. 2 fitters handling Lifting gear Fall from Potential crane Too many (pull push failure height topple stretching) procedures High cost for Fear of working at Use of Excessive equipment to be edge of tank crane coordination adhered to. Potential Crane Trip and fall failure risks/problems Transport excessive tools and accessories to the tank top. Wind sock comes in different sizes Housekeeping Windy Change of bearing Fall from height Materials Vapour smell from the tank hatch Lightning risk Oil leak from crane Exhaust from crane Environment when changing wind sock Analytical Techniques To reduce all problems by75% 75% To reduce all factors by Safety 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 Method Time Human Cost Proposed Solutions Proposal 1 - Telescopic Structure: – – – – Proposal 2 - Pulley System: – – – – Simple and effective idea Not practical; Corrodes easily and flimsy. Expose to inclement weather; possibility of the wind sock structure to topple. Expose to caught in between hazard while adjusting the telescopic pole Not effective. Design not suitable for strong wind condition. Rope can get entangled with wind sock and pulley. Pulley requires maintenance Proposal 3 - Two-Section Structure – – – Safe, effective and strong Easy to implement. Minimum maintenance was required. Proposed Solutions – Selection Proposed Solution Safety & Installation Cost Effectiveness Within Health Cost Saving & Efficiency Team’s Rating Rating Rating Rating Capability Rating Total score (Higher the score the better) 1. Telescopic Solution 6 8 7 7 9 37 2. Pulley System 6 8 6 6 9 35 3. TwoSection Structure 9 8 7 9 9 42 Selection Criteria Rating Safety and Health - 1 is high (high risk) and 10 is low (0 hazard) Installation Cost - 1 is high cost (>S$ 20, 000) and 10 is low cost (<S$ 1000) Cost savings - 1 is less savings (<S$ 1000) and 10 is high savings (>S$ 20, 000) Effectiveness and Efficiency - 1 is low (Less effective and efficient) and 10 is high (Very Less effective and efficient) Within Team Capability - 1 is low (take more than> 12 months to implement proposal & and 10 is high (take less than 3 months to implement proposal ) Finalizing Selection Selection of Proposal. Based on the ranking score and comparison made in the evaluation of proposed solutions, the team selected the “Two Section Structure” solution. Management Presentation. – Short presentation of the study was tabled for the management’s endorsement. – Team was commended for its efforts and the proposed solution was endorsed for implementation. Risk Assessment – After Implementation Infineum Singapore Risk Assessment Rev 2 Jun 06 Job/Tasks: Changing of Wind Socks on top of tank tops Conducted by: Rajandran, Cheng, Jagan, Foo SK, Kalai Reviewed by: Yeo Soo Hock – HSE Manager Date of Conduct: 15 Jan 07 S/No Facilitator Hazard Identification 1 Man fall from height -There is no longer a requirement to work using a man-cage. Remote A Occa B Freq C Major 1 Med risk Hi risk Hi risk Mod’ 2 Low risk Med risk Hi risk Minor 3 Low risk Low risk Med risk (MOM Risk Matrix) Existing Control Measures (MOM Risk Matrix) Risk Level No hazards. - From Minimal exposure to manual handling.medium to low risk No hazards. 2 Manual handling (pull, push, stretching) 3 No exhaustion – Each wind sock take no longer than 30min to be fitted 4. No usage of crane No hazards. 5. No usage of lifting gear No hazards. 6 Labourer not understanding hazard. Work is now simplified and straight forward. However, Last Minute Risk Assessment (LMRA) is still enforced. Low Risk, A2 7 Trip and fall Labourer only needs to bring an extra wind sock up to the tank top. Less materials on tank top. However, proper housekeeping must be enforced at all times. Low Risk, B3 8 Oil leak from crane- No usage of crane No hazards. 9 Inhalation of vapour from tank hatch Stop work and inform Shift Superintendent. Low Risk, A2 10 Inclement weather Stop work if there is risk of lightning and strong wind. Low Risk, A3 From medium to low risk Low Risk, B3 - - - Implementation Steps of Operation AFTER Implementing Selected Solution. Step 1: Preparation Standby man and spare wind sock Step 2: Administration Apply cold work permit only Conduct LMRA (Last Minute Risk Assessment) Reduce/less Step 3: Change wind sock Change wind sock •Steps •Admin work •Coordination => Leads to reduction in time => Less exposure to HAZARDS Re-Location of Windsocks – After Implementation Relocate all to Tank/Roof-Top. For better accessibility and proper/stable platform Illustration of Changing Wind SockAfter Implementation Illustration of Changing Wind Sock- After Implementation Removing Securing Pin Replacing Wind Sock Fixing Back Wind Sock Structure Lowering Upper Section Total Cost for Implementation & Installation Each location: S$600/-Structure” solution. Five Locations: One-time Cost of S$3,000/- only Results Achieved – Tangible Results Cost Savings Before Implementation After Implementation Crane Service $300 $0 Labour Charge $1000 (5 Men) $200 (OMO) Service bearing $100 $0 For 5 locations: $1400 x 5= $7000 $200 x 5 = $1000 P.E. Certification (one-time) $500 $0 Total $7500 $1000 Items Annual Cost reduction by: 86% Results Achieved – Tangible Results Save Time Before implementation : – Operation used to take two to three hours per location – For five locations: Approx: 15hrs After Implementation: Time reduction by (every year): 83% – – Operation now takes 30min per location The above calculations are done according to yearly maintenance schedule. However, there are instances where ad-hoc maintenance Formay fivebelocations: Approx: 2.5Hrs required. Therefore, further reductions can be expected. Time Reduction by: 83% Results Achieved – Intangible Results Safe operation and very minimum hazard exposure. Reduce work steps (no machinery used, less man/ materials utilized and minimum administration) Increase productivity and morale of workers. Enhance efficiency and maintenance effectiveness. Less time waste (no need to wait for crane and applying permit) No possibility of environmental issues. Confidence in our team’s ability to address and overcome problems has been enhanced. Teamwork, sense of team identity and team morale has improved. Variation of Results Between Results & Initial Target: Safety 5 4.5 4 3.5 3 2.5 2 Method Human 1.5 1 0.5 0 Time Cost Risk Reduction In Summary Before Implementation After Implementation Number of Hazards 10 5 Risk level Medium Risk Low Risk Crane & man cage (inherent high risk) Crane/ man cage not required. Human Factor 5 men OMO Exposure (Duration) 15Hrs 2.5 Hrs (Reduce by 83%) System/ Procedure Need to comply with many procedures/ requirements Simplified/ reduction in procedures to enhance safety Equipment Standardization Documentation Management was kept abreast of the success. Updated procedures. Amended JSA was endorsed by the management JSA maintained in accordance with WSH (Risk Assessment) Regulations. Review & Sustenance Review for Future Improvement No negative feedback but only positive on the implementation Receptive to new ideas and future improvements Continuous improvements to the existing projects Team’s Next Project. Working on with the second project under the project prioritization; i.e “Problems/ Risks Involved Using Emergency Chlorine Shut-Off Valve”. Review & Sustenance Self Examination. Team made up of committed colleagues and contractors. Great success of this project reflects on the positive participation and co-operation of the team members. Project has given the team greater confidence and morale. It has also revealed that with good team work and overwhelming management support anything can be achieved. Conclusion Infineum Maintenance Team has always believed in making our plant a safe working environment for our colleagues, contractors and visitors. The Maintenance Team looks forward for more challenges and opportunity to enhance the safety and health in Infineum Lastly, we all know that lifting equipment is the second highest contributor of workplace deaths in 2006 and it has always been in the area of safety concern. Safety as a Culture in Infineum, we have taken steps to prevent such occurrences in the plant and at the same time contributing to a healthier nationwide safety statistics The Maintenance Team Thanks you Question Time