Computer Performance and Storage Devices
advertisement

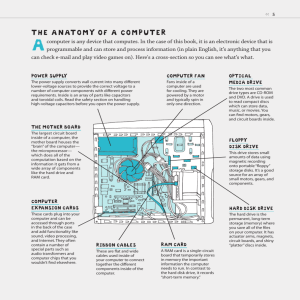
Computer Performance & Storage Devices Computer Technology Computer Performance Boot Process Sequence of events that occurs between the time you turn on a computer and the time that it becomes ready to accept commands. Purposes • Runs a diagnostic test to make sure everything is working. • Loading the operating system, so the computer can carry out basic operations. 6 events of the boot process: Power up Start boot program Power-on self-test Identify peripheral devices Load operation system Check configuration and customization Circuits The path from one component of a computer to another that data uses to travel. Circuits run between RAM and the microprocessor RAM and various storage devices Silicon Chip Silicon is melted sand. What the circuits are embedded into to keep them together. Megahertz (mHz) A measurement used to describe the speed of the system clock. A megahertz is equal to one million cycles (or pulses) per second. 1.3 GHz means that the microprocessor’s clock operates at a speed of 1.3 BILLION cycles per second. Pentium Name of the CPU. Pentium is the 5th generation of the Intel processor. Other generations were called • • • • 80-88 286 386 486 RAM vs. ROM RAM “Random Access Memory” The ability of a storage device to go directly to a specific storage location without having to search sequentially from a beginning location. Very volatile • Cannot hold data when the power is off. • Looses all data when power is lost. ROM “Read only memory” Drives can read data from disks, but cannot store new data on them. One or more integrated circuits that contain permanent instructions that the computer uses during the boot process. Binary Number System A method for representing letters or numbers using only two digits, 0 and 1. Bit • Each 0 or 1 Byte • 8 bits Also referred to as Base 2 Binary Code. Memory Measurements Bit Byte Approximately 1 million bytes Exactly 1,048,576 bytes Gigabyte Approximately 1,000 bytes Exactly 1,024 bytes Megabyte 8 bits Kilobyte Each 0 or 1 Approximately 1 billion bytes Terabyte Approximately 1 trillion bytes Storage Devices Used to keep data when the power to the computer is turned off. Medium/media Location where data is stored. Hard Disk Usually mounted inside the computer’s system unit. Can store billions of characters of data. Stated in forms of bytes: • Megabytes or Gigabytes Magnetic Storage Recording of data onto disks or tape by magnetizing particles of an oxide based surface coating. A fairly permanent type of storage that can be modified. Floppy Disk Round piece of flexible Mylar plastic covered with a thin layer of magnetic oxide and sealed inside a protective covering. May be referred to as a “floppy” 3½ disk capacity is 1.44 MB or 1,440,000 bytes Floppy Disk Options Formatted Preparing the disk for use by the computer. Write-protected Setting the disk so that it can not be written to by the computer. Zip Disk Floppy disk technology manufactured by Iomega. Available in 100 MB and 250 MB versions Digital Audio Tape Method of storing large amounts of data on tape using helical scan technology to write data at high densities across the tape at an angle. Optical Storage Means of recording data as light and dark spots on CD or DVD. Reading is done through a low-power laser light. Pits • Dark spots Lands • Lighter, non-spotted surface areas CD-ROM “CD – Read Only Memory” Also called CD-R CD-Read Storage device that uses laser technology to read data that is permanently stored on compact disks, cannot be used to write data to a disk. CD-RW “CD-Read Write” A storage device that reads data from CD’s and also can write data to CD’s. Similar to a CD-ROM, but has the ability to write to CD. DVD-ROM “Digital Video Disks – Read Only Memory” Reads data from CD’s (audio and data) and DVD’s (data or movie) Cannot be used to write data to a disk.