Firestop System Selection
advertisement

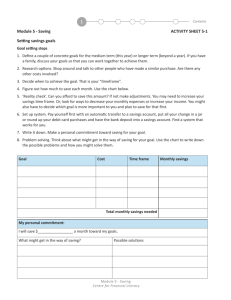
FIRESTOP SYSTEM SELECTION Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Using the UL Directory • Fire Resistance Directory • Alpha Numeric Numbering System • Different for Joints and Penetrations • Website is Most Current Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC • UL Approved No Such Thing (Only AHJ approves products/systems • UL Classified Lab has used the country requirements to evaluate the product for specific hazards or properties • UL Listed Passes the standard test and is in the lab’s directory Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Finding a Through-Penetration Firestop System Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC SYSTEM No. C-AJ-1379 F Ratings T Ratings – 3 Hr – 0 Hr 1. What type of building assembly is requiring firestopping? – Floor or Wall 2. What type of material is the building assembly – Concrete, CMU, Gypsum, Wood Frame 3. What is the penetrating item(s)? – Metallic, Nonmetallic, Cables, Insulated, Construction Joints, etc. 4. What are the specific descriptions regarding the 1A. Floor or Wall Assembly – Min 4-1/2 in. thick reinforced normal weight (150 pcf) concrete. Wall may also be constructed of any UL classified Concrete Blocks*. Max diam of opening is penetrants? 26-1/2 in. – See Concrete Blocks (CAZT) category in the Fire Resistance Rating Directory for names of manufacturers. Diameter, quantity, type of plastic, type & thickness of insulation, 1B. Metallic Sleeve (optional) – Nom 16 in. (or smaller), Schedule 10 (or heavier) steel pipe etc.sleeve, cast or grouted into floor or wall assembly. 2. Through Penetrants – One metallic pipe or tubing to be installed concentrically or eccentrically into opening such that the annular space between the pipe and the periphery of the opening is min 0 in. (point of contact) to max 2-1/2 in. Pipe to be firmly supported on both sides of opening. The following types and sizes of pipes may be used: (a) Nom. 24 in. diam (or smaller) Schedule 30 (or heavier) steel or iron pipe. (b) Nom. 4 in. diam (or smaller) electrical metallic tubing. 3. Packing Material – Mineral wool insulation of min 4 pcf firmly pressed into opening as a permanent form. Insulation material to be recessed by min depth of 1/2 in. from top surface of floor or both surfaces of wall. 4. Fill, Void, or Cavity Materials* – Caulk – Min 1/2 in. thickness of fill material applied within the annulus, flush with top surface of floor or both surfaces of wall. A min 1/4 in. crown of the caulking material shall be applied around the entire circumference of the pipe at the level of the floor surface or both wall surfaces. W. R. GRACE – CONN. Sealant – FlameSafe® FS900+ Company ABC&–CO. SuperDuper 5. What is the hourly rating you are looking for? – F Rating, T Rating 6. Are there any special considerations? – Movement, Environmental exposure Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through* Fire and Smoke Containment Bearing the UL Classification Marking. ©2004 IFC Navigating UL Example 1: UL Listed - Through Penetration System C-AJ-1079 Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Navigating UL: THROUGH PENETRATION FIRESTOP SYSTEMS (XHEZ) First Alpha Character – signifies what is being penetrated F = W = C = Floors Walls Walls and Floors C-AJ-1079 Combination – Floor or Wall Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Navigating UL: THROUGH PENETRATION FIRESTOP SYSTEMS (XHEZ) Following Alpha Character(s) – wall or floor construction type A = B = C = D = E-I = J = K = L = M = N-Z = Concrete floors 5 inch thick Concrete floors 5 inch thick Framed floors Steel decks in marine vessels Reserved for future use Concrete or masonry walls 8 inch thick Concrete or masonry walls 8 inch thick Framed walls Bulkheads in marine vessels Reserved for future use C-AJ-1079 Construction Type of Floor or Wall Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Navigating UL: THROUGH PENETRATION FIRESTOP SYSTEMS (XHEZ) Numeric Component – first digit identifies the type of penetrant, next three are sequential system numbering 0000-0999 1000-1999 2000-2999 3000-3999 4000-4999 5000-5999 6000-6999 7000-7999 8000-8999 9000-9999 = = = = = = = = = = C-AJ-1079 No Penetrant Metallic pipe, conduit or tubing Nonmetallic pipe, conduit or tubing Electrical cables Cable trays with electrical cables Insulated pipes Busways HVAC ducts Mixed multiple penetrations Reserved for future use Penetrant Type C-AJ-1079 Individual System Number Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Finding a Fire-Resistive Joint System Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC 1. What type of building assemblies is the joint formed by? – 2. Floor/Floor, Floor/Wall, Wall/Wall, Top of Wall/Ceiling What type of material is the building assembly – 3. Concrete, CMU, Gypsum What is the hourly rating you are looking for? – 4. 5. Assembly rating (1 – 4 hour) How big of a joint is required (inches) How much movement is required? – 6. Must accommodate building movement (% of joint size) Are there any special considerations? – Unique construction condition, environmental exposure Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Navigating UL Example 2: UL System - Joints HW-D-0034 Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Navigating UL: JOINT SYSTEMS (XHBN) First Two Alpha Characters – identify the type of joint system FF WW FW HW = = = = Floor-to-Floor Wall-to-Wall Floor-to-Wall Head-of-Wall HW-D-0034 Barriers That Form The Joint Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Navigating UL: JOINT SYSTEMS (XHBN) Next Alpha Character – identifies the movement capabilities of the system D = Dynamic (movement capabilities) S = Static (no movement capabilities) HW-D-0034 Movement: Static or Dynamic? Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Navigating UL: JOINT SYSTEMS (XHBN) Numeric Component – first digit identifies the width of the joint system, next three are sequential system numbering 0000-0999 1000-1999 2000-2999 3000-3999 4000-4999 = = = = = joint 2 inch joint 2 inch 6 inch joint 6 inch 12 inch joint 12 inch 24 inch joint 24 inch HW-D-0034 Joint Width HW-D-0034 Individual System Number Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Finding a Perimeter Joint System Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC 1. What is the makeup of the exterior wall? – 2. Concrete panel, Spandrel Glass, Aluminum Panel, Brick Veneer, etc. What supports the exterior wall? – 3. Steel stud, aluminum mullions, etc. What is the hourly rating you are looking for? – 4. F rating (1 – 2 hour) How big of a joint is required (inches) – 5. Measured from edge of slab to nearest point of curtain wall How much movement is required? – 6. Must accommodate building movement (% of joint size) Are there any special considerations? – Unique construction condition, environmental exposure Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Example 3: OPL System - Fire Resistive Joints - Perimeter Barriers CEJ 205 P CEJ 148 H Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Deciphering Alphanumeric Numbering - OPL - Fire Resistive Joints - Perimeter Fire Barriers First Three Alpha Characters – identify the type of construction CEJ = Construction/Expansion Joints CEJ 205 P CEJ 148 H Construction/Expansion Joint Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Deciphering Alphanumeric Numbering - OPL - Fire Resistive Joints - Perimeter Fire Barriers Numeric Digits – identify the individual system number CEJ 205 P CEJ 148 H Individual System Number Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Deciphering Alphanumeric Numbering - OPL - Fire Resistive Joints - Perimeter Fire Barriers Suffix – identify the type of joint system F = Floor-to-Floor H = Head-of-Wall W = Wall-to-Wall P = Perimeter FW = Floor-to-Wall CEJ 205 P CEJ 148 H Type of Joint System Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Engineering Judgments (EJs): • • • • What are they? When are they acceptable? When are they not appropriate? What are the guidelines? Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC When are they acceptable? – – – – – When tested systems do not exist. When modifying the application is unrealistic. When existing test data supports the interpolation. When the author has experience with and knowledge of the conditions. When an illustration is provided to aid in installation. Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Sources of Engineering Judgements • • • • Manufacturer Third party labs (UL) Fire Protection Engineer Professional Engineer Must be based on sound engineering practice and knowledge of both field application and capabilities of system components Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC – According to the International Firestop Council “listed firestop systems can be broadened within the context of their originally tested and rated conditions through the careful and restricted application of accepted engineering principles and fire protection testing guidelines.” Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC About the IFC The International Firestop Council is a not-for-profit association of manufacturers, distributors and installers of fire protective materials and systems. IFC's mission is to promote the technology of fire containment in modern building construction through research, education and development of safety standards and code provisions. Website - www.firestop.org Email - Info@firestop.org Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC Available educational seminars on our website include….. • Firestop 101 – An introduction to firestopping • Perimeter Curtain Wall Fire Protection • Firestop System Selection • Flexible Duct Wrap Systems • Fire Protection of Construction Joints Saving Lives and Property Saving Lives Through Passive Fire Protection Through Fire and Smoke Containment ©2004 IFC